AI isn’t just changing how we work—it’s changing who does the work. As machines get smarter and automation becomes more advanced, one question keeps coming up: Will AI replace jobs? It’s a concern that’s no longer limited to factory floors or data entry roles—AI is moving into creative fields, customer service, and even decision-making positions.
In this blog, we’ll unpack the real impact of AI on employment. Which jobs are most at risk? Which industries are adapting? And how can workers stay ahead in a world where machines keep getting better? If you’ve ever wondered will AI replace jobs—or what it means for your career—you’re in the right place.
In this blog, we’ll decode the jobs that will thrive and the ones that will go obsolete in the following years.
The Rise of Generative AI
Generative AI has been an idea in the making for decades, but only recently has it stepped into the spotlight, thanks to groundbreaking advances in deep learning. With the ability to process massive datasets and recognize complex patterns, modern AI systems can now generate content—whether it’s text, images, music, or even code—that closely mimics human creativity.
What once seemed like science fiction is now powering real-world applications, blurring the lines between human-made and machine-generated content.
At the core of this revolution are powerful foundation models—large-scale AI systems trained on diverse datasets to perform a wide range of tasks. OpenAI’s GPT-4, Google’s PaLM, and other leading models have set the stage, pushing the limits of what generative AI can achieve.
These models aren’t just confined to general tasks; they’ve inspired an entire ecosystem of specialized tools tailored for specific industries, such as:
- In healthcare, LLMs assist in diagnosing diseases and personalizing treatment plans.
- In marketing, they generate compelling copy and customer insights.
- In creative industries like film and music, AI is becoming a collaborator rather than just a tool.
This surge in generative AI doesn’t just represent technological progress—it signals a shift in how we approach creativity, problem-solving, and productivity. As more sectors adopt LLM-driven solutions, the possibilities for innovation seem limitless, marking a new era in the AI revolution.
Explore more about LLM Use Cases – Top 10 industries that can benefit from using them
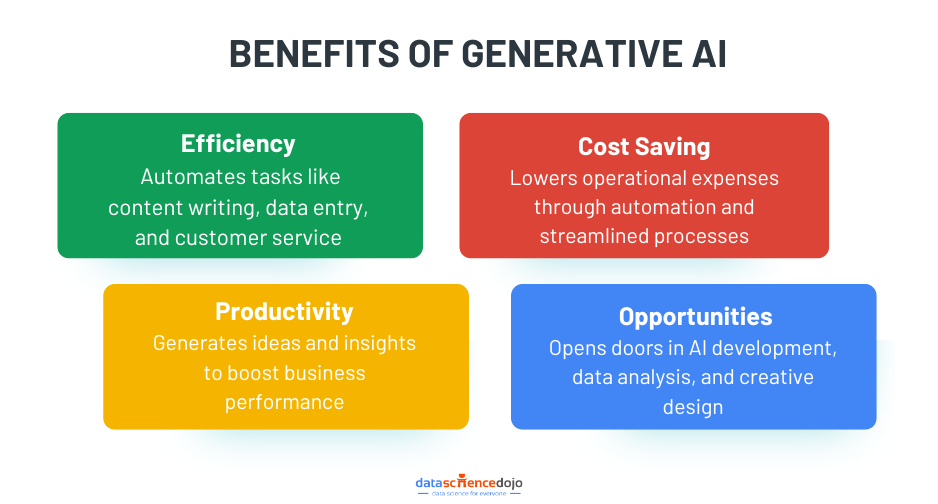
Potential Benefits of Generative AI
Generative AI goes beyond simple automation—it introduces transformative potential that reshapes industries, redefines roles, and creates new value streams. Here’s a deeper look at how generative AI is driving meaningful benefits beyond surface-level efficiency and cost savings:
1. Expanding Human Creativity
Generative AI doesn’t just replicate human work; it amplifies creativity. By handling the heavy lifting of idea generation, drafting, and prototyping, AI allows individuals and teams to push creative boundaries further and faster.
