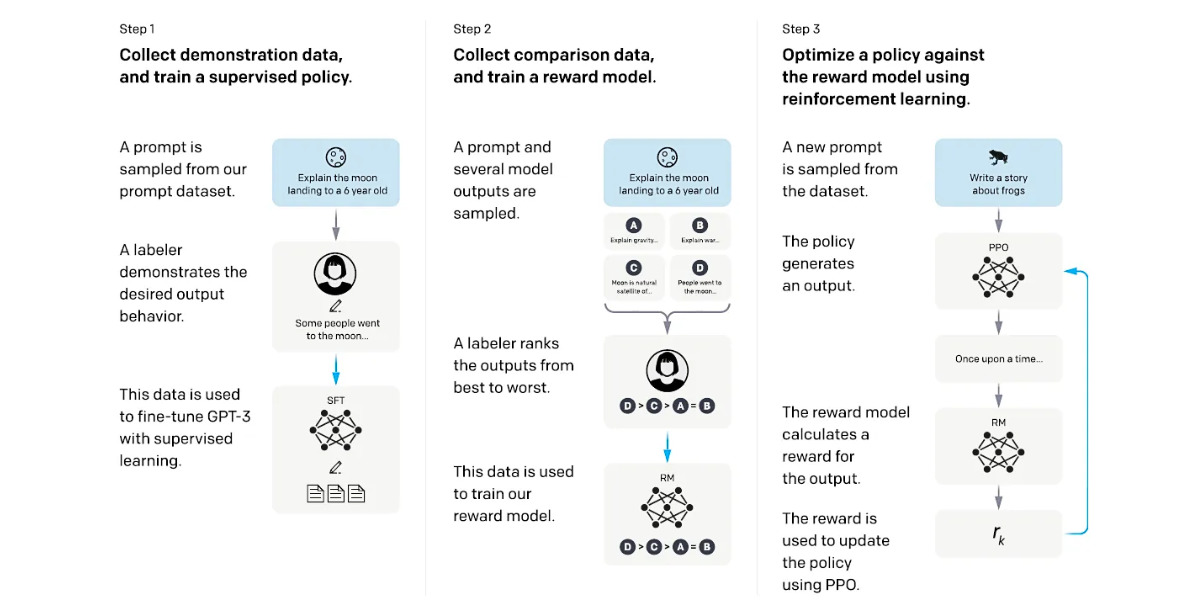
Have you ever read a sentence in a book that caught you off guard with its meaning? Maybe it started in one direction and then, suddenly, the meaning changed, making you stumble and re-read it. These are known as garden-path sentences, and they are at the heart of a fascinating study on human cognition—a study that also sheds light on the capabilities of AI, specifically the language model ChatGPT.
Certainly! Here is a comparison table outlining the key aspects of language processing in ChatGPT versus humans based on the study:
| Feature | ChatGPT | Humans |
|---|---|---|
| Context Use | Utilizes previous context to predict what comes next. | Uses prior context and background knowledge to anticipate and integrate new information. |
| Predictive Capabilities | Can predict human memory performance in language-based tasks . | Naturally predict and create expectations about upcoming information. |
| Memory Performance | Relatedness ratings by ChatGPT correspond with actual memory performance. | Proven correlation between relatedness and memory retention, especially in the presence of fitting context. |
| Processing Manner | Processes information autoregressively, using the preceding context to anticipate future elements . | Sequentially processes language, constructing and updating mental models based on predictions. |
| Error Handling | Requires updates in case of discrepancies between predictions and actual information . | Creation of breakpoints and new mental models in case of prediction errors. |
| Cognitive Faculties | Lacks an actual memory system, but uses relatedness as a proxy for foreseeing memory retention. | Employs cognitive functions to process, comprehend, and remember language-based information. |
| Language Processing | Mimics certain cognitive processes despite not being based on human cognition. | Complex interplay of cognitive mechanisms for language comprehension and memory. |
| Applications | Potential to assist in personalized learning and cognitive enhancements, especially in diverse and elderly groups. | Continuous learning and cognitive abilities that could benefit from AI-powered enhancement strategies |
This comparison table synthesizes the congruencies and distinctions discussed in the research, providing a broad understanding of how ChatGPT and humans process language and the potential for AI-assisted advancements in cognitive performance.
The Intrigue of Garden-Path Sentences
Certainly! Garden-path sentences are a unique and useful tool for linguists and psychologists studying human language processing and memory. These sentences are constructed in a way that initially leads the reader to interpret them incorrectly, often causing confusion or a momentary misunderstanding. The term “garden-path” refers to the idiom “to be led down the garden path,” meaning to be deceived or misled.
