In a world where speed and efficiency are paramount, edge computing is a game-changer. With the rise of IoT devices and AI-driven applications, the demand for real-time data processing has never been greater.
Instead of relying on distant cloud servers, businesses are shifting toward edge computing. By processing data closer to its source, they can reduce latency, enhance security, and improve performance.
From smart cities and autonomous vehicles to healthcare and industrial automation, edge computing is reshaping industries.
In this article, we will delve into its advantages, explore real-world applications, and discuss how it is driving the next wave of technological advancement.
Explore Data Science Newsletter to stay up-to-date with the latest data science trends
Understanding Edge Computing
Imagine you have a smart security camera. If it had to send every second of footage to a cloud server for analysis, it would slow down your internet and cause delays. Instead, with edge computing (or local processing), the camera itself detects motion, recognizes faces, and sends alerts instantly—no need to rely on a distant data center.
Why does this matter? Because waiting for data to travel back and forth is frustrating—think buffering videos and slow-loading websites. Edge computing keeps processing close to the source, making devices faster, more efficient, and less dependent on the internet. Instead of flooding the cloud with raw data, smart devices handle tasks on their own or use nearby local servers, ensuring speed, reliability, and seamless performance.
Also learn how distributed systems transform data processing
The Biggest Benefits
- Speed – Instant processing means faster responses, perfect for self-driving cars, gaming, and real-time health monitoring.
- Less Internet Load – With less data sent to the cloud, your network stays fast and smooth.
- Better Security – Keeping data close means less risk of hacking.
- Works Offline – Even with no internet, local processing keeps devices running—great for remote areas.
Where Do We See Edge Computing?
- Smart Homes: Alexa, Google Nest, and security cameras process commands instantly.
- Healthcare: Wearables track heart rates and alert doctors without needing constant internet access.
- Retail: AI-powered self-checkouts scan and process items in real-time.
- Factories: Machines detect problems early, preventing breakdowns and saving money.
Data Processing at the Edge
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way data is handled by shifting processing closer to its source. This localized approach not only minimizes delays but also enhances efficiency, making it a game-changer for industries that rely on split-second decision-making. Instead of sending vast amounts of data to a centralized cloud, edge devices analyze and filter information instantly, ensuring that only the most relevant insights are transmitted.
Explore the important steps in the data preprocessing
This streamlined method is particularly valuable in high-stakes environments, such as healthcare, where wearable monitors can detect anomalies in a patient’s vitals and alert doctors in real-time.
In industrial automation, sensors can identify performance issues in machinery before a breakdown occurs, preventing costly downtime. By reducing the dependency on constant internet connectivity, local processing enables seamless operations even in remote or bandwidth-limited locations.
Real-Time Analytics and Insights
The ability to process and interpret data instantaneously gives businesses a crucial advantage. Traditional data processing methods often introduce delays, limiting how quickly organizations can react to new developments. With edge computing, businesses can make data-driven decisions the moment information is generated, improving agility and responsiveness.
For instance, in financial services, transaction patterns can be analyzed on the spot to detect fraudulent activities before they escalate. Similarly, in smart agriculture, edge-powered sensors monitor soil conditions and adjust irrigation without needing input from a distant server, optimizing water usage and crop health.
By embedding intelligence directly into devices, organizations can automate complex processes, reduce operational costs, and enhance customer experiences. As industries continue to adopt local processing , the ability to leverage real-time analytics will be a defining factor in staying ahead of the competition.
Enhancing Data Security and Privacy
One other big advantage of edge computing is its ability to strengthen data security and privacy. By processing information closer to where it is generated, edge computing reduces reliance on centralized servers, minimizing the risks associated with transmitting sensitive data over long distances.
Since data stays within local networks rather than constantly traveling across external cloud servers, the chances of cyberattacks, unauthorized access, and data breaches are significantly lower. This is especially critical in industries such as healthcare, finance, and government, where protecting confidential information is a top priority.
