Keeping up with emerging AI trends and tools is crucial to developing a standout website in 2024. So, we can expect web developers across the globe to get on board with AI trends and use AI web-building tools that will automate tasks, provide personalized suggestions, and enhance the user’s experience.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing web development by introducing innovative trends that enhance both functionality and user experience. AI plays a pivotal role in automating repetitive tasks, allowing developers to focus on more complex aspects of web design.
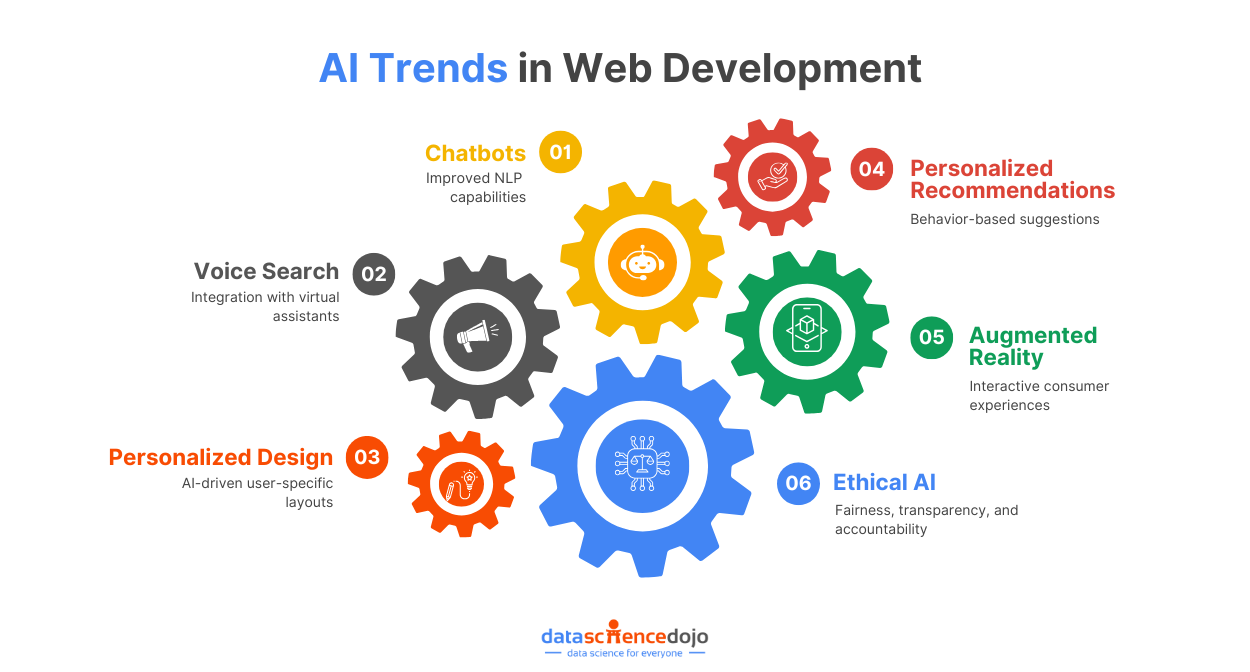
AI Trends in Web Development
AI-powered tools will offer personalized user experiences by analyzing data and adapting content accordingly. Additionally, these tools will improve accessibility and engagement through features like voice search and chatbots, making websites more interactive and user-friendly.
Learn how to build AI-based chatbots in Python
As AI continues to evolve, web developers will increasingly integrate these technologies to create smarter, more dynamic websites. Let’s take a look at some leading AI trends that are crucial to consider for web development
Chatbots
An AI chatbot uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand spoken and written human language. This means they can detect the intent of a customer query and deliver the response they deem appropriate.
As NLP advances in 2024, we can expect AI chatbots to listen to and respond to human language even better. Adding an AI-powered chatbot to your website makes customer service interactions more effective and efficient for your customers.
Explore 7 NLP Techniques and Tasks to Implement Using Python
In addition, having AI chatbots as the first point of contact allows human customer service representatives to deal with more complex queries.
