The rapid growth of AI technologies has increased demand for personalized text generation. Advanced generative systems now tailor responses based on audience, context, and user needs. Businesses, educators, and marketers leverage AI-driven content to enhance engagement and efficiency. As AI evolves, personalized text generation is reshaping digital communication across industries.
The Evolution of Text Generation
Researchers have explored customized text generation in various applications, including product reviews, chatbots, and social media interactions. These models have proven effective in specific domains but often remain task-specific, relying on predefined features for a particular use case.
This means they perform well within their niche but struggle to generalize across different contexts. There has been less focus on developing a universal approach—one that can generate personalized text across multiple domains without extensive retraining.
In the past, text generation was entirely manual. If you needed a document, you had to write it from scratch.
The rise of AI-driven text generation has changed this significantly. Early AI models followed structured templates or rule-based systems, making them rigid and predictable.
Modern large language models (LLMs), however, generate dynamic, human-like text, adapting their tone and style based on input. This shift has made AI-powered text generation more flexible, intuitive, and scalable across various applications.
What is Individualized Text Generation?
One of the most exciting advancements in AI is individualized text generation, where AI systems create text tailored to a specific person or context. Unlike generic text generation, which produces broad, one-size-fits-all content, individualized AI adapts to the recipient’s preferences, interests, and communication style.
For example:
- Personalized Emails: Instead of sending a generic marketing email, AI can craft a message tailored to the recipient’s past purchases, preferences, and engagement history.
- Chatbots & Virtual Assistants: AI-driven chatbots can provide personalized responses based on past interactions, making conversations feel more natural and engaging.
- Social Media Posts: AI can generate posts or captions that match a user’s tone and style, maintaining a consistent online presence.
Enhancing Individualized Text Generation
To make AI-generated text more personalized and context-aware, researchers and developers use a variety of techniques. Two key approaches include training on specific datasets and using auxiliary tasks to enhance the AI’s understanding of the individual or context.
1. Training on Personalized Datasets
One of the most effective ways to improve individualized text generation is by training AI models on datasets that are directly relevant to the user or context. Instead of relying on general text data, the model learns from a dataset that reflects the specific writing style, tone, and preferences of an individual.
Also explore Sora for video generation
For example:
- Personalized Emails – If an AI model is trained on past emails written and received by an individual, it can generate new emails that match their tone, vocabulary, and phrasing.
- Customer Support Chatbots – Training a chatbot on past customer interactions allows it to respond in a way that aligns with a company’s brand voice and individual customer preferences.
- Social Media Content – AI models trained on a user’s previous social media posts can generate content that fits their personal style and engagement patterns.
The more relevant the training data, the better the AI model can adapt to an individual’s unique way of writing.
2. Using Auxiliary Tasks to Enhance Learning
Another method to improve personalized text generation is incorporating auxiliary tasks, which are additional learning objectives beyond the primary task of text generation. These tasks help the AI model develop a deeper understanding of the user or context, ultimately improving the quality of the generated text.
Examples of auxiliary tasks include:
- Sentiment Analysis: Before generating a response, the AI first determines the sentiment of the input text (positive, negative, or neutral). This allows it to generate responses that match the user’s mood.
- Topic Classification: AI models can classify the topic of a conversation (e.g., work, travel, hobbies) before generating text, ensuring responses remain relevant to the discussion.
- Style Adaptation: By learning to recognize different writing styles—formal, casual, humorous—the AI can adjust its tone accordingly.
- User Preference Modeling: The AI can predict what kind of content a user is likely to engage with and generate text accordingly, such as recommending certain topics in an article or adjusting word choice.
These auxiliary tasks act as extra layers of learning, allowing the AI to refine its responses and generate text that feels truly tailored to the individual.