In design, AI tools can suggest layouts or color palettes, allowing designers to focus on refining aesthetics and storytelling. In writing, AI can draft multiple content variations, freeing up writers to focus on voice and messaging nuance.
This synergy between human creativity and AI-driven ideation accelerates innovation. Instead of starting from scratch, teams can build upon AI-generated foundations, leading to richer, more diverse outcomes in less time.
2. Accelerating Innovation Cycles
Generative AI significantly reduces the time it takes to move from concept to execution. In industries like product design, AI can generate multiple prototypes based on user input, design constraints, and market data in a fraction of the time it would take human teams.
This rapid prototyping allows businesses to test and iterate ideas quickly, reducing time-to-market and increasing agility.
Pharmaceutical companies, for example, use generative AI to model potential drug compounds, accelerating research that traditionally takes years. Similarly, in architecture, AI assists in generating multiple design layouts that meet both aesthetic and structural requirements, streamlining the design process.
3. Enabling Hyper-Personalization
One of generative AI’s standout benefits is its ability to deliver hyper-personalized content and experiences at scale. Whether it’s customizing marketing messages, tailoring product recommendations, or creating unique user interfaces, AI can analyze individual preferences and generate content that feels specifically crafted for each user.
For instance, e-commerce platforms can use AI to generate personalized product descriptions and marketing copy, enhancing the customer experience and improving conversion rates. In entertainment, AI can create dynamic content—such as personalized playlists or storylines—that adapts to user behavior and preferences.
Explore more about AI-driven personalization in marketing
4. Democratizing Content Creation
Generative AI lowers the barrier to entry for content creation across industries. Individuals and businesses without extensive resources or specialized skills can now produce high-quality content, designs, or code with AI assistance. This democratization empowers small businesses, startups, and independent creators to compete with larger organizations.
A small business owner, for example, can use AI tools to design marketing materials, write website copy, and even generate product images without hiring a full creative team. This not only reduces costs but also enables faster and more diverse content production.
5. Driving Data-Backed Decision-Making
Beyond creating content, generative AI plays a crucial role in data analysis and insight generation. AI systems can process vast amounts of unstructured data, identify patterns, and present actionable insights that inform strategic decisions. Businesses can leverage these insights to optimize operations, identify market trends, and develop more effective campaigns.
In finance, AI can generate risk assessments and investment strategies by analyzing historical market data. In healthcare, AI-driven analysis of patient data can reveal patterns that inform treatment plans and predict potential health risks. This ability to transform data into meaningful, actionable information enhances decision-making across industries.
6. Unlocking New Economic Opportunities
Generative AI is not only transforming existing roles but also creating entirely new markets and career paths. As AI-generated content and tools become more integrated into industries, demand for professionals skilled in AI development, ethical AI oversight, and AI-human collaboration is growing.
Industries are also seeing the emergence of niche markets—such as AI-generated art, virtual fashion, and synthetic media—where generative AI becomes the core product rather than just a tool. This opens new economic opportunities for businesses and creatives willing to explore the possibilities AI offers.
Learn how Generative AI is reshaping the society including the career, education and tech landscape. Watch our full podcast Future of Data and AI now!
Will AI Replace Jobs? Yes.
Yes, AI will replace some jobs, especially in roles and industries most vulnerable to automation. It thrives at handling repetitive tasks, data processing, and rule-based decision-making, reducing the need for human input in certain positions.
As businesses increasingly adopt AI technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs, specific job categories face a higher risk of being phased out or significantly altered. Here’s a closer look at the fields most likely to be impacted:
1. Manufacturing and Assembly
Manufacturing has been one of the earliest adopters of automation, with robots already performing repetitive tasks on assembly lines. With advancements in AI, machines are becoming smarter—capable of performing quality control, precision assembly, and even predictive maintenance with minimal human intervention.
