Can AI in cybersecurity help defend against evolving threats? Yes. The need to safeguard networks, systems, and data from diverse threats, such as malware, phishing, and ransomware, has never been more urgent.
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) offers a ray of hope. AI is rapidly transforming various industries, leveraging the power of computers to mimic human intelligence, learn, reason, and make informed decisions.
Together, let’s delve into the world of AI in cybersecurity, exploring how this cutting-edge technology is revolutionizing threat detection and response. As we navigate the potential biases, risks, and ethical considerations, we’ll also uncover the promising future prospects of AI in safeguarding our digital realm.

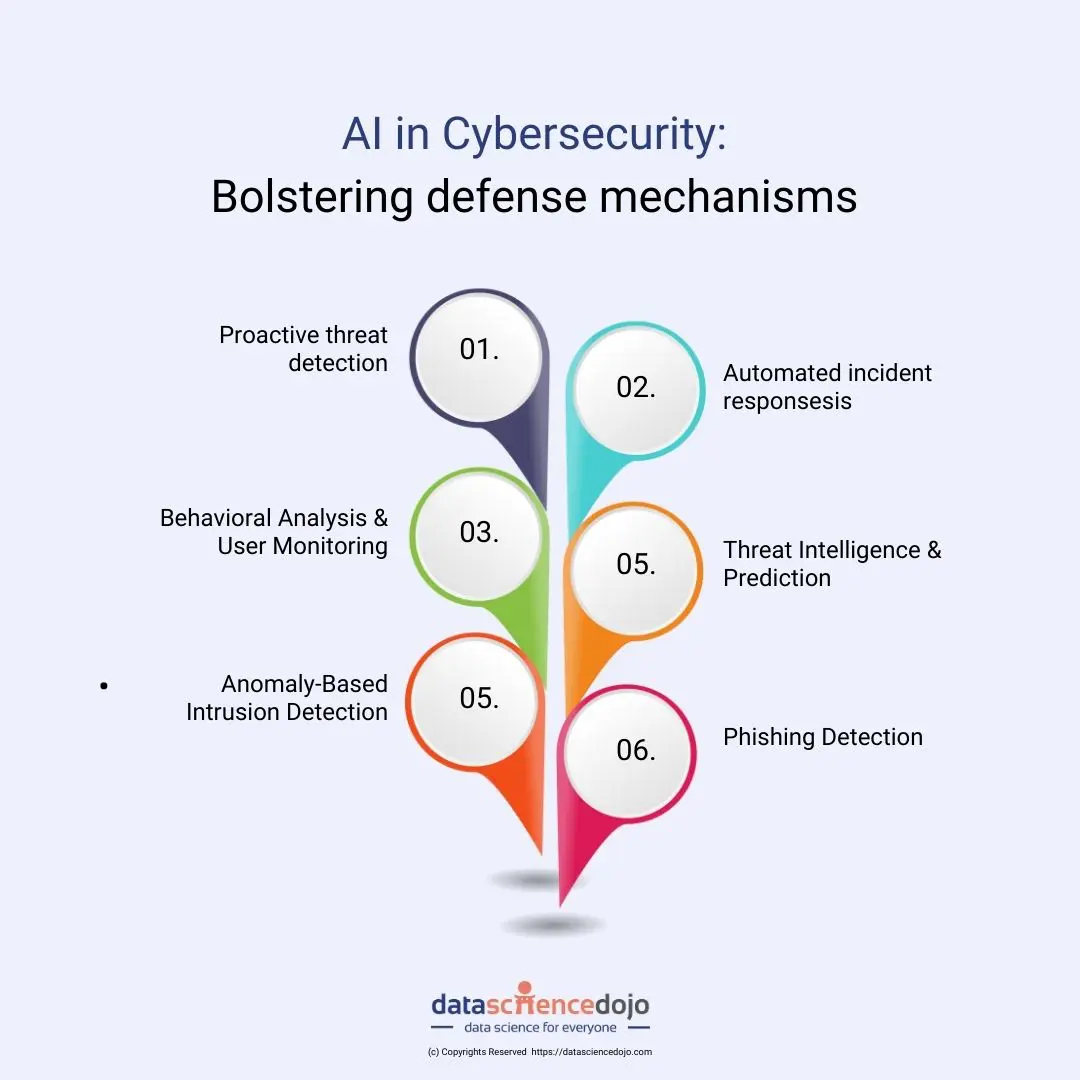
AI in cybersecurity: Bolstering defense mechanisms against cyber threats
1. Proactive threat detection:
AI can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, spotting anomalies and potential threats with high accuracy. This is because AI can learn patterns in data that humans cannot, and it can identify threats that may be missed by traditional security tools. For example, AI can be used to analyze network traffic to identify suspicious patterns, such as a large number of connections from a single IP address.
