Welcome to the world of open source large language models (LLMs), where the future of technology meets community spirit. By breaking down the barriers of proprietary systems, open language models invite developers, researchers, and enthusiasts from around the globe to contribute to, modify, and improve upon the foundational models.
This collaborative spirit not only accelerates advancements in the field but also ensures that the benefits of AI technology are accessible to a broader audience. As we navigate through the intricacies of open-source language models, we’ll uncover the challenges and opportunities that come with adopting an open-source model, the ecosystems that support these endeavors, and the real-world applications that are transforming industries.
Benefits of Open Source LLMs
As soon as ChatGPT was revealed, OpenAI’s GPT models quickly rose to prominence. However, businesses began to recognize the high costs associated with closed-source models, questioning the value of investing in large models that lacked specific knowledge about their operations.
In response, many opted for smaller open LLMs, utilizing Retriever-And-Generator (RAG) pipelines to integrate their data, achieving comparable or even superior efficiency.
There are several advantages to closed-source large language models worth considering.
-
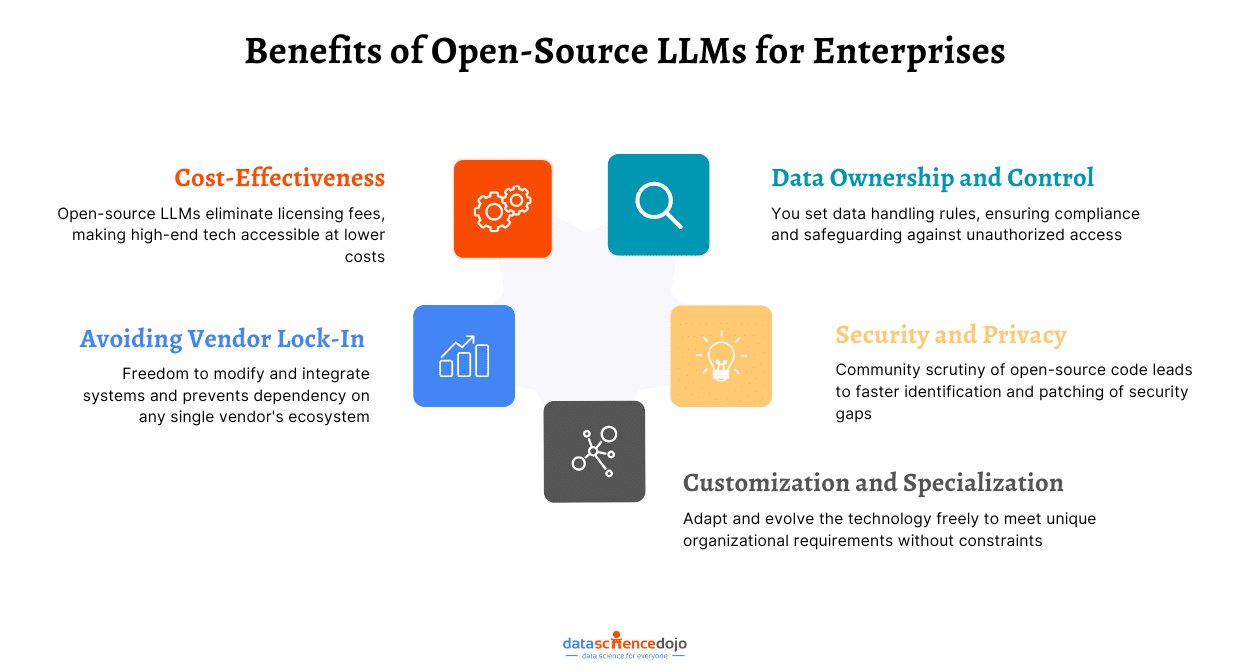
Cost-Effectiveness:
Open-source Large Language Models (LLMs) present a cost-effective alternative to their proprietary counterparts, offering organizations a financially viable means to harness AI capabilities.
- No licensing fees are required, significantly lowering initial and ongoing expenses.
- Organizations can freely deploy these models, leading to direct cost reductions.
- Open large language models allow for specific customization, enhancing efficiency without the need for vendor-specific customization services.
-
Flexibility:
Companies are increasingly preferring the flexibility to switch between open and proprietary (closed) models to mitigate risks associated with relying solely on one type of model.
This flexibility is crucial because a model provider’s unexpected update or failure to keep the model current can negatively affect a company’s operations and customer experience.
Companies often lean towards open language models when they want more control over their data and the ability to fine-tune models for specific tasks using their data, making the model more effective for their unique needs.
-
Data Ownership and Control:
Companies leveraging open-source language models gain significant control and ownership over their data, enhancing security and compliance through various mechanisms. Here’s a concise overview of the benefits and controls offered by using open large language models:
Data hosting control:
- Choice of data hosting on-premises or with trusted cloud providers.
- Crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Internal data processing:
- Avoids sending sensitive data to external servers.
- Reduces the risk of data breaches and enhances privacy.
Customizable data security features:
- Flexibility to implement data anonymization and encryption.
- Helps comply with data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA.
Transparency and audibility:
- The open-source nature allows for code and process audits.
- Ensures alignment with internal and external compliance standards.
Enterprises Using Open Source LLMs
Here are examples of how different companies around the globe have started leveraging open language models.
-
VMWare
VMWare, a noted enterprise in the field of cloud computing and digitalization, has deployed an open language model called the HuggingFace StarCoder. Their motivation for using this model is to enhance the productivity of their developers by assisting them in generating code.
This strategic move suggests VMware’s priority for internal code security and the desire to host the model on their infrastructure. It contrasts with using an external system like Microsoft-owned GitHub’s Copilot, possibly due to sensitivities around their codebase and not wanting to give Microsoft access to it
-
Brave
Brave, the security-focused web browser company, has deployed an open-source large language model called Mixtral 8x7B from Mistral AI for their conversational assistant named Leo, which aims to differentiate the company by emphasizing privacy.
Previously, Leo utilized the Llama 2 model, but Brave has since updated the assistant to default to the Mixtral 8x7B model. This move illustrates the company’s commitment to integrating open LLM technologies to maintain user privacy and enhance their browser’s functionality.
-
Gab Wireless
Gab Wireless, the company focused on child-friendly mobile phone services, is using a suite of open-source models from Hugging Face to add a security layer to its messaging system. The aim is to screen the messages sent and received by children to ensure that no inappropriate content is involved in their communications.
This usage of open language models helps Gab Wireless ensure safety and security in children’s interactions, particularly with individuals they do not know.
-
IBM
IBM actively incorporates open models across various operational areas.
- AskHR application: Utilizes IBM’s Watson Orchestration and open language models for efficient HR query resolution.
- Consulting advantage tool: Features a “Library of Assistants” powered by IBM’s wasonx platform and open-source large language models, aiding consultants.
- Marketing initiatives: Employs an LLM-driven application, integrated with Adobe Firefly, for innovative content and image generation in marketing.
-
Intuit
Intuit, the company behind TurboTax, QuickBooks, and Mailchimp, has developed its language models incorporating open LLMs into the mix. These models are key components of Intuit Assist, a feature designed to help users with customer support, analysis, and completing various tasks.
The company’s approach to building these large language models involves using open-source frameworks, augmented with Intuit’s unique, proprietary data.
-
Shopify
Shopify has employed publically available language models in the form of Shopify Sidekick, an AI-powered tool that utilizes Llama 2. This tool assists small business owners with automating tasks related to managing their commerce websites.
It can generate product descriptions, respond to customer inquiries, and create marketing content, thereby helping merchants save time and streamline their operations.
-
LyRise
LyRise, a U.S.-based talent-matching startup, utilizes open language models by employing a chatbot built on Llama, which operates similarly to a human recruiter. This chatbot assists businesses in finding and hiring top AI and data talent, drawing from a pool of high-quality profiles in Africa across various industries.
-
Niantic
Niantic, known for creating Pokémon Go, has integrated open-source large language models into its game through the new feature called Peridot. This feature uses Llama 2 to generate environment-specific reactions and animations for the pet characters, enhancing the gaming experience by making character interactions more dynamic and context-aware.
-
Perplexity
Here’s how Perplexity leverages open source LLMs
- Response generation process:
When a user poses a question, Perplexity’s engine executes approximately six steps to craft a response. This process involves the use of multiple language models, showcasing the company’s commitment to delivering comprehensive and accurate answers.
In a crucial phase of response preparation, specifically the second-to-last step, Perplexity employs its own specially developed open-source language models. These models, which are enhancements of existing frameworks like Mistral and Llama, are tailored to succinctly summarize content relevant to the user’s inquiry.
The fine-tuning of these models is conducted on AWS Bedrock, emphasizing the choice of open models for greater customization and control. This strategy underlines Perplexity’s dedication to refining its technology to produce superior outcomes.
- Partnership and API integration:
Expanding its technological reach, Perplexity has entered into a partnership with Rabbit to incorporate its open-source large language models into the R1, a compact AI device. This collaboration facilitated through an API, extends the application of Perplexity’s innovative models, marking a significant stride in practical AI deployment.
-
CyberAgent
CyberAgent, a Japanese digital advertising firm, leverages open language models with its OpenCALM initiative, a customizable Japanese language model enhancing its AI-driven advertising services like Kiwami Prediction AI. By adopting an open-source approach, CyberAgent aims to encourage collaborative AI development and gain external insights, fostering AI advancements in Japan.
