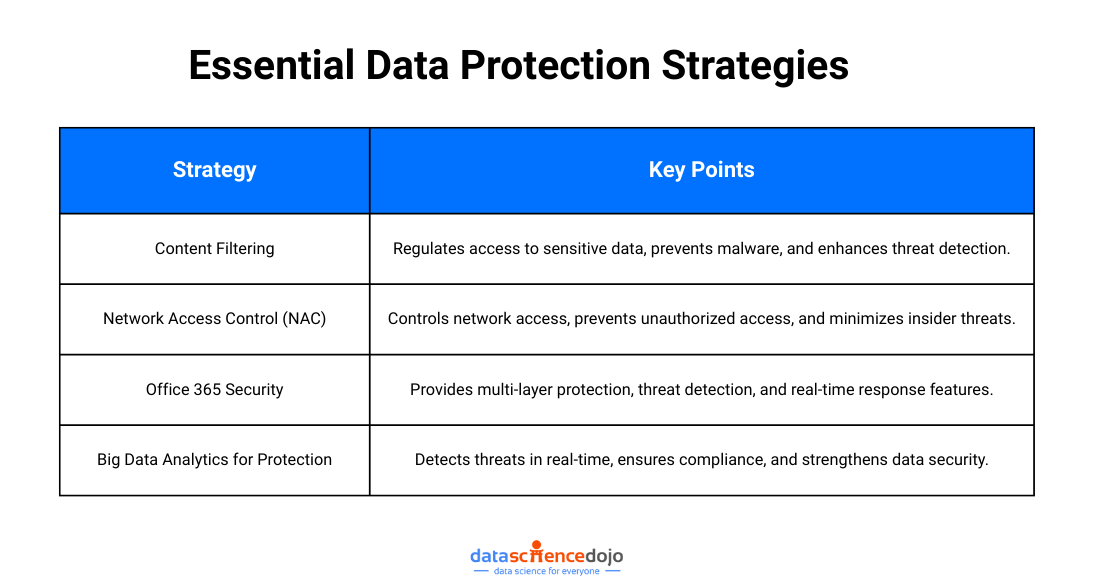
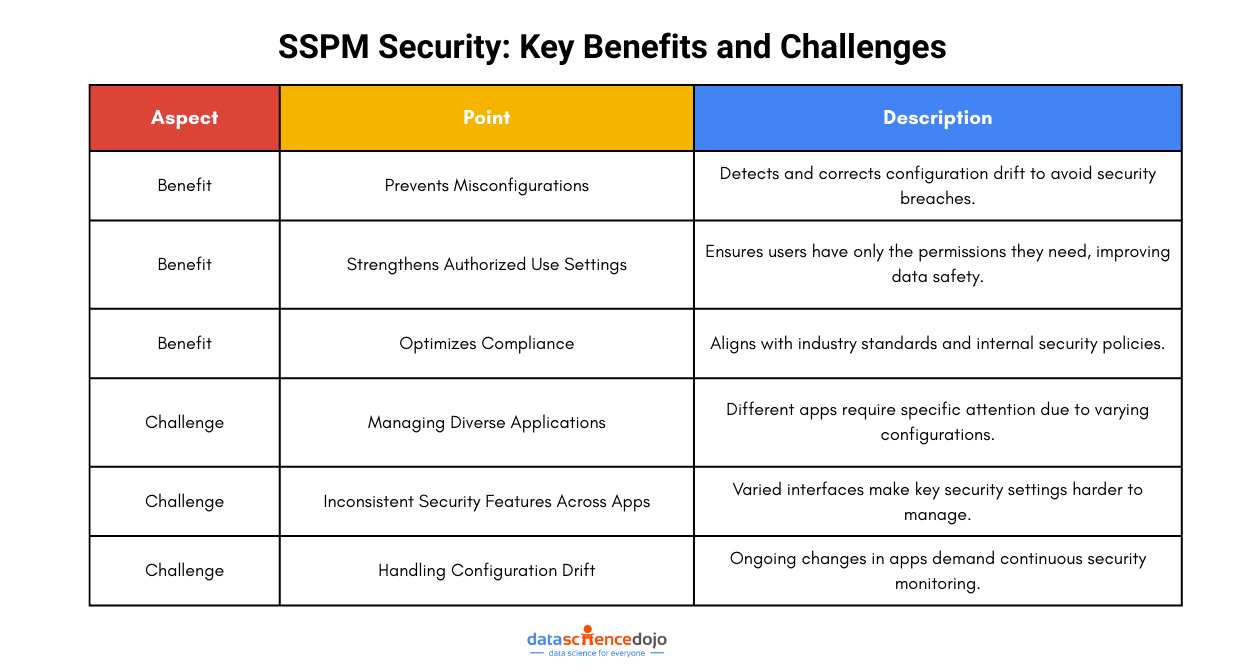
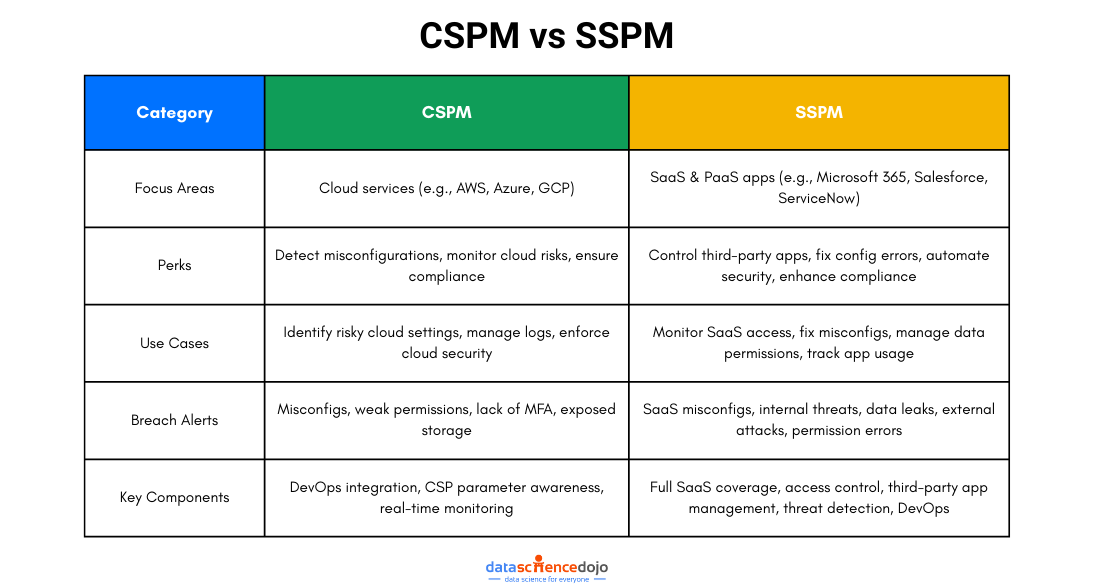
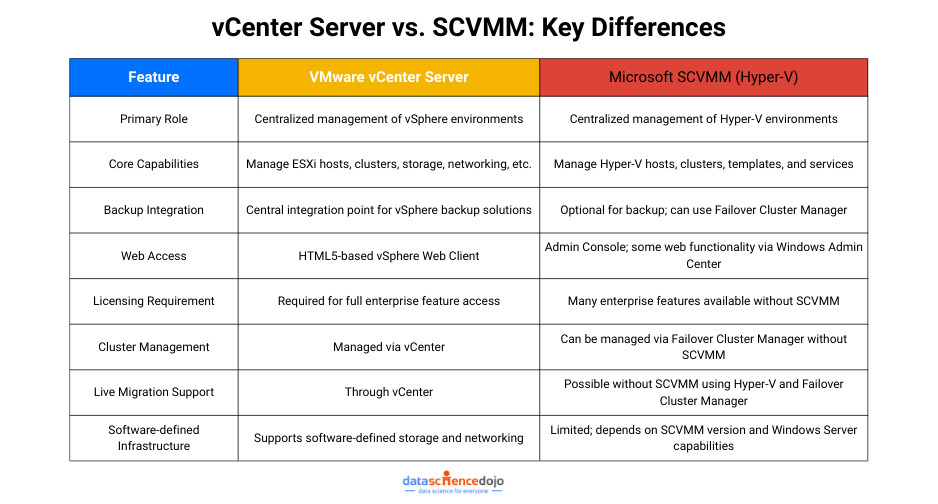
Data erasure is a software-based process that involves data sanitization or, in plain words, ‘data wiping’ so that no traces of data remain recoverable. This helps with the prevention of data leakage and the protection of sensitive information like trade secrets, intellectual property, or customer information.
By 2025, it is estimated that data will grow up to 175 Zettabytes, and with great data comes great responsibility. Data plays a pivotal role in both personal and professional lives. May it be confidential records or family photos, data security is important and must always be endorsed.
