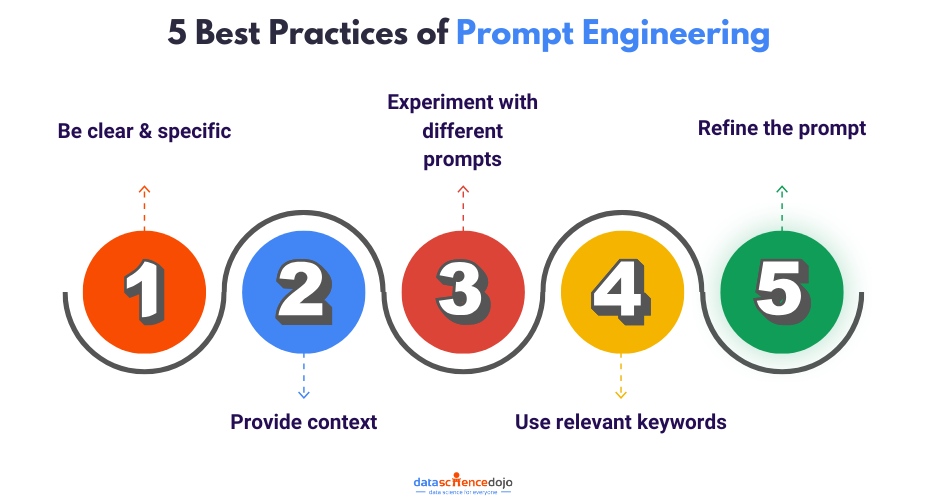
In today’s era of advanced artificial intelligence, language models like OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 have captured the world’s attention with their astonishing ability to generate human-like text. However, to harness the true potential of these models, it is crucial to master the art of prompt engineering strategies.
How to Curate a Good Prompt?
A well-crafted prompt holds the key to unlocking accurate, relevant, and insightful responses from language models. In this blog post, we will explore the top characteristics of a good prompt and discuss why everyone should learn prompt engineering. We will also delve into the question of whether prompt engineering might emerge as a dedicated role in the future.
Prompt engineering refers to the process of designing and refining input prompts for AI language models to produce desired outputs. It involves carefully crafting the words, phrases, symbols, and formats used as input to guide the model in generating accurate and relevant responses. The goal of prompt engineering is to improve the performance and output quality of the language model.
Here’s a Simple Example to Illustrate Prompt Engineering:
Imagine you are using a chatbot AI model to provide information about the weather. Instead of a generic prompt like “What’s the weather like?”, prompt engineering involves crafting a more specific and detailed prompt like “What is the current temperature in New York City?” or “Will it rain in London tomorrow?”
Read about —> Which AI chatbot is right for you?
By providing a clear and specific prompt, you guide the AI model to generate a response that directly answers your question. The choice of words, context, and additional details in the prompt can influence the output of the AI model and ensure it produces accurate and relevant information.
Prompt engineering is crucial because it helps optimize the performance of AI models by tailoring the input prompts to the desired outcomes. It requires creativity, understanding of the language model, and attention to detail to strike the right balance between specificity and relevance in the prompts.
Different resources provide guidance on best practices and techniques for prompt engineering, considering factors like prompt formats, context, length, style, and desired output. Some platforms, such as OpenAI API, offer specific recommendations and examples for effective prompt engineering.
Why Everyone Should Learn About Prompt Engineering Strategies
1. Empowering communication: Effective communication is at the heart of every interaction. By mastering prompt engineering, individuals can enhance their ability to extract precise and informative responses from language models. Whether you are a student, professional, researcher, or simply someone seeking knowledge, prompt engineering equips you with a valuable tool to engage with AI systems more effectively.
2. Tailored and relevant information: A well-designed prompt allows you to guide the language model towards providing tailored and relevant information. By incorporating specific details and instructions, you can ensure that the generated responses align with your desired goals. Prompt engineering enables you to extract the exact information you seek, saving time and effort in sifting through irrelevant or inaccurate results.
