In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, Large Language Models (LLMs) have become pivotal in transforming industries ranging from healthcare to finance. These models, powered by advanced algorithms, are capable of understanding and generating human-like text, making them invaluable tools for businesses and researchers alike.
However, the effectiveness of these models hinges on robust evaluation metrics that ensure their accuracy, reliability, and fairness. This blog aims to unravel the complexities of LLM evaluation metrics, providing insights into their uses and real-life applications.
Understanding LLM Evaluation Metrics
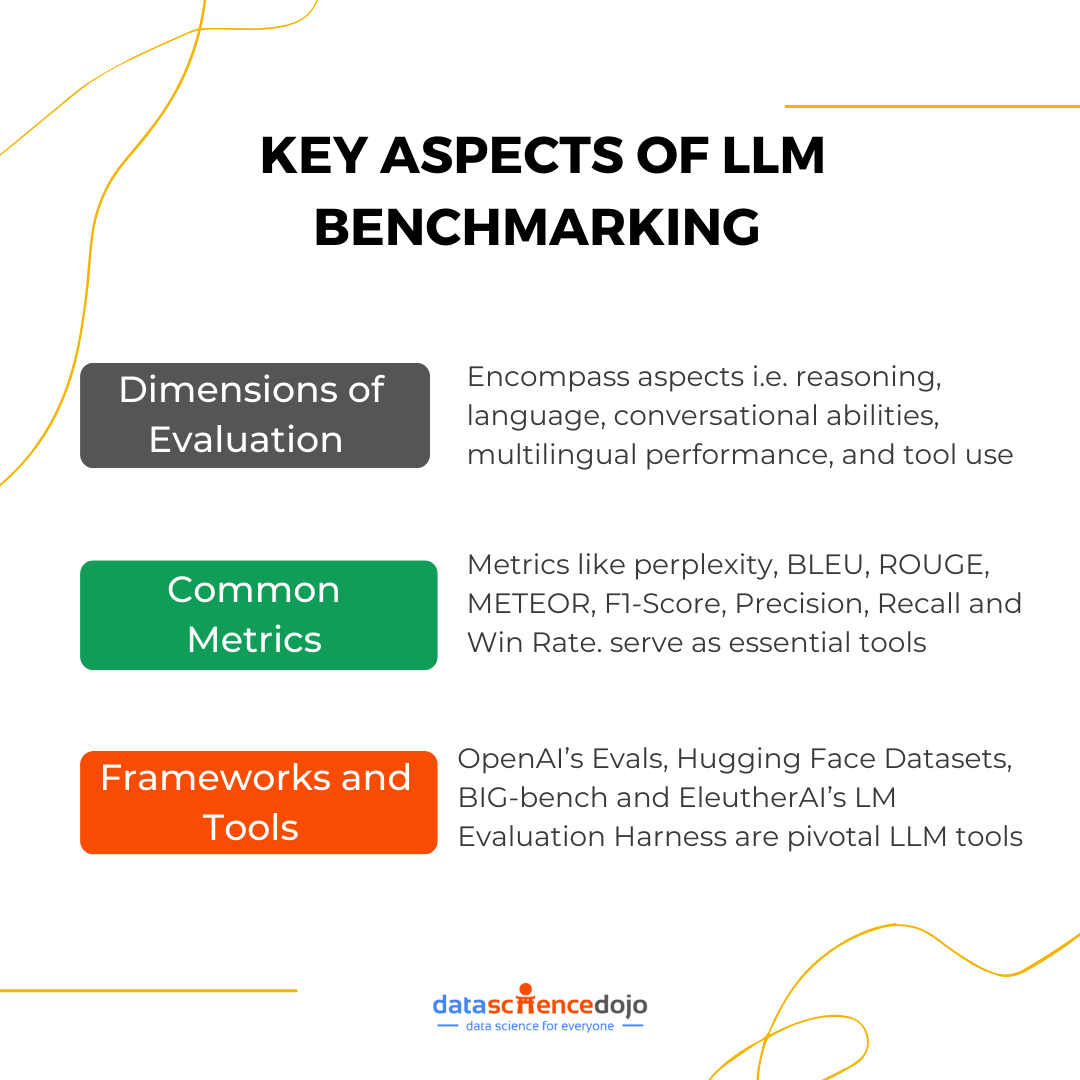
LLM Evaluation metrics are the benchmarks used to assess the performance of LLMs. They serve as critical tools in determining how well a model performs in specific tasks, such as language translation, sentiment analysis, or text summarization. By quantifying the model’s output, LLM evaluation metrics help developers and researchers refine and optimize LLMs to meet the desired standards of accuracy and efficiency.