Jobs that involve routine, manual labor are particularly at risk, as AI-driven robots can operate 24/7 without fatigue, leading to increased productivity and reduced operational costs.
2. Retail and Customer Service
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are reshaping customer service. Many businesses now use automated systems to handle basic inquiries, process returns, and even recommend products based on customer behavior. In retail, self-checkout kiosks and AI-driven inventory management are reducing the need for cashiers and stock clerks.
While human representatives are still essential for complex issues, a significant portion of front-line customer service roles is being automated.
3. Transportation and Logistics
The rise of autonomous vehicles and AI-driven logistics platforms is set to transform the transportation industry. Self-driving trucks are already in testing phases, promising to reduce the need for long-haul drivers.
In logistics, AI algorithms optimize delivery routes, manage warehouse inventories, and even coordinate supply chains, minimizing the need for human oversight. As these technologies mature, many driving and coordination roles could be replaced or significantly reduced.
4. Finance and Accounting
AI is revolutionizing the finance sector by automating tasks that once required human precision. Algorithmic trading already dominates stock markets, with AI systems making split-second decisions based on real-time data.
In accounting, AI tools handle invoice processing, expense management, and even tax preparation, reducing the need for entry-level accountants. As these tools become more sophisticated, roles focused on data entry and routine financial analysis are at high risk.
5. Administrative and Clerical Work
One of the most vulnerable sectors to AI automation is administrative support. Tasks like scheduling meetings, managing emails, and data entry can now be handled by intelligent virtual assistants.
AI can also draft reports, manage customer databases, and organize workflows, reducing the demand for human administrative staff. As AI becomes more integrated into office environments, traditional clerical roles may see significant reductions.
6. Media and Content Creation
AI is increasingly making inroads into content creation. AI-driven writing tools can now draft articles, social media posts, and even product descriptions with minimal human input. In graphic design, AI tools can generate logos, layouts, and marketing materials based on simple prompts.
While creative fields still require human oversight for originality and emotional resonance, many entry-level content creation roles are at risk as businesses adopt AI to scale content production quickly and cheaply.
Will AI Replace Jobs Entirely? No.
AI might snatch some jobs, but it’s not taking over everything—it’s not God, after all.
While it transforms industries and automates certain tasks, it’s reshaping work rather than eliminating the human workforce.
Key points include:
-
Human Expertise Remains Crucial:
Complex problem-solving, strategic thinking, and interpersonal communication keep many fields human-driven. Fields like legal consulting, strategic business planning, and specialized technical roles demand a level of expertise, negotiation skills, and critical analysis that AI can’t fully replicate. -
New Opportunities Arise:
As businesses adopt AI-driven technologies, roles in AI development, machine learning engineering, data analysis, and AI ethics are booming—creating career paths that didn’t exist a decade ago.
AI also enhances jobs instead of replacing them outright. For example:
- In journalism, AI can draft basic reports or summarize data, but it’s the journalist who adds depth and storytelling.
- In design, AI tools might suggest layouts and styles, yet the creative vision remains with the designer.
This mix of human skills and AI support is shaping the future of work.