Another interesting read: Real-time data processing with AI
Additionally, edge devices can implement real-time security measures, detecting and responding to threats instantly rather than waiting for cloud-based analysis. This proactive approach helps prevent potential security incidents before they escalate. In environments where privacy regulations are strict, such as GDPR and HIPAA compliance, edge computing ensures that sensitive data is handled in a way that meets regulatory standards while maintaining user trust.
By keeping data processing closer to home, edge computing not only enhances security but also ensures faster, more reliable, and private digital interactions in an increasingly connected world.
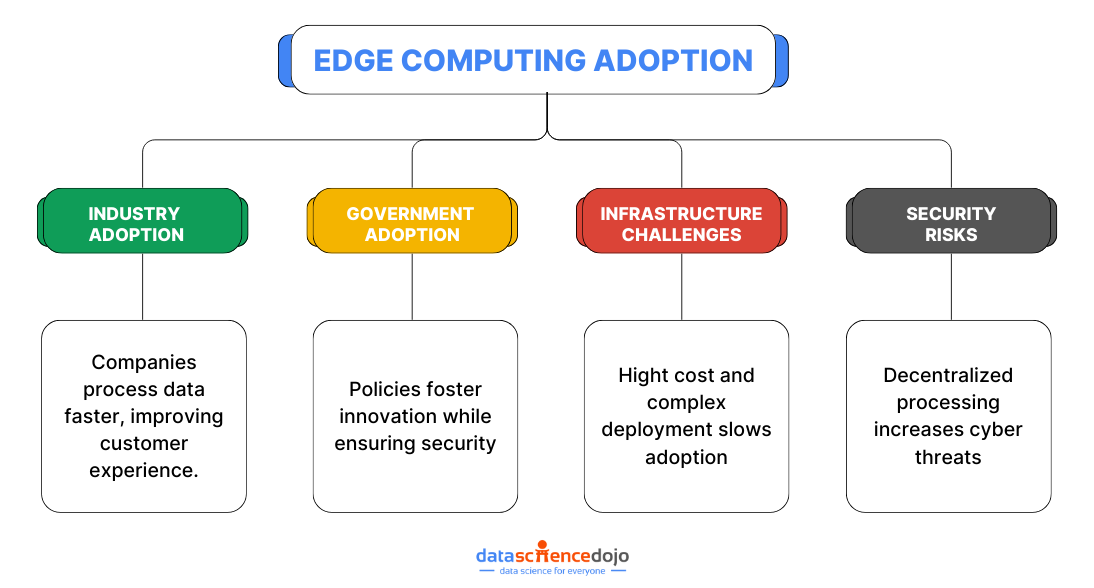
Business Adoption of Edge Computing
Across industries, companies are rapidly integrating edge computing into their operations to enhance efficiency, optimize processes, and deliver more responsive services. By processing data closer to its source, businesses can reduce latency, improve system reliability, and personalize customer experiences in ways that were previously challenging.
For instance, in retail, edge-powered systems analyze customer behavior in real-time, allowing businesses to offer tailored recommendations and optimize inventory management.
In manufacturing, edge-enabled predictive maintenance helps prevent equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime and operational costs. This widespread adoption highlights the real-world impact of edge computing, offering companies a competitive advantage in an increasingly digital marketplace.
Learn 5 tips to enhance customer service using data science
Government policies and regulations
Governments worldwide recognize the transformative potential of edge computing and are actively shaping policies to support its integration across various sectors. These regulations aim to balance innovation with security, ensuring that edge technology is deployed in ways that protect user data while fostering technological advancements.
Many countries are investing in 5G infrastructure, cybersecurity frameworks, and AI-driven edge solutions, helping businesses and public institutions adopt edge computing at scale. Additionally, data protection laws are evolving to address the unique challenges of decentralized data processing, reinforcing privacy and security standards in an increasingly connected world.
Infrastructure challenges
Despite its advantages, scaling edge computing requires significant infrastructure investments. Unlike traditional cloud computing, which relies on centralized data centers, edge computing demands widespread deployment of specialized hardware and software at multiple locations.
