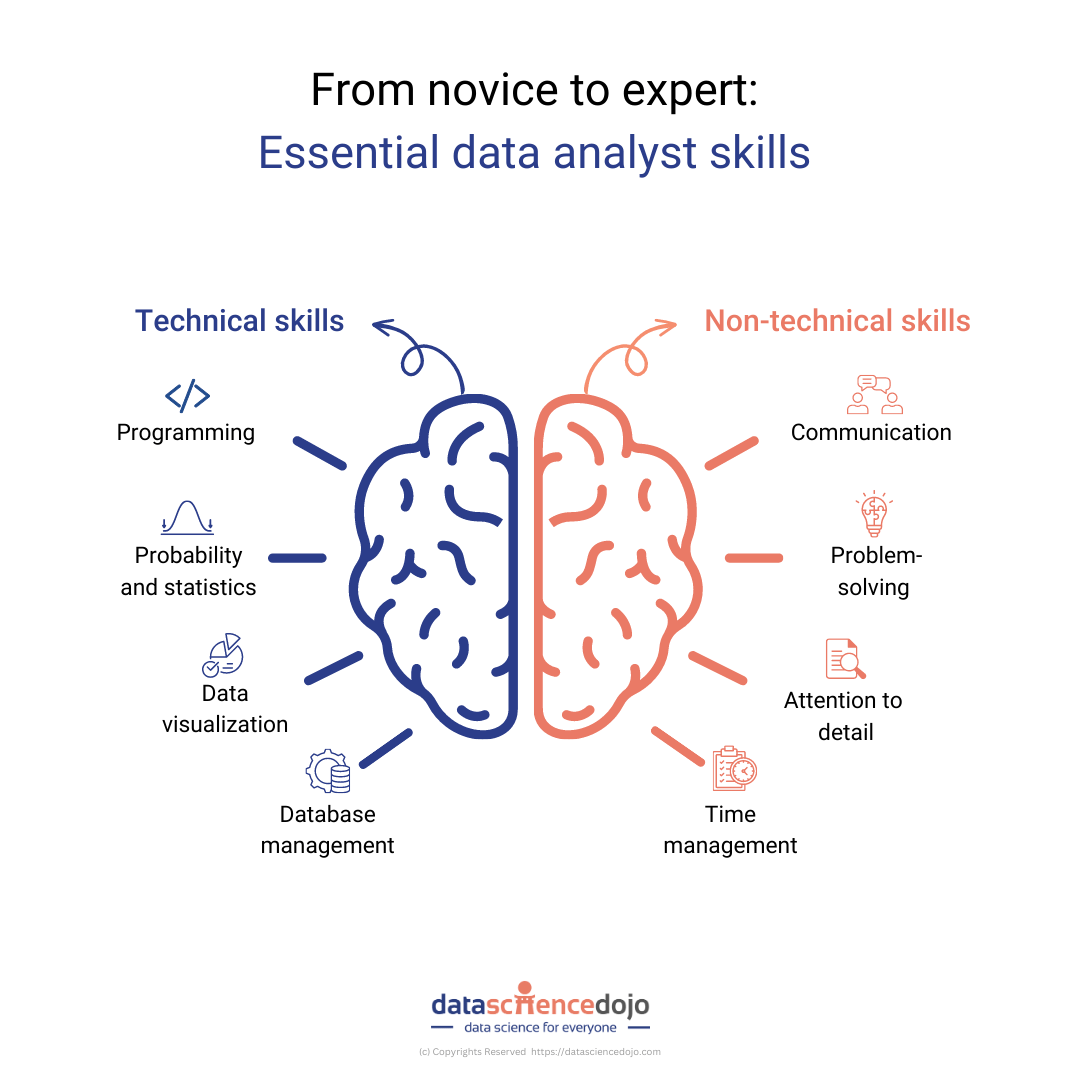
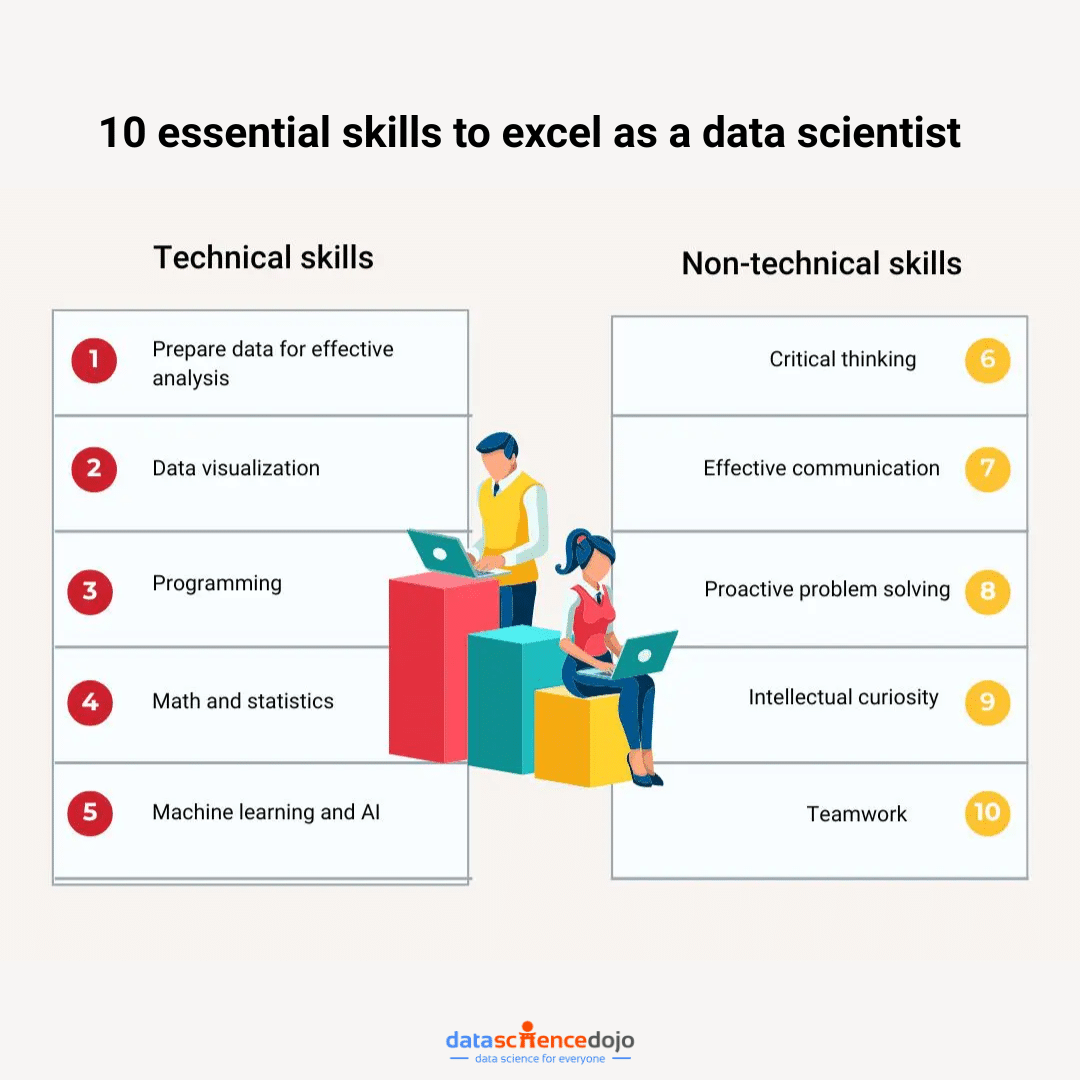
As data science evolves and grows, the demand for skilled data scientists is also rising. A data scientist’s role is to extract insights and knowledge from data and to use this information to inform decisions and drive business growth. To be successful in this field, certain skills are essential for any data scientist to possess.
By developing and honing these skills, data scientists will be better equipped to make an impact in any organization and stand out in a competitive job market. While a formal education is a good starting point, there are certain skills essential for any data scientist to possess to be successful in this field. These skills include non-technical skills and technical skills.
Technical Skills
Data science is a rapidly growing field, and as such, the skills required for a data scientist are constantly evolving. However, certain technical skills are considered essential for a data scientist to possess. These skills are often listed prominently in job descriptions and are highly sought after by employers.