3. Enhancing critical thinking: Crafting prompts demand careful consideration of context, clarity, and open-endedness. Engaging in prompt engineering exercises cultivates critical thinking skills by challenging individuals to think deeply about the subject matter, formulate precise questions, and explore different facets of a topic. It encourages creativity and fosters a deeper understanding of the underlying concepts.
4. Overcoming bias: Bias is a critical concern in AI systems. By learning prompt engineering, individuals can contribute to reducing bias in generated responses. Crafting neutral and unbiased prompts helps prevent the introduction of subjective or prejudiced language, resulting in more objective and balanced outcomes.
Top Characteristics of a Good Prompt With Examples
A good prompt possesses several key characteristics that can enhance the effectiveness and quality of the responses generated. Here are the top characteristics of a good prompt:
1. Clarity:
A good prompt should be clear and concise, ensuring that the desired question or topic is easily understood. Ambiguous or vague prompts can lead to confusion and produce irrelevant or inaccurate responses.
Example:
Good Prompt: “Explain the various ways in which climate change affects the environment.”
Poor Prompt: “Climate change and the environment.”
2. Specificity:
Providing specific details or instructions in a prompt help focus the generated response. By specifying the context, parameters, or desired outcome, you can guide the language model to produce more relevant and tailored answers.
Example:
Good Prompt: “Provide three examples of how rising temperatures due to climate change impact marine ecosystems.”
Poor Prompt: “Talk about climate change.”
3. Context:
Including relevant background information or context in the prompt helps the language model understand the specific domain or subject matter. Contextual cues can improve the accuracy and depth of the generated response.
Example:
Good Prompt: “In the context of agricultural practices, discuss how climate change affects crop yields.”
Poor Prompt: “Climate change effects
4. Open Endedness:
While specificity is important, an excessively narrow prompt may limit the creativity and breadth of the generated response. Allowing room for interpretation and open-ended exploration can lead to more interesting and diverse answers.
Example:
Good Prompt: “Describe the short-term and long-term consequences of climate change on global biodiversity.”
Poor Prompt: “List the effects of climate change.”
5. Conciseness:
Keeping the prompt concise helps ensure that the language model understands the essential elements and avoids unnecessary distractions. Lengthy or convoluted prompts might confuse the model and result in less coherent or relevant responses.
Example:
Good Prompt: “Summarize the key impacts of climate change on coastal communities.”
Poor Prompt: “Please explain the negative effects of climate change on the environment and people living near the coast.”
6. Correct Grammar and Syntax:
A well-structured prompt with proper grammar and syntax is easier for the language model to interpret accurately. It reduces ambiguity and improves the chances of generating coherent and well-formed responses.
Example:
Good Prompt: “Write a paragraph explaining the relationship between climate change and species extinction.”
Poor Prompt: “How species extinction climate change.”
7. Balanced Complexity:
The complexity of the prompt should be appropriate for the intended task or the model’s capabilities. Extremely complex prompts may overwhelm the model, while overly simplistic prompts may not challenge it enough to produce insightful or valuable responses.
Example:
Good Prompt: “Discuss the interplay between climate change, extreme weather events, and natural disasters.”
Poor Prompt: “Climate change and weather.”
8. Diversity in Phrasing:
When exploring a topic or generating multiple responses, varying the phrasing or wording of the prompt can yield diverse perspectives and insights. This prevents the model from repeating similar answers and encourages creative thinking.
Example:
Good Prompt: “How does climate change influence freshwater availability?” vs. “Explain the connection between climate change and water scarcity.”
Poor Prompt: “Climate change and water.
9. Avoiding Leading or Biased Language:
To promote neutrality and unbiased responses, it’s important to avoid leading or biased language in the prompt. Using neutral and objective wording allows the language model to generate more impartial and balanced answers.
Example:
Good Prompt: “What are the potential environmental consequences of climate change?”