2.Automated incident response:
AI can automate incident handling, minimizing damage and enabling quick recovery. This is because AI can quickly identify and respond to threats, without the need for human intervention. For example, AI can be used to automatically quarantine infected devices, or to roll back changes that were made by a malicious actor.
3. Behavioral analysis & user monitoring:
AI can detect suspicious user activities, protecting against insider threats. This is because AI can learn normal user behavior, and it can identify deviations from that behavior. For example, AI can be used to detect if a user is trying to access sensitive data from an unauthorized location.
4. Threat intelligence and prediction:
AI can process threat intelligence data to predict and prevent potential threats. This is because AI can learn about known threats, and it can use that knowledge to identify potential threats that may not yet be known. For example, AI can be used to predict which systems are most likely to be targeted by a particular threat actor.
5. Anomaly-based intrusion detection:
AI can detect deviations from normal behavior, identifying zero-day attacks. This is because AI can learn normal behavior, and it can identify deviations from that behavior. For example, AI can be used to detect if a system is behaving abnormally, which could be a sign of a zero-day attack.
6. Enhanced phishing detection:
AI can analyze emails and URLs to distinguish phishing attempts from legitimate communications. This is because AI can learn about the characteristics of phishing emails and URLs, and it can use that knowledge to identify phishing attempts. For example, AI can be used to detect if an email is coming from a suspicious sender, or if a URL is pointing to a malicious website.
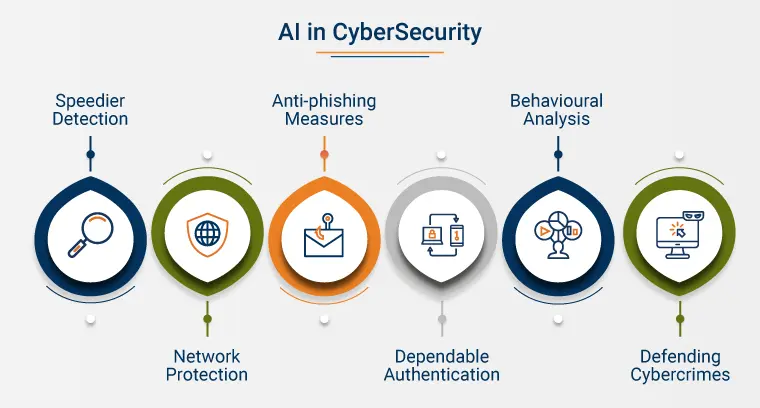
Cybersecurity for threat detection, analysis, and response
AI is used in cybersecurity for a variety of purposes, including:
- Threat detection: AI can be used to detect cyber threats more quickly and accurately than traditional methods. This is done by using machine learning to analyze large amounts of data and identify patterns that may indicate a potential attack.
- Threat analysis: AI can be used to analyze cyber threats in order to understand their nature and impact. This information can then be used to develop effective mitigation strategies.
- Threat response: AI can be used to respond to cyber threats more quickly and effectively. This is done by using machine learning to identify and block malicious traffic, as well as to automate the process of incident response.
- Network Traffic Analysis: AI identifies malicious activities hidden in legitimate network traffic.
