In today’s rapidly evolving technological world, the economic potential of generative AI and other cutting-edge industrial developments is more pronounced than ever before. AI and the chip industry are pivotal in modern-day innovations and growth.
It is important to navigate the impact and economic potential of generative AI in the chip design industry as it maps out the technological progress and innovation in the digital world. The economic insights can highlight new investment avenues by informing policymakers and business leaders of the changing economic landscape timely.
As per McKinsey’s research, generative AI is set to potentially unlock 10 to 15 percent of the overall R&D costs in productivity value, raising its stakes in the economic impact. Since the economic potential of generative AI can create staggering changes and unprecedented opportunities, let’s explore it.
Major Players in the Economic Landscape of AI and Chip Industry
While generative AI is here to leave a lasting impact on the technological world, it is important to recognize the major players in the industry. As trends, ideas, and innovation are the focus of leading names within the chip industry, following their progress provides insights into the economic potential of generative AI.
Some of the common industry giants of generative AI within the chip industry include:
NVIDIA
It is one of the well-established tech giants, holding a dominant position within the AI chip industry. It is estimated to hold almost 80% of the global market for GPUs (Graphics Processing Units). Its robust software ecosystem includes frameworks like CUDA and TensorRT, simplifying generative AI development.
However, the rise of the production of specialized chips has led to an evolving landscape for generative AI. NVIDIA must adapt and innovate within the changing demands of the AI chip industry to maintain its position as a leading player.
Take a glimpse into the unprecedented growth of NVIDIA
Intel
While Intel has been a long-standing name in the semiconductor industry, it is a new player within the AI chip industry. Some of its strategic initiatives as an AI chip industry player include the acquisition of Habana Labs which provided them expertise in the AI chip technology.
They used the labs to design a Gaudi series of AI processors that specialize in the training of large language models (LLMs). Compared to established giants like NVIDIA, Intel is a fairly new player in the AI chip industry. However, with the right innovations, it can contribute to the economic potential of generative AI.
Microsoft
Microsoft holds a unique position, being one of the leading consumers of the AI chip industry, while aiming to become a potential contributor. Since the generative AI projects rely on chips from companies like NVIDIA, Microsoft has shown potential to create custom AI chips.
Within the economic potential of generative AI in the chip industry, Microsoft describes its goal to tailor and produce everything ‘from silicon to service‘ to meet the AI demands of the evolving industry.
Google AI
Like Microsoft, Google AI is also both a consumer and producer of AI chips. At the forefront, the development of its generative AI models is leading to innovation and growth. While these projects lead to the consumption of AI chips from companies like NVIDIA, Google AI contributes to the development of AI chips through research and collaboration.
Unlike other manufacturers focused on developing the new chips for businesses, Google AI plays a more collaborative role. It partners with these manufacturers to contribute through research and model development.
Groq
Groq has emerged as a new prominent player within the AI chip industry. Its optimized chips for generative AI applications are different from the generally developed GPUs. Groq is focused on creating LPUs (Liquid Programmable Units).
LPUs are designed to handle specific high-performance generative AI tasks like inferencing LLMs or generating images. With its new approach, Groq can boost the economic potential of generative AI within the chip industry. altering the landscape altogether.
Here’s your one-stop guide to large language models
Each of these players brings a unique perspective to the economic landscape of generative AI within the AI chip industry. The varying stages of chip development and innovation promise a competitive environment for these companies that is conducive to growth.
Now that we recognize some leading players focused on exploring the economic potential of generative AI in the chip industry, it is time to understand some of the major types of AI chip products.