Explore 5 Top AI Translation Tools to Diversify Your Business
The importance of LLM evaluation metrics cannot be overstated. They provide a standardized way to compare different models and approaches, ensuring that the best-performing models are identified and deployed. Moreover, they play a crucial role in identifying areas where a model may fall short, guiding further development and improvement.
In essence, LLM evaluation metrics are the compass that navigates the complex landscape of LLM development, ensuring that models are not only effective but also ethical and fair.
Key LLM Evaluation Metrics
Accuracy
Accuracy is one of the most fundamental LLM evaluation metrics. It measures the proportion of correct predictions made by the model out of all predictions. In the context of LLMs, accuracy is crucial for tasks where precision is paramount, such as medical diagnosis tools. Here are some of the key features:
- Measures the proportion of correct predictions
- Provides a straightforward assessment of model performance
- Easy to compute and interpret
- Suitable for binary and multiclass classification tasks
This metric is straightforward and provides a clear indication of a model’s overall performance.
Benefits
Accuracy is crucial for applications where precision is paramount and has mainly the following benefits:
- Offers a clear and simple metric for evaluating model effectiveness
- Essential for tasks requiring high precision, such as medical diagnostics
- Facilitates quick comparison between different models or algorithms
High accuracy ensures that models can be trusted to make reliable decisions.
Applications
In healthcare, accuracy is crucial for diagnostic tools that interpret patient data to provide reliable diagnoses. For instance, AI models used in radiology must achieve high accuracy to correctly identify anomalies in medical images, reducing the risk of misdiagnosis and improving patient outcomes.
In finance, accuracy is used to predict market trends, helping investors make data-driven decisions. High accuracy in predictive models can lead to better investment strategies and risk management, ultimately enhancing financial returns. Companies like Bloomberg and Reuters rely on accurate models to provide real-time market analysis and forecasts.
For example, IBM’s Watson uses LLMs to analyze medical literature and patient records, assisting doctors in making informed decisions. In finance, accuracy is used to predict market trends, helping investors make data-driven decisions.
Precision and Recall
Precision and recall are two complementary metrics that provide a deeper understanding of a model’s performance. Precision measures the ratio of relevant instances among the retrieved instances, while recall measures the ratio of relevant instances retrieved over the total relevant instances. Here are some of the key features:
- Provides a more nuanced view of model performance
- Useful in scenarios with imbalanced datasets
7 Innovative Techniques to Handle Imbalanced Data
Benefits
Precision is beneficial in reducing false positives, which is crucial in applications like spam detection, where users need to trust that legitimate emails are not mistakenly flagged as spam.
- Precision reduces false positives, enhancing user trust
- Recall ensures comprehensive retrieval, minimizing missed information
- Balances the trade-off between false positives and false negatives
This is one of the LLM evaluation metrics that ensures that all relevant information is retrieved, minimizing the risk of missing critical data.
Learn how Cybersecurity revolutionized with data science
Applications
In spam detection systems, precision and recall are used to balance the need to block spam while allowing legitimate emails. High precision ensures that users are not overwhelmed by false positives, while high recall ensures that spam is effectively filtered out, maintaining a clean inbox.
In information retrieval systems, these metrics ensure that relevant data is not overlooked, providing users with comprehensive search results. For example, search engines like Google use precision and recall to refine their algorithms, ensuring that users receive the most relevant and comprehensive results for their queries. It is used in spam detection systems where precision reduces false positives, and recall ensures no spam is missed.