Usually, the first part of a garden-path sentence sets up an expectation that is violated by the later part, which forces the reader to go back and reinterpret the sentence structure to make sense of it. This reanalysis process is of great interest to researchers because it reveals how people construct meaning from language, how they deal with syntactic ambiguity, and how comprehension and memory interact.
The classic example given,
“The old man the boat,”
relies on the structural ambiguity of the word “man.”
Initially, “The old man” reads like a noun phrase, leading you to expect a verb to follow.
But as you read “the boat,” confusion arises because “the boat” doesn’t function as a verb.
Here’s where the garden-path effect comes into play:
To make sense of the sentence, you must realize “man” is being used as a verb, meaning to operate or staff, and “the old” functions as the subject. The corrected interpretation is that older individuals are the ones operating the boat.
Other examples of garden-path sentences might include:
- “The horse raced past the barn and fell.” At first read, you might think the sentence is complete after “barn,” making “fell” seem out of place. However, the sentence means the horse that was raced past the barn is the one that fell.
- “The complex houses married and single soldiers and their families.” Initially, “complex” might seem to be an adjective modifying “houses,” but “houses” is in fact a verb, and “the complex” refers to a housing complex.
These sentences demonstrate the cognitive work involved in parsing and understanding language. By examining how people react to and remember such sentences, researchers can gain insights into the psychological processes underlying language comprehension and memory formation
ChatGPT’s Predictive Capability
Garden-path sentences, with their inherent complexity and potential to mislead readers temporarily, have allowed researchers to observe the processes involved in human language comprehension and memory. The study at the core of this discussion aimed to push boundaries further by exploring whether an AI model, specifically ChatGPT, could predict human memory performance concerning these sentences.
The study presented participants with pairs of sentences, where the second sentence was a challenging garden-path sentence, and the first sentence provided context. This context was either fitting, meaning it was supportive and related to the garden-path sentence, making it easier to comprehend, or unfitting, where the context was not supportive and made comprehension more challenging.
ChatGPT, mirroring human cognitive processes to some extent, was used to assess the relatedness of these two sentences and to predict the memorability of the garden-path sentence.
The participants then participated in a memory task to see how well they recalled the garden-path sentences. The correlation between ChatGPT’s predictions and human performance was significant, suggesting that ChatGPT could indeed forecast how well humans would remember sentences based on the context provided.
For instance, if the first sentence was
“Jane gave up on the diet,” followed by the garden-path sentence
“Eating carrots sticks to your ribs,” the fitting context (“sticks” refers to adhering to a diet plan), makes it easier for both humans and
ChatGPT to make the sentence memorable. On the contrary, an unfitting context like
“The weather is changing” would offer no clarity, making the garden-path sentence less memorable due to a lack of relatability.
This reveals the role of context and relatability in language processing and memory. Sentences placed in a fitting context were rated as more memorable and, indeed, better remembered in subsequent tests. This alignment between AI assessments and human memory performance underscores ChatGPT’s predictive capability and the importance of cohesive information in language retention.
Memory Performance in Fitting vs. Unfitting Contexts
In the study under discussion, the experiment involved presenting participants with two types of sentence pairs. Each pair consisted of an initial context-setting sentence (Sentence 1) and a subsequent garden-path sentence (Sentence 2), which is a type of sentence designed to lead the reader to an initial misinterpretation.
In a “fitting” context, the first sentence provided would logically lead into the garden-path sentence, aiding comprehension by setting up the correct framework for interpretation.
For example, if Sentence 1 was “The city has no parks,” and Sentence 2 was “The ducks the children feed are at the lake,” the concept of feed here would fit with the absence of city parks, and the readers can easily understand that “the children feed” is a descriptive action relating to “the ducks.”
Conversely, in an “unfitting” context, the first sentence would not provide a supportive backdrop for the garden-path sentence, making it harder to parse and potentially less memorable.
If Sentence 1 was “John is a skilled carpenter,” and Sentence 2 remained “The ducks the children feed are at the lake,” the relationship between Sentence 1 and Sentence 2 is not clear because carpentry has no apparent connection to feeding ducks or the lake.
Participants in the study were asked to first rate the relatedness of these two sentences on a scale. The study found that participants rated fitting contexts as more related than unfitting ones.
The second part of the task was a surprise memory test where only garden-path sentences were presented, and the participants were required to recall them. It was discovered that the garden-path sentences that had a preceding fitting context were better remembered than those with an unfitting context—this indicated that context plays a critical role in how we process and retain sentences.
ChatGPT, a generative AI system, predicted this outcome. The model also rated garden-path sentences as more memorable when they had a fitting context, similar to human participants, demonstrating its capability to forecast memory performance based on context.
This highlights not only the role of context in human memory but also the potential for AI to predict human cognitive processes.