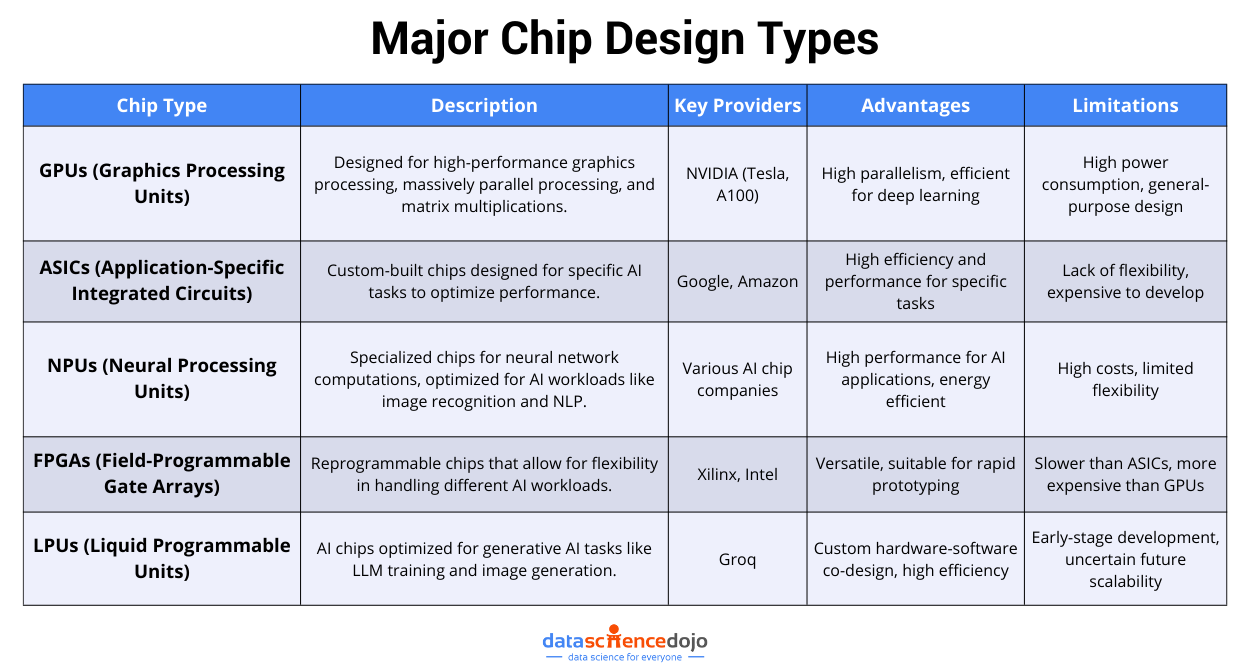
Types of AI chips Within the Industry
The rapidly evolving technological landscape of the AI chip industry has promoted an era of innovation among competitors. It has led to the development of several types of chips that are available for use today.
Let’s dig deeper into some of the major types of AI chips.
GPUs – Graphics Processing Units
These are designed to handle high-performance graphics processing. Some of its capabilities include massively parallel processing and handling large matrix multiplications. NVIDIA is a major provider of GPUs, like NVIDIA Tesla and NVIDIA A100.
ASICs – Application-Specific Integrated Circuits
As the name indicates, these are customized chips that are built for any specified task. Companies usually build ASICs to cater to the particular demands of the application development process. Google and Amazon rely on ASICs built specifically to handle their specific AI needs.
While the specificity offers enhanced performance and efficiency, it also diminishes the flexibility of an AI chip. The lack of versatility prevents it from performing a wide variety of tasks or applications.
NPUs – Neural Processing Units
These are custom-built AI chips that specialize in handling neural network computations, like image recognition and NLP. The differentiation ensures better performance and efficiency of the chips. The parallel processing architecture enables the AI chips to process multiple operations simultaneously.
Like ASICs, NPUs also lack versatility due to their custom-built design. Moreover, these chips are also expensive, incurring high costs to the users, making their adoption within the industry limited.
FPGAs – Field-Programmable Gate Arrays
FPGAs are an improvement to custom-built chip design. Its programmability makes them versatile as the chips can be reprogrammed after each specific use. It makes them more flexible to handle various types of AI workloads. They are useful for rapid prototyping and development.
LPUs – Liquid Programmable Units
Also called linear processing units, these are a specific chip design developed by Groq. These are designed to handle specific generative AI tasks, like training LLMs and generating images. Groq claims its superior performance due to the custom architecture and hardware-software co-design.
While LPUs are still in their early stage of development, they have the potential to redefine the economic landscape of the AI chip industry. The performance of LPUs in further developmental stages can greatly influence the future and economic potential of generative AI in the chip industry.
Among these several chip designs available and under development, the choice within the market relies on multiple factors. Primarily, the choice is dictated by the needs of the AI application and its developmental stage. While a GPU might be ideal for early-stage processing, ASICs are more useful for later stages.
Moreover, the development of new AI chip designs has increased the variety of options for consumers. The manufacturers of these chips must keep these factors in mind during their research and development phases so the designed chips are relevant in the market, ensuring a positive impact on the economic landscape.
What is the Economic Potential of Generative AI in Chip Design?
The fast-paced technological world of today is marked by developments in generative AI. According to Statista Market Insights, the generative AI market size is predicted to reach $70 billion in 2030. Hence, it is crucial to understand the role and impact of AI in the modern economy.
From our knowledge of different players and the types of chip designs, we can conclude that both factors are important in determining the economic potential of generative AI in chip design. Each factor adds to the competitiveness of the market, fostering growth and innovation.
Thus, the impact of generative AI is expected to grow in the future, subsequently leading to the growth of AI chip designs. The increased innovation will also enhance its impact on the economic landscape.