F1 Score
The F1 Score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, providing a single metric that balances both. It is particularly useful in scenarios where a trade-off between precision and recall is necessary, such as in search engines. A search engine must return relevant results (precision) while ensuring that all potential results are considered (recall). Here are some of the key features:
- The harmonic mean of precision and recall
- Balances the trade-off between precision and recall
- Provides a single metric for evaluating models
- Ideal for imbalanced datasets
Benefits
The F1 Score offers a balanced view of a model’s performance, making it ideal for evaluating models with imbalanced datasets. Following are some of the key features:
- Offers a balanced view of a model’s performance
- Useful in scenarios where both precision and recall are important
- Helps in optimizing models to achieve a desirable balance between precision and recall, ensuring that both false positives and false negatives are minimized
- Provides a single metric for evaluating models where both precision and recall are important
- Useful in scenarios with imbalanced datasets
Applications
Search engines use the F1 Score to optimize their algorithms, ensuring that users receive the most relevant and comprehensive results. By balancing precision and recall, search engines can provide users with accurate and diverse search results, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement. –
In recommendation systems, the F1 Score helps balance accuracy and coverage, providing users with personalized and diverse recommendations. Companies like Netflix and Amazon use F1 Score to refine their recommendation algorithms, ensuring that users receive content that matches their preferences while also introducing them to new and diverse options.
Perplexity
Perplexity is a metric that measures how well a probability model predicts a sample. In the context of LLMs, it gauges the model’s uncertainty and fluency. Lower perplexity indicates a better-performing model.
Perplexity measures a model’s uncertainty and fluency in generating text. It is calculated as the exponentiated average negative log-likelihood of a sequence. Lower perplexity indicates a better-performing model, as it suggests that the model is more confident in its predictions. Here are some key features:
- Measures model uncertainty and fluency
- Lower perplexity indicates better model performance
- Essential for assessing language generation quality
- Calculated as the exponentiated average negative log-likelihood
Benefits
Perplexity is essential for assessing the naturalness of language generation, making it a critical metric for conversational AI systems. It helps in improving the coherence and context-appropriateness of generated responses, enhancing user experience.
- Helps in assessing the naturalness of language generation
- Essential for improving conversational AI systems
- Enhances user experience by ensuring coherent responses
Applications
This metric is crucial in conversational AI, where the goal is to generate coherent and contextually appropriate responses. Chatbots rely on low perplexity scores to provide accurate and helpful responses to user queries. By minimizing perplexity, chatbots can generate responses that are more fluent and contextually appropriate, improving user satisfaction and engagement.
Listen to Top 10 trending AI podcasts – Learn artificial intelligence and machine learning
In language modeling, perplexity is used to enhance text generation quality, ensuring that generated text is fluent and contextually appropriate. This is particularly important in applications like automated content creation and language translation, where naturalness and coherence are critical.
BLEU Score
The BLEU (Bilingual Evaluation Understudy) Score is a metric for evaluating the quality of text that has been machine-translated from one language to another. It compares the machine’s output to one or more reference translations.
BLEU is widely used in translation services to ensure high-quality output. It measures the overlap of n-grams between the machine output and reference translations, providing a quantitative measure of translation quality. Here are some key features.
- Evaluate the quality of machine-translated text
- Compares machine output to reference translations
- Measures the overlap of n-grams between outputs and references
- Provides a quantitative measure of translation quality
Benefits
BLEU Score helps in refining translation algorithms, ensuring that translations are not only accurate but also contextually appropriate. It provides a standardized way to evaluate and compare different translation models, facilitating continuous improvement.
- Helps in refining translation algorithms for better accuracy
- Provides a standardized way to evaluate translation models
- Facilitates continuous improvement in translation quality
Applications
Translation services like Google Translate use BLEU scores to refine their algorithms, ensuring high-quality output. By comparing machine translations to human references, the BLEU Score helps identify areas for improvement, leading to more accurate and natural translations.