Examples of AI-powered cybersecurity tools and applications
There are a number of AI-powered cybersecurity tools and applications available, including:
- CrowdStrike Falcon: CrowdStrike Falcon is an AI-powered cybersecurity platform that provides threat detection, analysis, and response capabilities.
- Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR: Palo Alto Networks Cortex XDR is an AI-powered cybersecurity platform that provides comprehensive visibility and control over your entire IT environment.
- IBM Security QRadar with Watson: IBM Security QRadar with Watson is an AI-powered cybersecurity platform that provides threat intelligence, analytics, and automation.
Read more –> Top 6 cybersecurity trends to keep an eye on in 2023
AI-Driven Threat Detection
Traditional threat detection methods have been effective to some extent, but they face several challenges and limitations. One significant challenge is the sheer volume of data generated by modern networks and systems, making it difficult for human analysts to manually identify potential threats in real-time.
Additionally, cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and can easily evade rule-based detection systems. Traditional methods may struggle to keep up with rapidly evolving attack techniques, leaving organizations vulnerable to advanced threats.
Moreover, false positives and false negatives can hamper the accuracy of threat detection, leading to wasted time and resources investigating non-threatening incidents or missing actual threats.
Threat detection: Advanced pattern recognition and anomaly detection
AI-driven threat detection systems leverage machine learning algorithms to overcome the limitations of traditional methods. These systems can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, detecting patterns and anomalies that may signify potential security breaches.
AI algorithms can learn from historical data and adapt to new threats, making them highly effective in identifying previously unseen attack vectors. The ability to detect unusual patterns and behaviors, even without explicit rules, allows AI-powered systems to uncover zero-day attacks and other advanced threats that traditional methods might miss.
Real-world examples: AI detecting cyber threats
- Network Intrusion Detection: AI-driven intrusion detection systems can monitor network traffic, identify suspicious activities, and detect intrusions from various attack vectors like malware, phishing attempts, and brute-force attacks.
- Behavioral Analysis: AI algorithms can analyze user behavior and identify deviations from normal patterns, enabling the detection of insider threats or compromised accounts.
- Advanced Malware Detection: AI can recognize previously unknown malware patterns and behaviors, facilitating early detection and containment.
AI-powered security analytics
AI in processing and analyzing vast amounts of security data
AI plays a crucial role in security analytics by processing and analyzing large volumes of data generated from different sources, such as logs, network traffic, user activity, and endpoint events. The algorithms can quickly sift through this data to identify potential security incidents, anomalies, and trends. This automated analysis significantly reduces the workload on human analysts and enables faster responses to emerging threats.
How AI-Driven analytics helps in identifying potential vulnerabilities
AI-driven analytics can identify potential vulnerabilities and weak points in an organization’s security posture by continuously monitoring and assessing the IT environment. The algorithms can detect configuration errors, outdated software, and misconfigurations that may create security gaps.
By correlating data from multiple sources, AI analytics can provide a holistic view of the security landscape and prioritize critical vulnerabilities, allowing security teams to address them proactively.
Case Studies of AI-Based security analytics
- Incident Response Automation: AI-powered security analytics can automate incident response by detecting threats, assessing their severity, and triggering appropriate responses. This helps in containing threats before they escalate, reducing response times, and minimizing potential damage.
- Threat Hunting: AI algorithms can assist security analysts in threat hunting activities by flagging suspicious patterns and highlighting potential threat indicators, making the hunt more efficient and effective.
- Predictive Security: By analyzing historical data, AI-driven security analytics can predict potential security threats and vulnerabilities, allowing organizations to take preventive measures to strengthen their defenses.
AI in incident response and mitigation
Traditional incident response is a manual process that can be time-consuming and error-prone. It typically involves the following steps:
- Detection: Identifying that an incident has occurred.
- Containment: Isolating the affected systems and preventing further damage.
- Investigation: Determining the root cause of the incident.
- Remediation: Fixing the vulnerability that allowed the incident to occur.
- Recovery: restoring the affected systems to their original state.
AI-driven incident response automates and accelerates many of these steps. This can help organizations to reduce response time and minimize damage.
