Maintaining the security and governance of data in a data warehousing is of utmost importance. As organizations increasingly rely on data warehousing for centralizing and analyzing their data, robust data security and governance practices are essential.
In this blog post, we will cover the technical aspects of data security and governance within data warehousing, focusing on key strategies and a step-by-step approach to ensure a secure data warehouse.
Data Security: A multi-layered approach
In data warehousing, data security is not a single barrier but a well-constructed series of layers, each contributing to protecting valuable information. This multi-layered approach is akin to constructing a fortress, where multiple lines of defense work collaboratively to safeguard your digital assets from potential threats.
-
Perimeter Security: The First Line of Defense
Perimeter security forms the initial line of defense for your data warehouse. Firewalls stand sentinel, filtering incoming and outgoing data traffic. Intrusion detection systems (IDS) are on constant watch, promptly alerting administrators to suspicious activities that could breach the outer defenses. Just like you wouldn’t allow unauthenticated individuals through a castle gate, perimeter security ensures that unauthorized access attempts fail before reaching the core data.
-
Encryption: Securing data in transit and at rest
Encryption serves as the digital lock and key, protecting data during transmission and at rest. Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols encrypt data during system communication. Any interceptors attempting to eavesdrop on the communication will only encounter scrambled data. For data at rest within the castle, Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithms ensure that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains indecipherable.
-
Access Control: Limiting entry to authorized individuals
Just like how you can control who can enter different castle areas, access control is pivotal in data warehousing. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) functions as the digital gatekeeper, permitting access to authorized personnel based on their organizational roles and responsibilities. Only those with legitimate reasons to access specific data can do so. Like different chambers within a castle have varying restricted access levels, RBAC enforces controlled access to data at different granularity levels.
-
Authentication and authorization: Verifying and granting access
Authentication and authorization provide the digital equivalent of verifying someone’s identity and permitting them to enter. Multi-factor authentication adds a supplementary layer of assurance by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access. Once authenticated, authorization ensures that the individual is allowed access only to the areas they are authorized to enter.
Data Governance: Setting the rules
Data governance takes on the role of a regulatory framework, guiding the responsible management, utilization, and protection of your organization’s most valuable asset—data. Just as a castle’s rules and regulations maintain order and ensure its longevity, data governance establishes the guidelines that dictate how data is acquired, stored, manipulated, and shared.
Defining data ownership: Assigning custodianship
Like a castle with appointed caretakers, data governance designates data owners responsible for different datasets. Data ownership extends beyond mere possession—it involves accountability for data quality, accuracy, and appropriate use. Clear data ownership ensures that data is adequately maintained, validated, and validated throughout its lifecycle.
Data retention policies: Time-stamped preservation
Data governance mandates the creation and adherence to data retention policies. These policies stipulate how long businesses retain different data types before being securely archived or disposed of. Like the archives house that stores historical records, data warehousing holds digital archives with valuable insights for future analysis.
Regulatory compliance: Adhering to laws and regulations
Data governance is a legal compass, ensuring your data practices align with industry regulations and legal requirements. Governance policies enforce adherence to GDPR, HIPAA, or SOX regulations. By establishing protection measures and privacy protocols, data governance minimizes non-compliance risk, safeguarding your organization’s reputation and the data subjects’ rights.
Data quality and standardization: Ensuring consistency
Data governance establishes data quality standards. This includes defining data formats, naming conventions, and validation rules. Data governance enhances data reliability by maintaining data consistency and accuracy and ensuring that analyses and decisions are based on trustworthy information.
Data lifecycle management: Guiding data flow
Data has a lifecycle, from its creation to its eventual archiving or deletion. Data governance maps out this journey, guiding data flow and transformation processes. It outlines how data is captured, transformed, and utilized. This organized approach enhances data visibility and simplifies data lineage tracking.
Monitoring and auditing: Continuous oversight
Monitoring and auditing assume the roles of vigilant sentinels, maintaining constant watch over the fortress of your data ecosystem. Just as guards patrol castle walls to prevent breaches, monitoring tools, and auditing processes ensure your data warehouse’s ongoing security, performance, and compliance. This continuous oversight is essential to detect anomalies, prevent unauthorized access, and uphold the integrity of your organization’s data.