In multilingual content generation, the BLEU Score is employed to ensure that translations maintain the intended meaning and context. This is crucial for businesses operating in global markets, where accurate and culturally appropriate translations are essential for effective communication and brand reputation.
Bonus Addition
While we have explored the top 5 LLM evaluation metrics you must consider, here are 2 additional options to explore. You can look into these as well if the top 5 are not suitable choices for you.
ROUGE Score
The ROUGE (Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation) score is a set of metrics used to evaluate the quality of text summarization. It measures the overlap of n-grams (such as unigrams, bigrams, etc.) between the generated summary and one or more reference summaries.
This overlap indicates how well the generated summary captures the essential content of the original text. Some of the key features are:
- Measures the quality of text summarization
- Compares the overlap of n-grams between generated summaries and reference summaries
- Provides insights into recall-oriented understanding
Benefits
In news aggregation services, ROUGE scores are crucial for ensuring that the summaries provided are both concise and accurate. For instance, platforms like Google News use ROUGE to evaluate and refine their summarization algorithms, ensuring that users receive summaries that accurately reflect the main points of news articles without unnecessary details.
- Useful for evaluating the performance of summarization models
- Helps in refining algorithms to produce concise and informative summaries. This helps users quickly grasp the essence of news stories, enhancing their reading experience.
Companies use human evaluation extensively to fine-tune chatbots for customer service. For example, a company like Amazon might employ human evaluators to assess the responses generated by their customer service chatbots.
Applications
In news aggregation services, ROUGE scores are crucial for ensuring that the summaries provided are both concise and accurate. For instance, platforms like Google News use ROUGE to evaluate and refine their summarization algorithms, ensuring that users receive summaries that accurately reflect the main points of news articles without unnecessary details. This helps users quickly grasp the essence of news stories, enhancing their reading experience.
The ROUGE (Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation) score is a set of metrics used to evaluate the quality of text summarization. It measures the overlap of n-grams (such as unigrams, bigrams, etc.) between the generated summary and one or more reference summaries. This overlap indicates how well the generated summary captures the essential content of the original text.
Used in evaluating the performance of news summarization tools, ensuring that generated summaries capture the essence of the original content.
Human Evaluation
Human evaluation in text summarization involves assessing the quality of generated summaries by human judges. Human evaluation focuses on subjective aspects such as coherence, readability, and relevance.
Human evaluators provide insights into how well the summary conveys the main ideas and whether it is understandable and engaging. Some of the key features include:
- Involves human judgment to assess model outputs
- Provides qualitative insights into model performance
- Essential for evaluating aspects like coherence, relevance, and fluency
Benefits
Human evaluation is essential for capturing nuances in model outputs that automated metrics might miss. While quantitative metrics provide a numerical assessment, human judgment can evaluate aspects like coherence, relevance, and fluency, which are critical for ensuring high-quality outputs.
- Offers a comprehensive evaluation that goes beyond quantitative metrics
- Helps in identifying areas for improvement that automated metrics might miss
Applications
It is used in conversational AI to assess the naturalness and appropriateness of responses, ensuring that chatbots and virtual assistants provide a human-like interaction experience. For A/B testing, these LLM evaluation metrics involve comparing two versions of a model output to determine which one performs better based on human judgment.
It helps understand user preferences and improve model performance. Collecting feedback from users who interact with the model outputs provides valuable insights into areas for improvement. This feedback loop is crucial for refining models to meet user expectations.
Companies use human evaluation extensively to fine-tune chatbots for customer service. For example, a company like Amazon might employ human evaluators to assess the responses generated by their customer service chatbots.
By analyzing human feedback, they can identify areas where the chatbot’s responses may lack clarity or relevance, allowing them to make necessary adjustments. This process ensures that the chatbot provides a more human-like and satisfactory interaction experience, ultimately improving customer satisfaction.
Explore the top 5 free tools for identifying Chatbots
Challenges in Evaluating LLMs
Following are the major challenges faced in evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs), highlighting the limitations of current metrics and the need for continuous innovation to keep pace with evolving model complexities.