The installation of high-performance edge servers, AI-powered processing units, and seamless network integration requires substantial financial and technological resources. For businesses operating in regions with limited connectivity or outdated infrastructure, these challenges can slow adoption and increase implementation costs. However, as 5G networks expand and hardware becomes more cost-effective, the barriers to edge computing deployment are gradually decreasing.
Security concerns
While edge computing enhances security by reducing data exposure to third-party cloud services, it also introduces new cybersecurity challenges. Unlike centralized systems, which have a single point of control, edge computing distributes data processing across multiple nodes, potentially increasing vulnerabilities to cyber threats.
Attackers could target local devices, IoT endpoints, or edge servers, leading to data breaches or unauthorized access. To counteract these risks, businesses and policymakers must implement robust encryption methods, secure device authentication, and real-time threat detection. As edge computing continues to evolve, ensuring strong cybersecurity frameworks will be crucial in maintaining user trust and data integrity.
Learn 5 Strategies for Data Security and Governance in Data Warehousing
Adoption Rates in Various Regions
The adoption of edge computing is progressing at different speeds across the globe, largely influenced by infrastructure, investment, and technological readiness.
Developed nations are leading the charge, leveraging their advanced networks, high-speed connectivity, and strong industry adoption to integrate edge computing across sectors like healthcare, manufacturing, and smart cities. Countries such as the United States, Germany, Japan, and South Korea are at the forefront, using edge technology to drive automation, AI, and IoT innovations.
Meanwhile, developing regions are adopting edge computing at a gradual pace, often hindered by limited network infrastructure and high implementation costs. However, as mobile and 5G networks expand, edge computing is becoming more accessible in emerging markets like India, Brazil, and parts of Africa, where it is being used to enhance telecommunications, agriculture, and financial services.
This global disparity in adoption highlights the importance of robust digital infrastructure in unlocking the full potential of edge computing. As more regions invest in high-speed connectivity and cloud-edge integration, the widespread implementation of edge technology is expected to accelerate, bridging the gap between developed and emerging markets.
Solutions and Future Direction
A collaborative approach between businesses and governments is emerging to navigate the complexities of implementing edge computing. Together, they craft strategies and policies that foster innovation while addressing potential hurdles such as security concerns and infrastructure development.
This united front is instrumental in shaping a conducive environment for the seamless integration and growth of edge computing in the coming years.
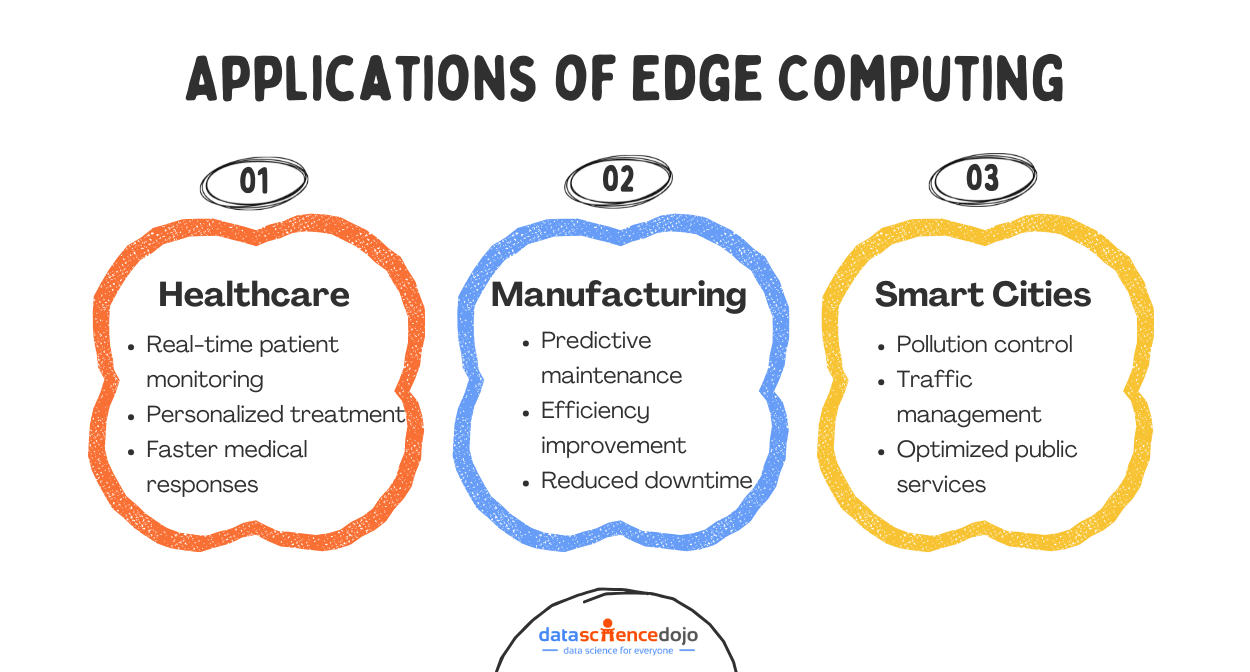
Healthcare Sector
In healthcare, computing is becoming a cornerstone for advancing patient care. It facilitates real-time monitoring and swift data analysis, providing timely interventions and personalized treatment plans. This enhances the accuracy and efficacy of healthcare services and potentially saves lives by enabling quicker responses in critical situations.
Manufacturing Industry