Furthermore, a partnership with Dell Technologies has upgraded their server and GPU capabilities, significantly boosting model performance (up to 5.14 times faster), thereby streamlining service updates and enhancements for greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
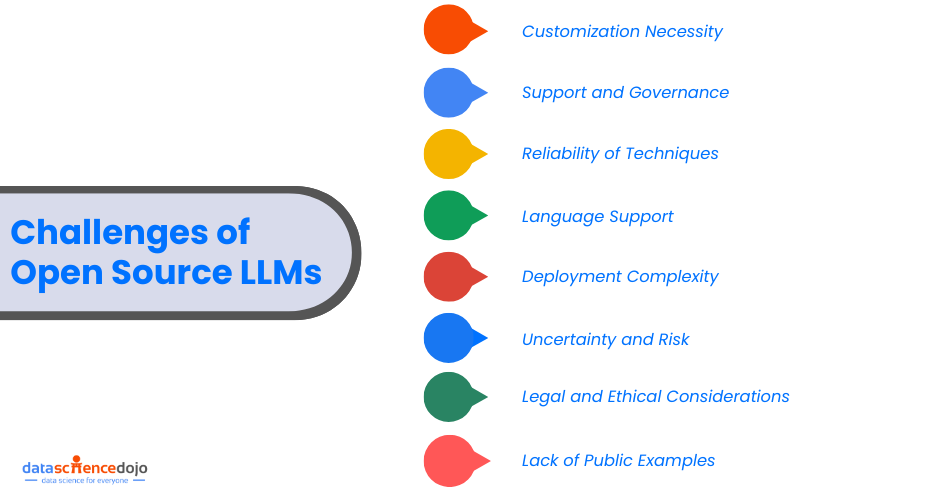
Challenges of Open Source LLMs
While open LLMs offer numerous benefits, there are substantial challenges that can plague the users.
-
Customization Necessity:
Open language models often come as general-purpose models, necessitating significant customization to align with an enterprise’s unique workflows and operational processes. This customization is crucial for the models to deliver value, requiring enterprises to invest in development resources to adapt these models to their specific needs.
-
Support and Governance:
Unlike proprietary models that offer dedicated support and clear governance structures, publically available large language models present challenges in managing support and ensuring proper governance. Enterprises must navigate these challenges by either developing internal expertise or engaging with the open-source community for support, which can vary in responsiveness and expertise.
-
Reliability of Techniques:
Techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation aim to enhance language models by incorporating proprietary data. However, these techniques are not foolproof and can sometimes introduce inaccuracies or inconsistencies, posing challenges in ensuring the reliability of the model outputs.
-
Language Support:
While proprietary models like GPT are known for their robust performance across various languages, open-source large language models may exhibit variable performance levels. This inconsistency can affect enterprises aiming to deploy language models in multilingual environments, necessitating additional effort to ensure adequate language support.
-
Deployment Complexity:
Deploying publically available language models, especially at scale, involves complex technical challenges. These range from infrastructure considerations to optimizing model performance, requiring significant technical expertise and resources to overcome.
-
Uncertainty and Risk:
Relying solely on one type of model, whether open or closed source, introduces risks such as the potential for unexpected updates by the provider that could affect model behavior or compliance with regulatory standards.
-
Legal and Ethical Considerations:
Deploying LLMs entails navigating legal and ethical considerations, from ensuring compliance with data protection regulations to addressing the potential impact of AI on customer experiences. Enterprises must consider these factors to avoid legal repercussions and maintain trust with their users.
Discover key insights on data ethics
-
Lack of Public Examples:
The scarcity of publicly available case studies on the deployment of publically available LLMs in enterprise settings makes it challenging for organizations to gauge the effectiveness and potential return on investment of these models in similar contexts.
Overall, while there are significant potential benefits to using publically available language models in enterprise settings, including cost savings and the flexibility to fine-tune models, addressing these challenges is critical for successful deployment
Open Source LLMs: Driving Flexibility and Innovation
In conclusion, open-source language models represent a pivotal shift towards more accessible, customizable, and cost-effective AI solutions for enterprises. They offer a unique blend of benefits, including significant cost savings, enhanced data control, and the ability to tailor AI tools to specific business needs, while also presenting challenges such as the need for customization and navigating support complexities.
Through the collaborative efforts of the global open-source community and the innovative use of these models across various industries, enterprises are finding new ways to leverage AI for growth and efficiency.
However, success in this endeavor requires a strategic approach to overcome inherent challenges, ensuring that businesses can fully harness the potential of publically available LLMs to drive innovation and maintain a competitive edge in the fast-evolving digital landscape.