Google’s Approach to Individualized Text Generation
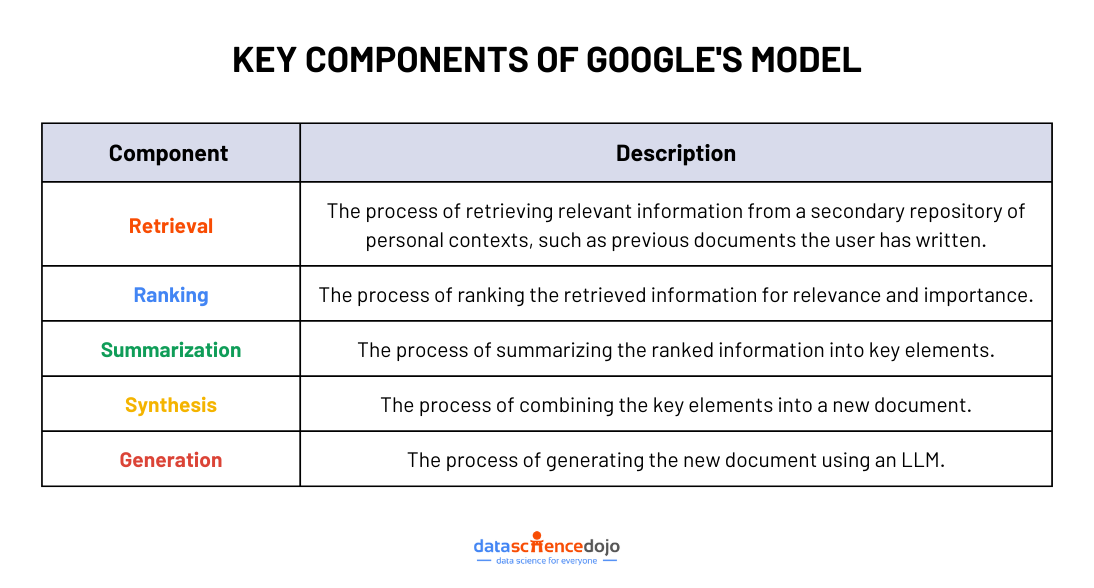
Google’s research introduces a structured, multi-stage approach to individualized text generation. Instead of relying solely on predefined templates or large datasets, this method mimics human writing strategies by breaking the process into key steps: retrieval, ranking, summarization, synthesis, and generation.
Key Components of Google’s Model
1. Retrieval – Finding Relevant Information
The first step is retrieval, where the AI searches for relevant information from external sources or a personal repository of user contexts. These sources may include:
- Past documents and writings (e.g., emails, reports, notes).
- Social media interactions and conversations for informal text.
- External research materials to provide factual grounding.
By retrieving information from varied, contextually rich sources, the AI ensures that generated text aligns with the user’s style and intent.
2. Ranking – Prioritizing the Most Useful Information
Once the relevant data is retrieved, the model ranks it based on importance and relevance. The ranking system filters out unnecessary details, ensuring that only high-quality information moves forward.
Ranking criteria include:
- Context relevance – How closely does the information align with the topic?
- Recency and reliability – Is the data up to date and from a trusted source?
- User-specific importance – Has the user frequently referenced similar sources?
This step prevents irrelevant or outdated content from influencing the final output.
3. Summarization – Extracting Key Elements
Instead of working with raw, lengthy documents, the model condenses the retrieved and ranked data into concise summaries. This process ensures that only essential information remains, making it easier for the AI to generate focused, relevant text.
Examples:
- A long email thread is summarized into key discussion points.
- A social media debate is distilled into core arguments.
- A customer review dataset is condensed into product sentiment highlights.
Summarization allows the AI to work with structured, digestible content before moving to text generation.
4. Synthesis – Combining Key Elements into a Cohesive Draft
Once the essential details are extracted, the AI integrates multiple sources into a well-structured draft. This step ensures:
- Logical flow and coherence across the content.
- Personalization that matches the user’s writing style.
- Context-awareness, ensuring all relevant details are incorporated.
At this stage, the AI transforms disparate pieces of information into a unified, high-quality response.
5. Generation – Producing the Final Text
In the final step, the AI uses a large language model (LLM) to generate polished, natural-sounding text. The model adapts its tone, structure, and wording to ensure the text feels engaging, human-like, and tailored to the user’s needs.
This output can take different forms, such as:
- Emails, reports, and official documents.
- Social media posts and casual conversations.
- Product reviews, summaries, or creative writing pieces.
Also learn about text mining
Improving the Reading Abilities of LLMs
Google researchers also recognized that stronger reading abilities lead to better writing performance. Inspired by language learning research, they introduced an auxiliary task to enhance the model’s comprehension:
The LLM is challenged to identify the authorship of a given text—a task commonly used in human reading assessments. By engaging in this challenge, the model:
- Develops a deeper understanding of writing styles.
- Learns to better interpret nuances in text.
- Becomes more effective at generating personalized responses.
Evaluating the Model’s Performance
To assess the effectiveness of this multi-stage, multi-task approach, Google researchers tested their model on three publicly available datasets:
- Email Correspondence – To evaluate formal, structured text generation.
- Social Media Debates – To test informal, conversational writing.
- Product Reviews – To measure how well AI can generate subjective and opinion-based content.
The results showed significant improvements over baseline models across all three datasets. This demonstrates that a structured, multitasking approach leads to more accurate, personalized, and compelling text generation.
Practical Applications of Personalized Text Generation
Personalized text generation isn’t just a futuristic concept—it’s already shaping how we interact with technology today. From AI companions to customizable assistants, let’s explore some real-world applications that are making a difference.