Poor Prompt: “How does climate change devastate the environment?”
10. Iterative Refinement:
Crafting a good prompt often involves an iterative process. Reviewing and refining the prompt based on the generated responses can help identify areas of improvement, clarify instructions, or address any shortcomings in the initial prompt.
Example:
Prompt iteration involves an ongoing process of improvement based on previous responses and refining the prompts accordingly. Therefore, there is no specific example to provide, as it is a continuous effort.
By considering these characteristics, you can create prompts that elicit meaningful, accurate, and relevant responses from the language model.
Read about —-> How LLMs (Large Language Models) technology is making chatbots smarter?
Two Different Approaches of Prompting
Prompting by instruction and prompting by example are two different approaches to guide AI language models in generating desired outputs. Here’s a detailed comparison of both approaches, including reasons and situations where each approach is suitable:
1. Prompting by Instruction:
- In this approach, the prompt includes explicit instructions or explicit questions that guide the AI model on how to generate the desired output.
- It is useful when you need specific control over the generated response or when you want the model to follow a specific format or structure.
- For example, if you want the AI model to summarize a piece of text, you can provide an explicit instruction like “Summarize the following article in three sentences.”
- Prompting by instruction is suitable when you need a precise and specific response that adheres to a particular requirement or when you want to enforce a specific behavior in the model.
- It provides clear guidance to the model and allows you to specify the desired outcome, length, format, style, and other specific requirements.
Examples of prompting by instruction:
- In a classroom setting, a teacher gives explicit verbal instructions to students on how to approach a new task or situation, such as explaining the steps to solve a math problem.
- In Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), a therapist provides a partial physical prompt by using their hands to guide a student’s behavior in the right direction when teaching a new skill.
- When using AI language models, an explicit instruction prompt can be given to guide the model’s behavior. For example, providing the instruction “Summarize the following article in three sentences” to prompt the model to generate a concise summary.
Tips for prompting by instruction:
-
- Put the instructions at the beginning of the prompt and use clear markers like “A:” to separate instructions and context.
- Be specific, descriptive, and detailed about the desired context, outcome, format, style, etc.
- Articulate the desired output format through examples, providing clear guidelines for the model to follow.
2. Prompting by Example:
- In this approach, the prompt includes examples of the desired output or similar responses that guide the AI model to generate responses based on those examples.
- It is useful when you want the model to learn from specific examples and mimic the desired behavior.
- For example, if you want the AI model to answer questions about a specific topic, you can provide example questions and their corresponding answers.
- Prompting by example is suitable when you want the model to generate responses similar to the provided examples or when you want to capture the style, tone, or specific patterns from the examples.
- It allows the model to learn from the given examples and generalize its behavior based on them.
Examples of prompting by example:
- In a classroom, a teacher shows students a model essay as an example of how to structure and write their own essays, allowing them to learn from the demonstrated example.
- In AI language models, providing example questions and their corresponding answers can guide the model in generating responses similar to the provided examples. This helps the model learn the desired behavior and generalize it to new questions.
- In an online learning environment, an instructor provides instructional prompts in response to students’ discussion forum posts, guiding the discussion and encouraging deep understanding. These prompts serve as examples for the entire class to enhance the learning experience.
Tips for prompting by example:
-
- Provide a variety of examples to capture different aspects of the desired behavior.
- Include both positive and negative examples to guide the model on what to do and what not to do.
- Gradually refine the examples based on the model’s responses, iteratively improving the desired behavior.
Which Prompting Approach is Right For You?
Prompting by instruction provides explicit guidance and control over the model’s behavior, while prompting by example allows the model to learn from provided examples and mimic the desired behavior. The choice between the two approaches depends on the level of control and specificity required for the task at hand. It’s also possible to combine both approaches in a single prompt to leverage the benefits of each approach for different parts of the task or desired behavior.
To become proficient in prompt engineering, register now in our upcoming Large Language Models Bootcamp