1. Limitations of Current Metrics Evaluating LLMs is not without its hurdles. Current metrics often fall short of capturing the full spectrum of a model’s capabilities. For instance, traditional metrics may struggle to assess the context or creativity of a model’s output.
This limitation can lead to an incomplete understanding of a model’s performance, especially in tasks requiring nuanced language understanding or creative generation.
2. Assessing Contextual Understanding and Creativity One of the significant challenges is evaluating a model’s ability to understand context and generate creative responses. Traditional metrics, which often focus on accuracy and precision, may not adequately capture these aspects, leading to a gap in understanding the model’s true potential.
3. Adapting to Rapid Evolution Moreover, the rapid evolution of LLMs necessitates continuous improvement and innovation in evaluation techniques. As models grow in complexity, so too must the methods used to assess them. This ongoing development is crucial to ensure that evaluation metrics remain relevant and effective in measuring the true capabilities of LLMs.
4. Balancing Complexity and Usability As evaluation methods become more sophisticated, there is a challenge in balancing complexity with usability. Researchers and practitioners need tools that are not only accurate but also practical and easy to implement in real-world scenarios.
5. Ensuring Ethical and Responsible Evaluation Another challenge lies in ensuring that evaluation processes consider ethical implications. As LLMs are deployed in various applications, it is essential to evaluate them in a way that promotes responsible and ethical use, avoiding biases and ensuring fairness.