Voice Search
Voice search has become popular in recent years, thanks to virtual assistants like Apple’s Siri, Amazon’s Alexa, and Google’s Assistant. In fact, in 2022, around 50% of consumers in the US said they use voice search every day.
Understand how LLM Development is making Chatbots smarter
AI plays a significant role in optimizing voice search. So, adopting these technologies to develop your website for voice search is one of the crucial AI trends to follow in 2024 as even more people use their voice to search online.
Personalized Design
Personalized design in web development refers to the creation of user experiences that are tailored to individual preferences and behaviors. By leveraging data analytics and AI technologies, developers can customize content, layout, and functionality to meet the unique needs of each user.
This approach enhances user engagement, as visitors are more likely to interact with a website that resonates with their interests and expectations. Personalized design not only improves satisfaction and retention but also helps businesses build stronger relationships with their audience by delivering relevant and meaningful experiences.
AI is expected to be more prominent in website design in 2024. Designs will look better and be more user-friendly as AI analyzes algorithms to understand a user’s tastes and needs and then personalized website designs to fit them accordingly.
Personalized Recommendations
AI will predict what a user wants to see and offer personalized recommendations based on their behaviors and preferences. This personal touch will enhance the user experience for consumers visiting your website.
Personalized recommendations in web development involve using data-driven insights to suggest content, products, or services tailored to an individual’s preferences and past behavior.