Stochastic Reasoning: A Potential Cognitive Mechanism
The study in question introduces the notion of stochastic reasoning as a potential cognitive mechanism affecting memory performance. Stochastic reasoning involves a probabilistic approach to understanding the availability of familiar information, also known as retrieval cues, which are instrumental in bolstering memory recall.
The presence of related, coherent information can elevate activation within our cognitive processes, leading to an increased likelihood of recalling that information later on.
Let’s consider an example to elucidate this concept. Imagine you are provided with the following two sentences as part of the study:
“The lawyer argued the case.”
“The evidence was compelling.”
In this case, the two sentences provide a fitting context where the first sentence creates a foundation of understanding related to legal scenarios and the second sentence builds upon that context by introducing “compelling evidence,” which is a familiar concept within the realm of law.
This clear and potent relation between the two sentences forms strong retrieval cues that enhance memory performance, as your brain more easily links “compelling evidence” with “lawyer argued the case,” which aids in later recollection.
Alternatively, if the second sentence was entirely unrelated, such as “The roses in the garden are in full bloom,” the lack of a fitting context would mean weak or absent retrieval cues. As the information related to law does not connect well with the concept of blooming roses, this results in less effective memory performance due to the disjointed nature of the information being processed.
The study found that when sentences are placed within a fitting context that aligns well with our existing knowledge and background, the relationship between the sentences is clear, thus providing stronger cues that streamline the retrieval process and lead to better retention and recall of information.
This reflects the significance of stochastic reasoning and the role of familiarity and coherence in enhancing memory performance.
ChatGPT vs. Human Language Processing
The paragraph delves into the intriguing observation that ChatGPT, a language model developed by OpenAI, and humans share a commonality in how they process language despite the underlying differences in their “operating systems” or cognitive architectures 1. Both seem to rely significantly on the surrounding context to comprehend incoming information and to integrate it coherently with the preceding context.
To illustrate, consider the following example of a garden-path sentence: “The old man the boat.” This sentence is confusing at first because “man” is often used as a verb, and the reader initially interprets “the old man” as a noun phrase.
The confusion is cleared up when provided with a fitting context, such as “elderly people are in control.” Now, the phrase makes sense—’man’ is understood as a verb meaning ‘to staff,’ and the garden-path sentence is interpreted correctly to mean that elderly people are the ones operating the boat.
However, if the preceding sentence was unrelated, such as “The birds flew to the south,” there is no helpful context to parse “The old man the boat” correctly, and it remains confusing, illustrating an unfitting context. This unfitness affects the recall of the garden-path sentence in the memory task, as it lacks clear, coherent links to preexisting knowledge or context that facilitate understanding and later recall.
The study’s findings depicted that when humans assess two sentences as being more related, which is naturally higher in fitting contexts than in unfitting ones, the memory performance for the ambiguous (garden-path) sentence also improves.
In a compelling parallel, ChatGPT generated similar assessments when given the same sentences, assigning higher relatedness values to fitting contexts over unfitting ones. This correlation suggests a similarity in how ChatGPT and humans use context to parse and remember new information.
Furthermore, the relatedness ratings were not just abstract assessments but tied directly to the actual memorability of the sentences. As with humans, ChatGPT’s predictions of memorability were also higher for sentences in fitting contexts, a phenomenon that may stem from its sophisticated language processing capabilities that crudely mimic cognitive processes involved in human memory.
This similarity in the use of context and its impact on memory retention is remarkable, considering the different mechanisms through which humans and machine learning models operate.
Broader Implications and the Future
The paragraph outlines the wider ramifications of the research findings on the predictive capabilities of generative AI like ChatGPT regarding human memory performance in language tasks. The research suggests that these AI models could have practical applications in several domains, including:
Education:
AI could be used to tailor learning experiences for students with diverse cognitive needs. By understanding how different students retain information, AI applications could guide educators in adjusting teaching materials, pace, and instructional approaches to cater to individual learning styles and abilities.
For example, if a student is struggling with remembering historical dates, the AI might suggest teaching methods or materials that align with their learning patterns to improve retention.
Eldercare:
The study indicates that older adults often face a cognitive slowdown, which could lead to more frequent memory problems. AI, once trained on data taking into account individual cognitive differences, could aid in developing personalized cognitive training and therapy plans aimed at enhancing mental functions in the elderly.
For instance, a cognitive enhancement program might be customized for an older adult who has difficulty recalling names or recent events by using strategies found effective through AI analysis.
Impact of AI on human cognition
The implications here go beyond just predicting human behavior; they extend to potentially improving cognitive processes through the intervention of AI.
These potential applications represent a synergistic relationship between AI and human cognitive research, where the insights gained from one field can materially benefit the other.
Furthermore, adaptive AI systems could continually learn and improve their predictions and recommendations based on new data, thereby creating a dynamic and responsive tool for cognitive enhancement and education.