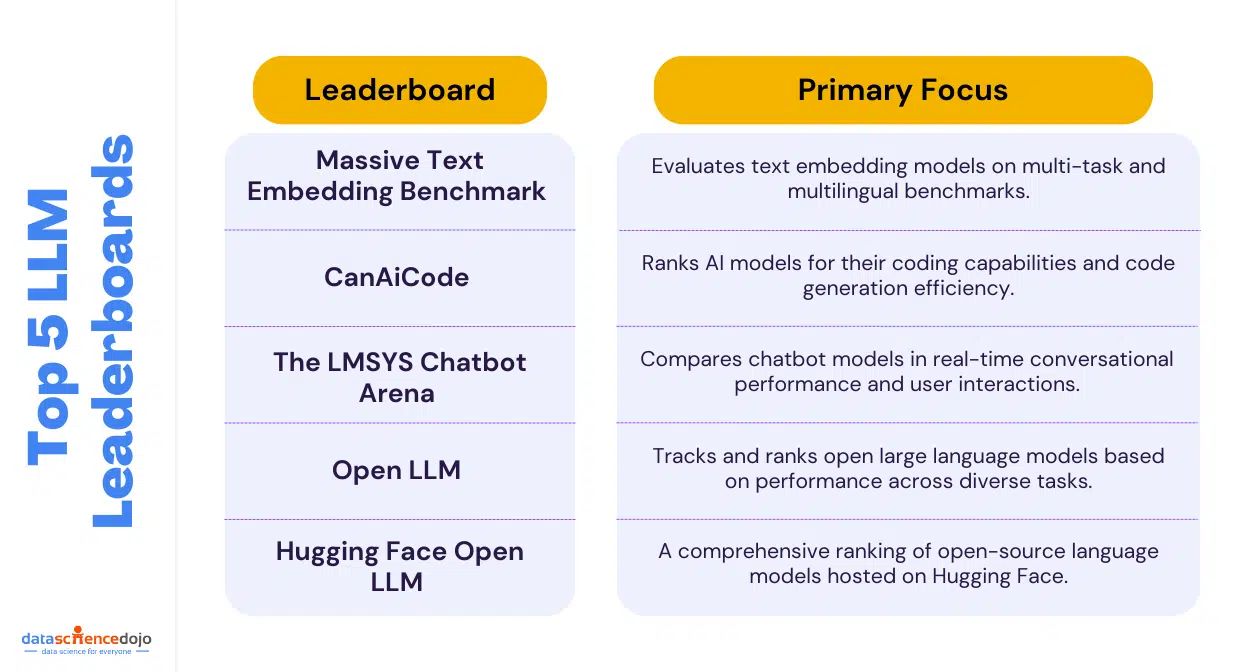
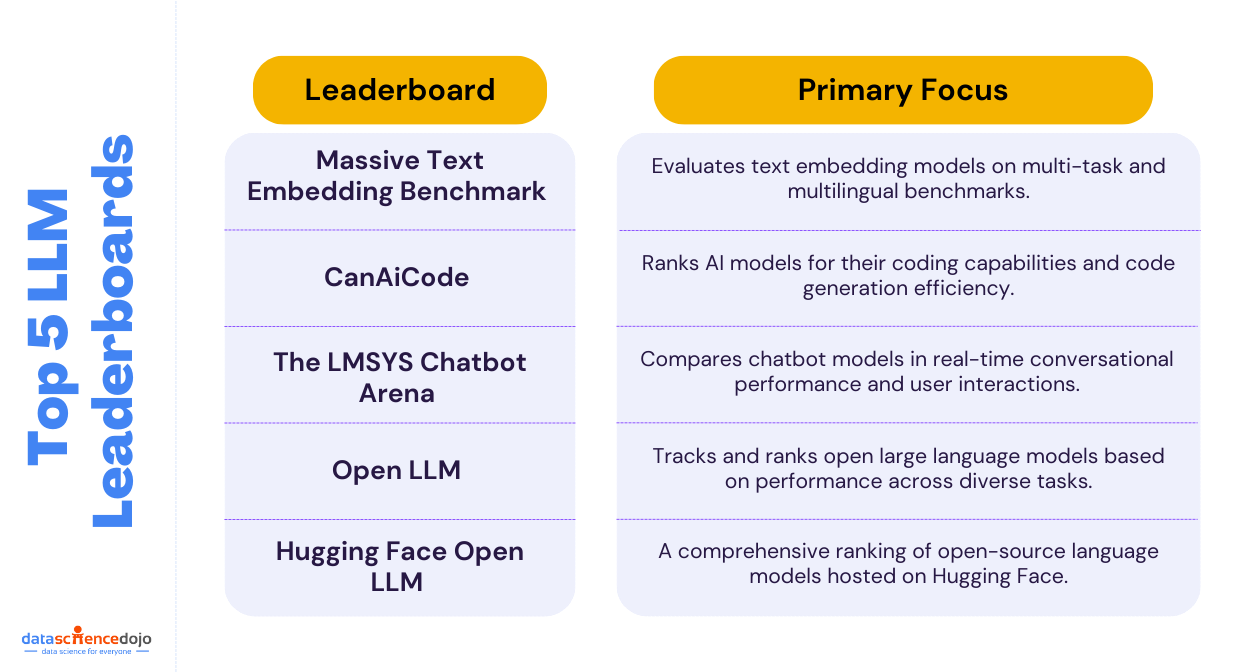
Learn more about the top 5 LLM leaderboards you can use
By addressing these challenges, the field of LLM evaluation can advance toward more comprehensive and effective methods, ultimately leading to a better understanding and utilization of these powerful models.
Future Trends in LLM Evaluation Metrics
The future of LLM evaluation is promising, with several emerging trends poised to address current limitations. New metrics are being developed to provide a more comprehensive assessment of model performance. These metrics aim to capture aspects like contextual understanding, creativity, and ethical considerations, offering a more holistic view of a model’s capabilities.
Understand AI ethics and associated ethical dilemmas
AI itself is playing a pivotal role in creating more sophisticated evaluation methods. By leveraging AI-driven tools, researchers can develop dynamic and adaptive metrics that better align with the evolving nature of LLMs. This integration of AI in evaluation processes promises to enhance the accuracy and reliability of assessments.
Looking ahead, the landscape of LLM evaluation metrics is set to become more nuanced and robust. As new metrics and AI-driven methods emerge, we can expect a more detailed and accurate understanding of model performance. This evolution will not only improve the quality of LLMs but also ensure their responsible and ethical deployment.