By employing AI and machine learning algorithms, websites can analyze user data, such as browsing history and purchase patterns, to deliver relevant suggestions that enhance the user experience. This approach not only increases user engagement and satisfaction but also boosts conversion rates by presenting users with options that align closely with their interests.
Explore 101 Machine Learning Algorithms for Data Science with Cheat Sheets
Personalized recommendations help businesses create more meaningful interactions with their audience, fostering loyalty and encouraging repeat visits.
Augmented Reality
Augmented reality (AR) overlaps digital elements onto your real-world surroundings by using the camera on a smartphone, as AI powers object recognition and scene understanding.
The number of consumers worldwide who use AR is expected to grow to 4.3 billion by 2025. So, among the different AI trends, we expect to see a rise in businesses using AR to offer a more interactive and immersive experience.
In 2024, try adding an AR experience to your website, which can differ depending on the products or services you offer. For example, allow consumers to virtually try on clothes and shoes, test out makeup shades, or view furniture in their rooms.
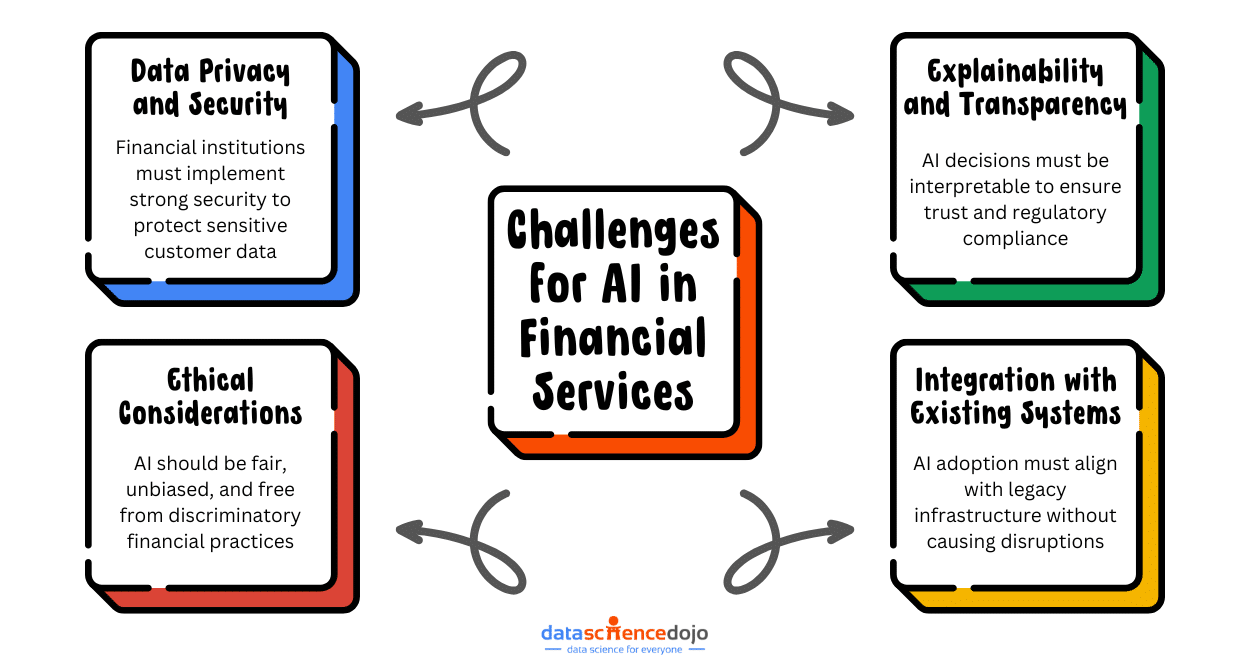
Ethical AI
As AI becomes a more significant part of our digital lives in 2024, finding proactive solutions for ethical concerns will be crucial so everyone can enjoy the benefits without worrying about issues that may arise.
So, we expect web developers to make ethical AI a top priority. Ethical AI refers to developing and deploying AI-powered technologies that give prominence to fairness, transparency, accountability, and respect for human values.
Ethical AI involves creating algorithms that are unbiased and inclusive, ensuring that data used for training AI models is representative of diverse populations. It also calls for transparency in AI processes, allowing users to understand how decisions are made.