AI Companionship: More Than Just Chatbots
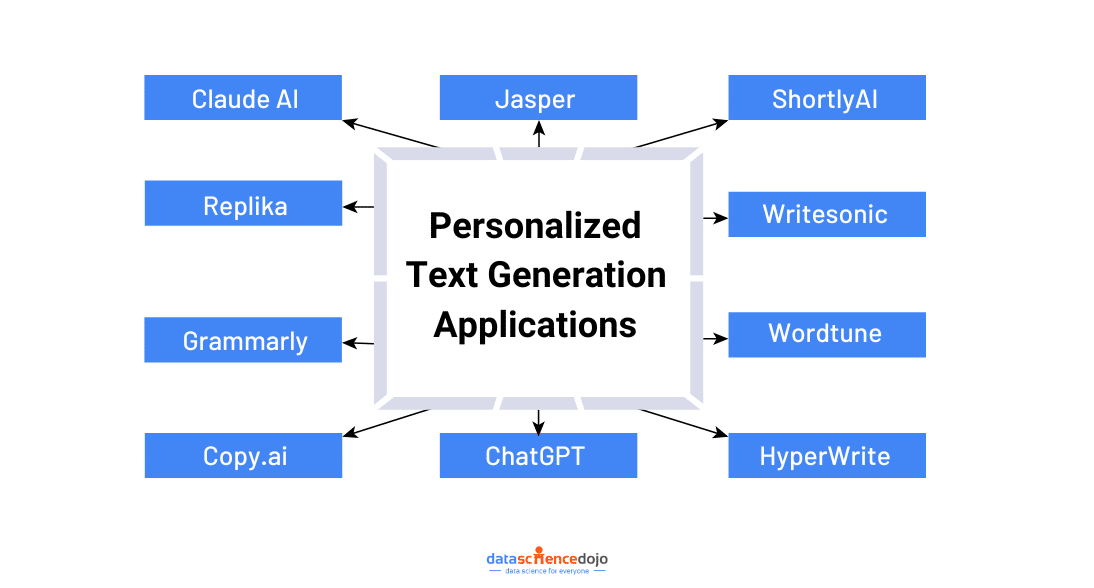
Imagine having an AI friend who remembers your conversations, understands your emotions, and offers thoughtful responses. That’s exactly what AI companionship services like Replika provide.
These AI avatars act as friends, therapists, and even romantic partners, adapting their responses based on user interactions. Whether someone needs emotional support, a casual chat, or even deep conversations, these AI companions learn and evolve, making each interaction feel personal and meaningful. This level of customization keeps users engaged and helps combat loneliness.
Customizable AI Assistants: Tailored to Your Style
Not all AI assistants need to sound the same. Anthropic’s Claude AI is changing the game by allowing users to customize how their chatbot responds.
Want a formal, professional tone? Or maybe a more casual and friendly style? Users can adjust the chatbot’s personality to match their preferences, making interactions feel more natural and aligned with their communication style. This is especially useful for businesses, content creators, and individuals looking for AI that truly feels like their own.
You might also like: 5 leading music generation models
Smart Content Creation: AI That Adapts to Your Voice
Creating content can be time-consuming, but what if AI could write in your unique style? That’s exactly what personalized AI-powered writing tools do. Platforms like Grammarly, Jasper, and Copy.ai use AI to generate content that aligns with an individual’s tone, vocabulary, and writing style.
For marketers, this means AI that adapts to brand voice and audience preferences. For bloggers and writers, it means AI-generated drafts that sound like them. These tools don’t just automate writing—they personalize it, making the process faster and more efficient while keeping the human touch intact.
As AI improves, content creation will feel even more seamless, helping businesses, creators, and everyday users communicate more effectively.
Ethical Challenges in Personalized AI
While personalized text generation offers exciting possibilities, it also comes with its fair share of challenges. From data privacy concerns to issues of trust and authenticity, here’s what we need to consider as AI becomes more deeply integrated into our daily interactions.
Data Privacy: Who Has Access to Your Information?
For AI to generate highly personalized responses, it needs access to user data—past conversations, preferences, writing style, and even personal details. But this raises an important question: How is this data collected, stored, and used?
Many users worry about whether their data is truly private. Could it be shared with third parties? Is it securely stored? Transparency is key—AI developers must ensure users have control over their data, with clear policies on data collection and the option to opt out. Without strong privacy protections, trust in AI systems could erode.
Authenticity and Trust: Is It AI or a Human?
As AI-generated content becomes more personalized, it’s becoming harder to distinguish between human and machine-written text. This can blur the lines of authenticity in digital interactions.
For instance, in customer service, social media, or even journalism, should AI be required to disclose when it’s generating content? If people can’t tell the difference, it could lead to misinformation, manipulation, or even ethical dilemmas in online communication. Establishing guidelines and transparency around AI-generated content is crucial to maintaining trust.
Finding the Balance
AI personalization is powerful, but it must be used responsibly. Striking a balance between customization and ethical safeguards will determine how AI shapes the future of communication. The question isn’t just about what AI can do—it’s about what it should do.
Conclusion
The Google research team’s work presents a promising approach to individualized text generation with LLMs. The multi-stage, multi-task framework is able to effectively incorporate personal contexts and improve the reading abilities of LLMs, leading to more accurate and compelling text generation.