In the manufacturing sector, it is vital to streamlining and enhancing production lines. By enabling real-time data analysis directly on the factory floor, it assists in fine-tuning processes, minimizing downtime, and predicting maintenance needs before they become critical issues.
Consequently, it fosters a more agile, efficient, and productive manufacturing environment, paving the way for heightened productivity and reduced operational costs.
Smart Cities
Smart cities envisioned as the epitome of urban innovation, are increasingly harnessing the power of edge computing to revolutionize their operations. By processing data in affinity to its source, edge computing facilitates real-time responses, enabling cities to manage traffic flows, thereby reducing congestion and commute times.
Furthermore, it aids in deploying advanced sensors that monitor and mitigate pollution levels, ensuring cleaner urban environments. Beyond these, edge computing also streamlines public services, from waste management to energy distribution, ensuring they are more efficient, responsive, and tailored to the dynamic needs of urban populations.
Role in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Edge computing stands poised to be a linchpin in the revolution of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Facilitating faster data processing and analysis at the source will empower these technologies to function more efficiently and effectively.
Understand the top 9 machine learning algorithms to use for SEO & marketing
This synergy promises to accelerate advancements in AI and ML, fostering innovations that could reshape industries and redefine modern convenience.
Integration with IoT and 5G
As we venture forward, edge computing is slated to meld seamlessly with burgeoning technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G networks. This integration is anticipated to unlock many benefits, including lightning-fast data transmission, enhanced connectivity, and the facilitation of real-time analytics.
Read more –> IoT | New trainings at Data Science Dojo
Consequently, this amalgamation is expected to catalyze a new era of technological innovation, fostering a more interconnected and efficient world.
Predictions for the Next Decade
In the forthcoming decade, the ubiquity of edge computing is set to redefine our interaction with data fundamentally. This technology, by decentralizing data processing and bringing it closer to the source, promises swifter data analysis and enhanced security and efficiency.
As it integrates seamlessly with burgeoning technologies like IoT and 5G, we anticipate a transformative impact on various sectors, including healthcare, manufacturing, and urban development. This shift towards edge computing signifies a monumental leap towards a future where real-time insights and connectivity are not just luxuries but integral components of daily life, facilitating more intelligent living and streamlined operations in numerous facets of society.
Conclusion
Edge computing is shaping up to be a significant player in the international data science trends. As we have seen, it offers many benefits, including faster data processing, improved security, and the potential to revolutionize industries like healthcare, manufacturing, and urban planning. As we look to the future, the prospects for edge computing seem bright, promising a new frontier in the world of technology.
Remember, the world of technology is ever-changing, and staying informed is the key to staying ahead. So, keep exploring data science courses, keep learning, and keep growing!