These skills include programming languages such as Python and R, statistics and probability, machine learning, data visualization, and data modeling. Many of these skills can be developed through formal education and business training programs, and organizations are placing an increasing emphasis on them as they continue to expand their analytics and data teams.
1. Prepare Data for Effective Analysis
One important data scientist skill is preparing data for effective analysis. This includes sourcing, gathering, arranging, processing, and modeling data, as well as being able to analyze large volumes of structured or unstructured data.
The goal of data preparation is to present data in the best forms for decision-making and problem-solving. This skill is crucial for any data scientist as it enables them to take raw data and make it usable for analysis and insights discovery. Data preparation is an essential step in the data science workflow, and data scientists should be familiar with various data preparation tools and best practices.
2. Data Visualization
Data visualization is a powerful tool for data scientists to effectively communicate their findings and insights to both technical and non-technical audiences.
Having a strong understanding of the benefits and challenges of using data visualization, as well as basic knowledge of market solutions, allows data scientists to create clear and informative visualizations that effectively communicate their insights.
This skill includes an understanding of best practices and techniques for creating data visualizations, and the ability to share results through self-service dashboards or applications.
Self-service analytics platforms allow data scientists to surface the results of their data science processes and explore the data in a way that is easily understandable to non-technical stakeholders, which is crucial for driving data-driven decisions and actions.
3. Programming
Data scientists need to have a solid foundation in programming languages such as Python, R, and SQL. These languages are used for data cleaning, manipulation, and analysis, and for building and deploying machine learning models.
Python is widely used in the data science community, with libraries such as Pandas and NumPy for data manipulation, and Scikit-learn for machine learning. R is also popular among statisticians and data analysts, with libraries for data manipulation and machine learning.
SQL is a must-have for data scientists as it is a database language and allows them to extract data from databases and manipulate it easily.
4. Ability to Apply Math and Statistics Appropriately
Exploratory data analysis is a crucial step in the data science process, as it allows data scientists to identify important patterns and relationships in the data, and to gain insights that inform decisions and drive business growth.
To perform exploratory data analysis effectively, data scientists must have a strong understanding of math and statistics. Understanding the assumptions and algorithms underlying different analytic techniques and tools is also crucial for data scientists.
Without this understanding, data scientists risk misinterpreting the results of their analysis or applying techniques incorrectly. It is important to note that this skill is not only important for students and aspiring data scientists but also for experienced data scientists.
5. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are rapidly advancing technologies that are becoming increasingly important in data science. However, it is important to note that these technologies will not replace the role of data scientists in most organizations.
Instead, they will enhance the value that data scientists deliver by providing new and powerful tools to work better and faster. One of the key challenges in using AI and machine learning is knowing if you have the right data. Data scientists must be able to evaluate the quality of the data, identify potential biases and errors, and determine.
Non-Technical Skills
In addition to technical skills, soft skills are also essential for data scientists to possess to succeed in the field. These skills include critical thinking, effective communication, proactive problem-solving, and intellectual curiosity.
These skills may not require as much technical training or formal certification, but they are foundational to the rigorous application of data science to business problems. They help data scientists to analyze data objectively, communicate insights effectively, solve problems proactively, and stay curious and driven to find answers.
Even the most technically skilled data scientist needs to have these soft skills to make an impact in any organization and stand out in a competitive job market.
6. Critical Thinking
The ability to objectively analyze questions, hypotheses, and results, understand which resources are necessary to solve a problem, and consider different perspectives on a problem.
7. Effective Communication
The ability to explain data-driven insights in a way that is relevant to the business and highlights the value of acting.
8. Proactive Problem Solving
The ability to identify opportunities, approach problems by identifying existing assumptions and resources, and use the most effective methods to find solutions.
9. Intellectual Curiosity
The drive to find answers, dive deeper than surface results and initial assumptions, think creatively, and constantly ask “why” to gain a deeper understanding of the data.
10. Teamwork
The ability to work effectively with others, including cross-functional teams, to achieve common goals. This includes strong collaboration, communication, and negotiation skills.
Bottom Line
All in all, data science is a growing field and data scientists play a crucial role in extracting insights from data. Technical skills like programming, statistics, and data visualization are essential, as are soft skills like critical thinking and effective communication. Developing these skills can help data scientists make a significant impact in any organization and stand out in a competitive job market.