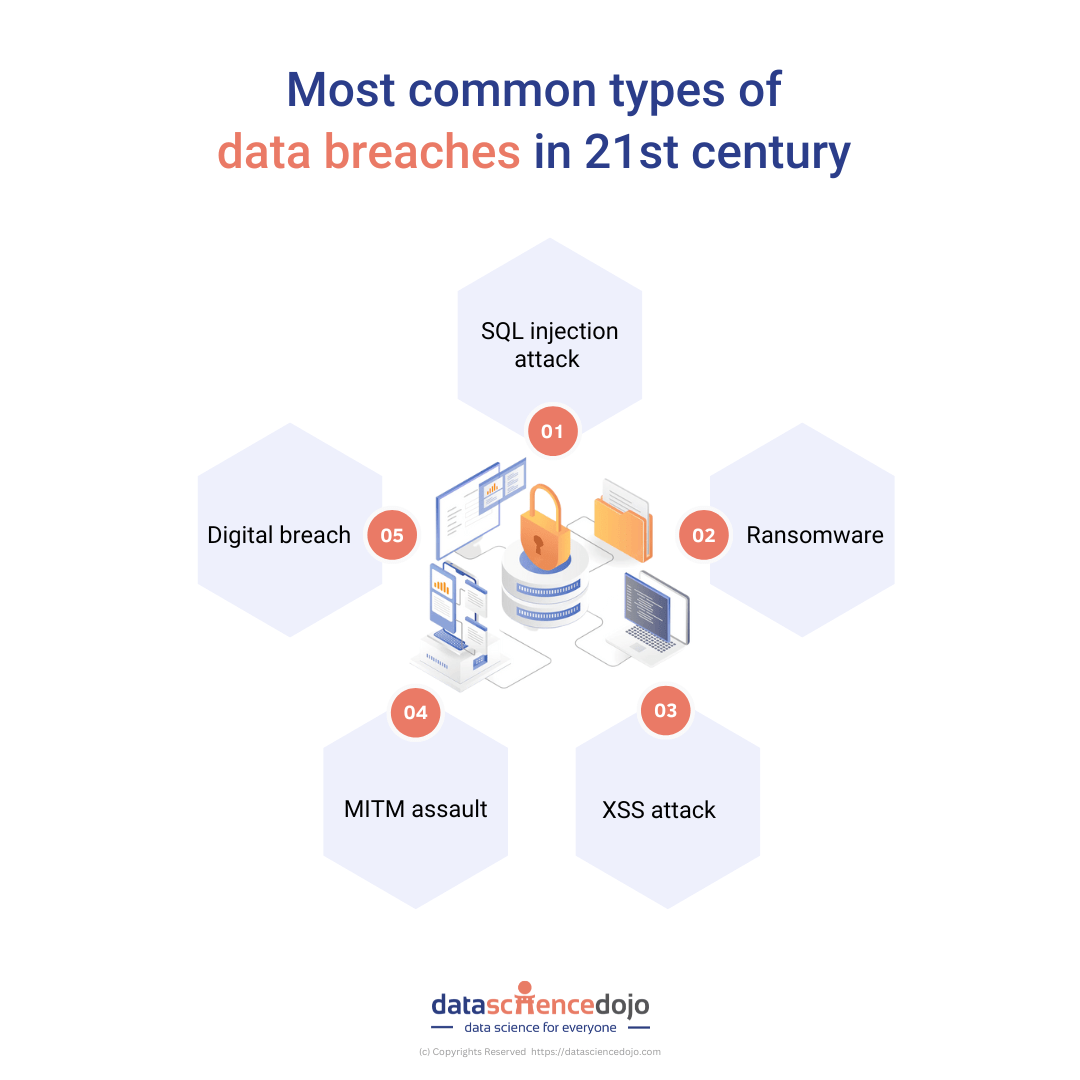
As the volume of digital information continues to grow, so does the need for safeguarding and securing data. Key data breach statistics show that 21% of all folders in a typical company are open to everyone, leading to malicious attacks, indicating a rise in data leakage and 51% criminal incidents.

Understanding Data Erasure
Data erasure is a fundamental practice in the field of data security and privacy. It involves the permanent destruction of data from storage devices like hard disks, solid-state devices, or any other digital media through software or other means.
What is Big Data Ethics and controversial experiments in data science?