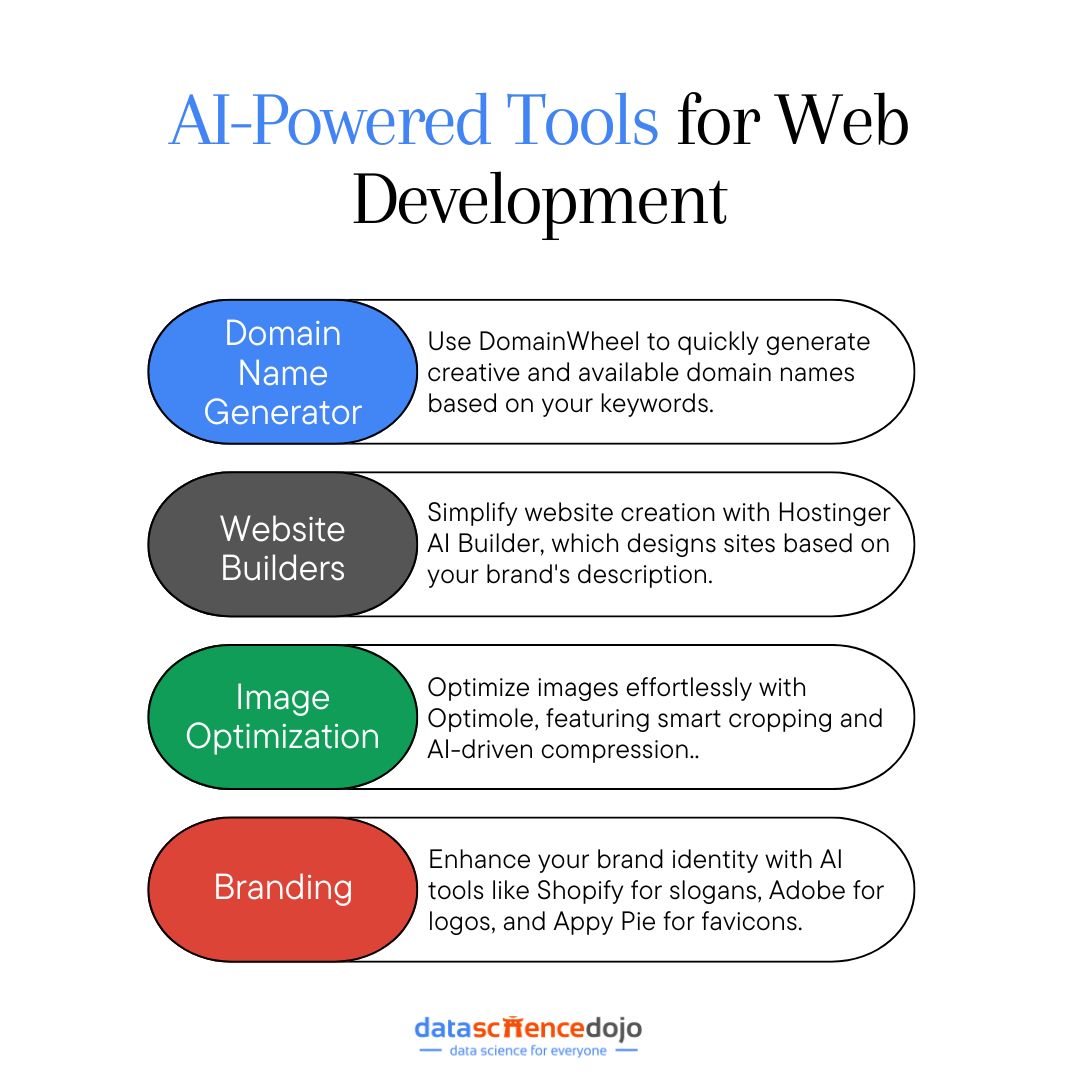
AI Web-Building Tools
In addition to the above six trends, we can expect to see the adoption of various AI-powered tools that will enhance a developer’s productivity by assisting with web development tasks such as:
Choosing a Domain Name
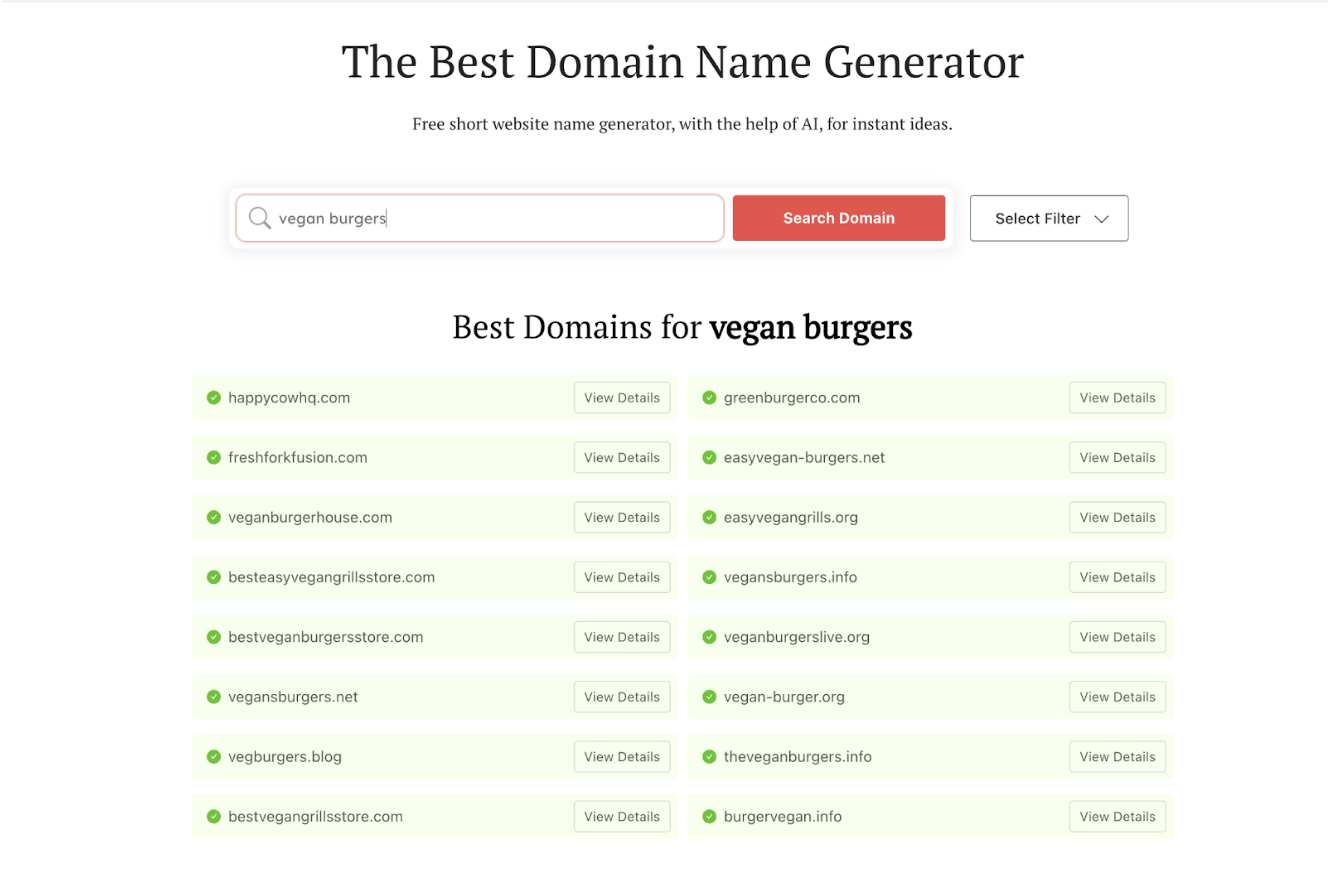
Choosing and registering an available domain name will be the first part of your web development journey. To make this part easier, use a free AI tool that generates domain name suggestions based on keywords representing your website’s products or services.
Using DomainWheel, you can enter a keyword or phrase and instantly get a list of available domain names across different domain extensions, including .com, .net, .org, .co.uk, and more.
The role of AI is to analyze keyword combinations and generate contextual domain name ideas based on words that sound like your keyword, words that rhyme with your keyword, or random suggestions based on your keyword meaning.
Building a Website
Building your website is one of the most important steps when starting a business. By taking advantage of various AI website builders, you don’t have to worry about having complex coding or design skills, as most of the work is already done for you.
Explore how AI aids Webmaster and content creators progress in 4 new ways
Using Hostinger’s AI website builder, your website, whether an online shop, blog, or portfolio, can be created for you based on a brief description of your brand. However, the robust design tools and drag-and-drop website editor still give you control over how your website looks and works.
Optimizing Images
Once your website is up and running, we recommend you add an image optimization plugin to save development time and storage. The WordPress plugin Optimole works automatically to store, edit, and scale your images.