Real-time surveillance
Imagine guards stationed along a castle’s walls, watching for any signs of intrusion. Similarly, monitoring tools actively observe the activities within your data warehouse. Real-time surveillance ensures that potential security threats are detected and addressed promptly, minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Performance optimization
Monitoring tools highlight performance bottlenecks within your data warehouse. By tracking query execution times, system resource utilization, and data load speeds, these tools reveal areas where optimization is required. This proactive approach helps maintain optimal system performance, ensuring users execute analytical queries efficiently and deliver insights without delay.
Compliance enforcement
Similar to guards ensuring that castle inhabitants adhere to rules, auditing enforces compliance within data warehousing. Regular audits review user activities, data access logs, and configuration changes. These audits ensure that data usage aligns with established policies and industry regulations. If any violations are detected, the auditing process generates reports that assist in corrective actions and demonstrate compliance efforts.
Forensic analysis
Just as guards investigate disturbances within the castle, auditing supports incident investigation within data warehousing. In case of security breaches or data anomalies, auditing logs provide a trail of events that led to the incident. This forensic analysis assists in understanding the root cause, identifying compromised data, and formulating strategies to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Ensuring security for data warehousing
Here’s how enterprises can establish robust data security measures for their data warehouses:
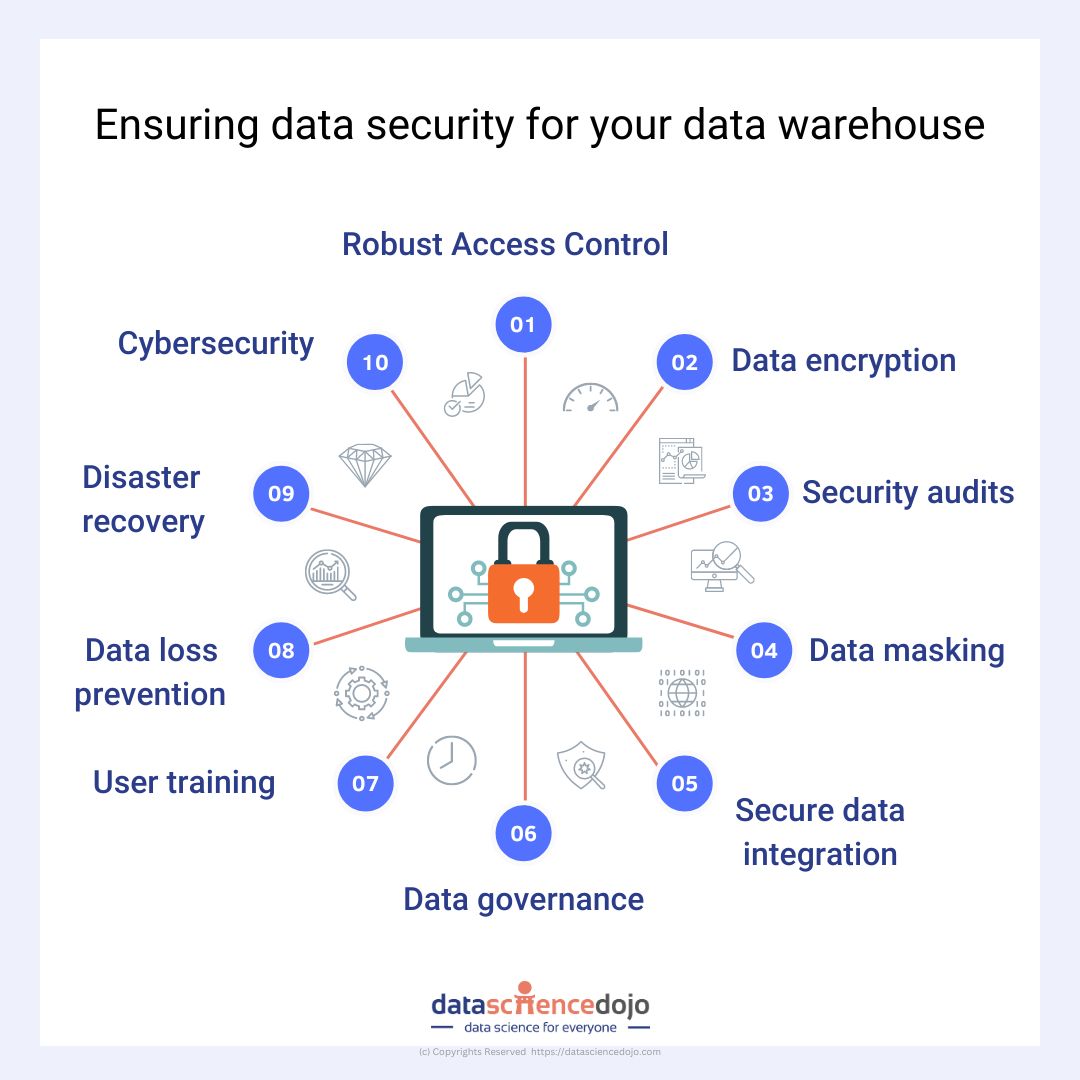
- Comprehensive Access Control Implementation: Implement robust access controls using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) principles. Define roles and permissions based on job responsibilities to ensure that users have access only to the data they require for their tasks. Regularly review and update access privileges to reflect changes in personnel roles or project requirements.
- Encryption at Rest and Transit: Employ encryption to protect data at rest and during transmission. Use robust encryption algorithms like Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for data storage and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) for secure data transmission between systems. Encryption ensures data remains unintelligible even if unauthorized access occurs.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular security audits to identify weaknesses and potential security gaps. Engage in penetration testing to simulate real-world attack scenarios and identify weaknesses in your data warehouse’s defenses. Regular assessments help you avoid possible threats and take strong measures to address them proactively.