This practice ensures that data remains completely unrecoverable through any data recovery methods while the device remains reusable (in case software is being used). Data erasure works in regard to an individual person who is disposing of a personal device as well as organizations handling sensitive business information. It guarantees responsible technology disposal.
The science behind data erasure
Data erasure is also known as ‘overwriting’, it involves a process of writing on data with a series of 0s and 1s, making it unreadable and undiscoverable. The overwriting process varies in the number of passes and patterns used.
The type of overwriting depends on multiple factors like the nature of the storage device, the type of data at hand, and the level of security that is needed.
The ‘number of passes’ refers to the number of times the overwriting process is repeated for a certain storage device. Each pass essentially overwrites the old data with new data. The greater the number of passes, the more thorough the data erasure process is, making it increasingly difficult to recover the demolished data.
‘Patterns’ can make data recovery extremely challenging. This is the reason why different sequences and patterns are written to the data during each pass. In essence, the data erasure process can be customized to cater to different types of scenarios depending upon the sensitivity of the data being erased. Moreover, data erasure is also used to verify whether the erasure process was successful.
Read more on how to master data security in warehousing
The Need for Data Erasure
Confidentiality of business data, prevention of data leakage, and regulation with compliance are some of the reasons we need methods like data erasure especially when someone is relocating, repurposing, or putting a device to rest.
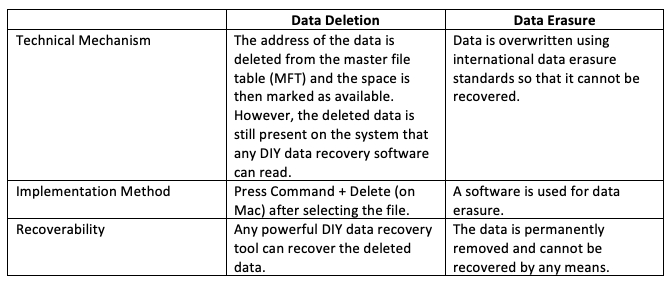
Traditional methods like data deletion make the data unavailable to the user, but provide the privilege of recovering it through different software. Likewise, the destruction of physical devices renders the device completely useless.
For this purpose, a software-based erasure method is required. Some crucial factors that drive the need are listed below:
Protection of sensitive information:
Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access is one of the primary reasons for having data erasure. Data branches or leakage of confidential information like customer information, trade secrets, or proprietary information can lead to severe consequences.
Thus, when the amount of data begins to get unmanageable and enterprises look forward to disposing of a portion of it, it is always advisable to destroy the data in a way that it is not recoverable for misuse later. Proper data erasure techniques help to mitigate the risk associated with cybercrimes.
Read more about Data privacy and data anonymization techniques
Data lifecycle management:
The data lifecycle management process includes secure storage and retrieval of data but alongside operational functionality, it is also necessary to dispose of the data properly. Data erasure is a crucial aspect of data lifecycle management and helps to responsibly remove data when it is no longer needed.
Effective data lifecycle management ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements while minimizing the risk of data breaches. Additionally, it optimizes storage resources and enhances data governance by maintaining data integrity throughout its lifecycle.
Review the relationship between data science and cybersecurity with the most common use cases.
Compliance with data protection regulations:
Data protection regulations in different countries require organizations to safeguard the privacy and security of an individual’s personal data. To avoid any legal consequences and potential damages from data theft, breach, or leakage, data erasure is a legal requirement to ensure compliance with the imposed regulations.
Additionally, adhering to these regulations helps build trust with stakeholders and demonstrates the organization’s commitment to responsible data handling practices.