Optimole’s main AI-powered features are smart cropping, which detects an image’s most important area, and compression quality prediction, which uses machine learning algorithms to compress images while maintaining an acceptable quality.
Branding
With the various AI tools available, branding your business to make your website stand out is easy.
First, create a catchy brand slogan that customers will remember. Shopify’s free slogan generator uses machine learning algorithms to generate slogan suggestions based on just one or two words that represent your brand. However, it is important that your consumers don’t detect AI writing and that the slogan matches your usual tone of voice.
Explore 3 Effective Ways of Employer Branding With Digital Marketing
Next, create a logo. Adobe is a great place to start when it comes to creating your logo. You can use their creative studio or their AI logo generator, which will ask you to answer prompts such as your brand name and slogan before allowing you to choose your favorite designs from a series of logo templates. You can also customize your logo’s size, font, colors, and content to suit your brand.
Finally, create a favicon (favorite icon). With Appy Pie’s Free AI Favicon Maker, you can choose from more than 250 templates or start your design with a prompt, and then use the editing tool to customize the favicon’s design, layout, font color, and text.
Conclusion
Not so long ago, artificial intelligence and machine learning were buzzwords for futuristic concepts. Now, it’s evident that these advancements have initiated AI trends that will revamp real-world technologies, transforming the field of web development and many other industries.
All those involved with website development should embrace these latest AI trends and give these tools a try to compete in today’s digital world.