How AI automates and accelerates incident detection, containment, and recovery
AI can be used to automate and accelerate incident detection in a number of ways. For example, AI can be used to monitor network traffic for malicious activity. It can also be used to analyze user behavior for signs of compromise.
Once an incident has been detected, AI can be used to automate the process of containment. This can involve isolating the affected systems and blocking malicious traffic.
AI can also be used to automate the process of recovery. This can involve restoring the affected systems to their original state and implementing mitigation measures to prevent future incidents.
Read more –> Top 6 cybersecurity trends to keep an eye on in 2023
Challenges and risks of AI in cybersecurity
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has shown great promise in enhancing cybersecurity, but it also comes with its own set of challenges and risks that need to be addressed. As AI becomes more prevalent in cybersecurity practices, organizations must be aware of the following potential pitfalls:
Potential biases and limitations of AI algorithms
AI algorithms are only as good as the data they are trained on, and if this data contains biases, the AI system can perpetuate and amplify those biases. For example, if historical data used to train an AI cybersecurity model is biased towards certain types of threats or attackers, it might overlook emerging threats from different sources. Ensuring diversity and inclusivity in training data and regularly auditing AI systems for biases are crucial steps to mitigate this risk.
Moreover, AI systems have limitations in understanding context and intent, which can lead to false positives or negatives. This limitation may result in the misidentification of legitimate activities as malicious or vice versa. Cybersecurity professionals must be vigilant in interpreting AI-generated results and validating them with human expertise.
Risk of AI being exploited by cyber attackers
As AI technologies evolve, cyber attackers can exploit them to their advantage. For instance, attackers can use AI to design and execute more sophisticated attacks that evade traditional cybersecurity defenses. AI-generated deepfakes and synthetic content can also be leveraged to deceive users and penetrate security measures.
To counter this risk, organizations should focus on developing adversarial AI capabilities to identify and defend against AI-driven attacks. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and updating of AI models to stay ahead of potential malicious use are essential.
Ethical considerations in using AI for cybersecurity
AI-driven cybersecurity raises ethical concerns, particularly regarding user privacy and surveillance. The collection and analysis of vast amounts of data to detect threats might infringe upon individual privacy rights. Striking the right balance between security and privacy is crucial to avoid violating ethical principles.
Transparency and explainability of AI algorithms are also vital in gaining user trust. Users and stakeholders need to understand how AI makes decisions and why certain actions are taken. Ethical guidelines should be established to ensure responsible AI use in cybersecurity practices.
Future prospects: AI and cybersecurity
AI’s potential in the cybersecurity domain is immense, and it opens up several opportunities for the future:
Predictions for the future of AI in the cybersecurity domain
In the future, AI is expected to become even more integral to cybersecurity. AI-driven threat detection and response systems will become increasingly sophisticated, enabling quicker identification and mitigation of cyber threats. AI will also play a significant role in automating routine security tasks, allowing cybersecurity professionals to focus on more complex challenges.
Countering emerging threats like AI-driven attacks
As AI-driven attacks become a reality, AI will be indispensable in defending against them. AI-powered security solutions will continuously adapt to evolving threats, making it more challenging for attackers to exploit AI vulnerabilities. Proactive measures, such as ethical hacking using AI, can also help identify and rectify potential weaknesses in AI-based cybersecurity systems.
Continuous research and development in AI for cybersecurity
The dynamic nature of cybersecurity demands continuous research and development in AI. Cybersecurity professionals and AI experts must collaborate to enhance AI models’ robustness, accuracy, and resilience. Investment in cutting-edge AI technologies and ongoing training for cybersecurity professionals are vital to stay ahead of cyber threats.
Conclusion
AI has the potential to revolutionize cybersecurity and make it more effective. By using AI, organizations can detect and respond to cyber threats more quickly and effectively, which can help to protect their networks, systems, and data from harm.
The future of cybersecurity is AI-driven. Organizations that want to stay ahead of the curve need to invest in AI-driven cybersecurity solutions.