- Data Masking and Anonymization: For non-production environments or when sharing data with third parties, consider implementing data masking or anonymization techniques. This process replaces sensitive data with realistic but fictional data, ensuring that privacy is maintained while still allowing data to be used for development, testing, or analytics.
- Secure Data Integration and ETL Processes: Implement secure data integration practices to ensure that data flowing into your warehouse is not compromised. Secure Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes using encryption and secure connections to prevent data leaks during data movement. Verify the data sources to avoid malicious or compromised data from entering the warehouse.
- Data Governance and Compliance Policies: Develop and enforce data governance policies that outline data ownership, retention, and usage guidelines. Align your data practices with industry regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, or industry-specific compliance standards. Implement automated tools to monitor and enforce compliance, generating alerts for policy violations.
- User Training and Awareness: Invest in regular training for employees and users who interact with the data warehouse. Educate them about security best practices, such as creating strong passwords, recognizing phishing attempts, and following proper data handling procedures. A well-informed workforce is your first line of defense against security breaches.
- Implement Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Measures: Deploy data loss prevention solutions that monitor and control data leaving your organization’s network. DLP solutions can detect and prevent unauthorized transfers of sensitive data, ensuring that critical information remains within the organization’s control.
- Regular Backup and Disaster Recovery Planning: Regularly back up your data warehouse to ensure availability and quick recovery in case of data breaches or disasters. Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that outlines steps to take in case of data loss or system compromise. Regularly test and update your disaster recovery plans to guarantee their effectiveness.
- Collaboration with Cybersecurity Experts: Engage with cybersecurity experts specializing in data warehousing and cloud security. Their expertise can provide valuable insights, recommendations, and guidance to help your enterprise stay ahead of emerging security threats and challenges.
Conclusion: A strong defense for data assets
Data security and governance within data warehousing play a critical role in safeguarding an organization’s data assets. A robust security strategy and effective governance practices ensure data integrity, authorized access, and adherence to regulations. By adopting these practices and drawing insights from practical examples, organizations can confidently manage data within the complex landscape of modern data warehousing.
Written by Ovais Naseem