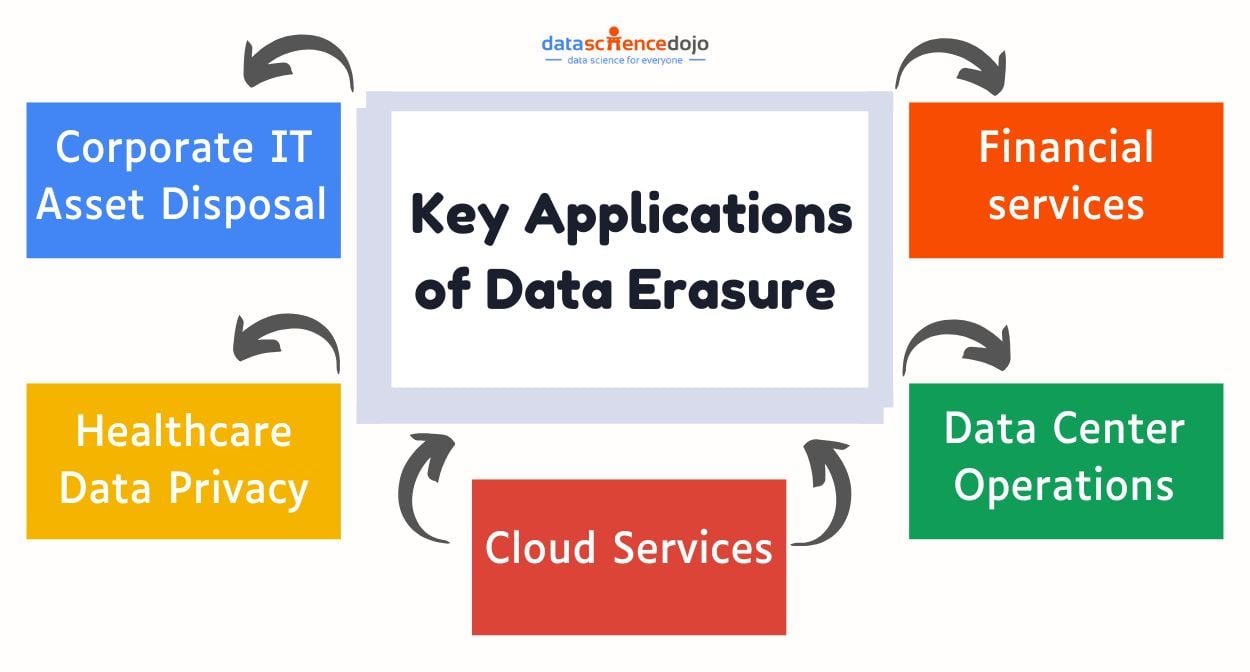
Key Applications of Data Erasure in Key Industries
Data erasure is vital for businesses handling sensitive information, ensuring secure disposal, regulatory compliance, and protection against data breaches. Below are examples of its implementation across industries:
Corporate IT asset disposal:
When a company decides to retire its previous systems and upgrade to new hardware, it must ensure that any old data that belongs to the company is securely erased from the older devices before they can be sold, donated or recycled.
This prevents sensitive corporate information from falling into the wrong hands. The IT department can use certified data erasure software to securely wipe all sensitive company data, including financial reports, customer databases, and employee records, ensuring that none of this information can be recovered from the devices.
Healthcare data privacy:
Like the corporate industry, Healthcare organisations tend to store confidential patient information in their systems. Hospitals erase patient data, including medical histories and test results, using techniques like cryptographic wiping and degaussing.
Explore the role of Data science in Healthcare
If the need arises to upgrade these systems, they must ensure secure data erasure to protect patient confidentiality and to comply with healthcare data privacy regulations. This safeguards privacy and ensures compliance with HIPAA and GDPR, mitigating risks of breaches and identity theft.
Cloud services:
Cloud service providers often have data erasure procedures in place to securely erase customer data from their servers when requested by customers or when the service is terminated.
Cloud providers erase deleted or decommissioned data using logical sanitization, cryptographic erasure, and secure overwriting. Retired servers undergo physical destruction, ensuring no data recovery is possible.
Data center operations:
Data centres often have strict data erasure protocols in place to securely wipe data from hard drives, SSDs, and other storage devices when they are no longer in use. This ensures that customer data is not accessible after the equipment is decommissioned.
Data centers securely erase sensitive data from decommissioned storage devices using multipass overwriting and cryptographic erasure. Compliance with standards like NIST 800-88 ensures secure protocols and protection of client data.
Financial services:
In a situation where a stock brokerage firm needs to retire its older trading servers. These servers would indefinitely contain some form of sensitive financial transaction data and customer account information.
Discover the top 8 data science in the finance industry
Prior to selling the servers, the firm would have to use hardware-based data erasure solutions to completely overwrite the data and render it irretrievable, ensuring client confidentiality and regulatory compliance.
Safeguard Your Business Data Today!
In the era where data is referred to as the ‘new oil’, safeguarding it has become paramount. Many times, individuals feel hesitant to dispose of their personal devices due to the possible misuse of data present in them.
The same applies to large organizations, when proper utilization of data has been done, standard measures should be taken to discard the data so that it does not result in unnecessary consequences. To ensure privacy and maintain integrity, data erasure was brought into practice. In an age where data is king, data erasure is the guardian of the digital realm.