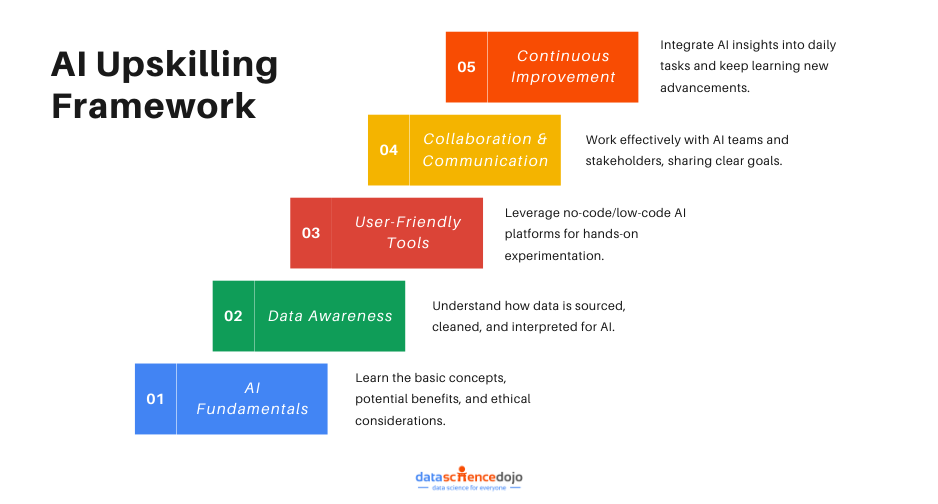
The Importance of Upskilling
The rapid rise of Generative AI (GenAI) is transforming industries and reshaping job roles, making upskilling more critical than ever. AI systems now handle tasks once done by humans—from content creation to data analysis—pushing workers to evolve alongside these technologies.
Why upskilling is essential in the GenAI era:
- AI is taking over traditional tasks, increasing the need for human-AI collaboration.
- Staying relevant now means understanding how these tools work and developing complementary skills.
A key aspect of this shift is the demand for hybrid skills—a mix of technical proficiency and domain-specific expertise. It’s no longer enough to just know how AI tools function; integrating them meaningfully into daily roles is vital, for instance:
- Marketers benefit from knowing how AI personalizes user experiences.
- Architects can use AI-generated design suggestions to refine their creative visions.
Adaptability is another crucial element. With AI evolving rapidly, workers need to stay agile and continuously update their skills.
- Explore fields like prompt engineering—crafting effective inputs for generative models.
- Understand AI-human interaction to optimize workflows and enhance productivity.
Good news: There’s a growing ecosystem of resources to support this upskilling journey.
- Online courses (Coursera, Udemy, LinkedIn Learning) offer flexible options—from coding in Python to mastering AI-enhanced design tools.
- Bootcamps provide hands-on, intensive training in areas like data science, AI development, and UX design, helping learners gain job-ready skills in months.
Ethical Considerations
The rise of generative AI also raises some ethical concerns, such as:
- Bias: Generative AI systems can be biased, which could lead to discrimination against certain groups of people.
- Privacy: Generative AI systems can collect and analyze large amounts of data, which could raise privacy concerns.
- Misinformation: Generative AI systems could be used to create fake news and other forms of misinformation.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Generative AI can copy or remix content, leading to copyright infringement and unauthorized use.
Also explore: People management in AI
- Deepfakes and Identity Theft: Generative AI can produce realistic fake media, enabling identity theft, fraud, and impersonation.
- Environmental Impact: Training large generative AI models consumes vast energy, increasing carbon footprints and environmental concerns.
- Lack of Accountability: When generative AI outputs harmful or misleading content, it’s often unclear who is responsible—the developers, the users, or the AI itself—creating a gray area in accountability and legal liability.
It is important to address these ethical concerns as GenAI technology continues to develop.
Government and Industry Responses
Governments and industries are starting to respond to the rise of GenAI. Some of the things that they are doing include:
- Developing regulations to govern the use of generative Artificial Intelligence.
- Investing in research and development of AI technologies.
- Providing workforce development programs to help workers upskill.
- Enhancing Data Privacy Laws: Strengthening policies to protect personal data from misuse by AI systems.
- Fostering Public Awareness: Running educational campaigns to inform the public about the benefits and risks of generative AI.
Leverage AI to Increase Your Job Efficiency
In summary, Artificial Intelligence is poised to revolutionize the job market. While offering increased efficiency, cost reduction, productivity gains, and fresh career prospects, it also raises ethical concerns like bias and privacy. Governments and industries are taking steps to regulate, invest, and support workforce development in response to this transformative technology.
As we move into the era of revolutionary AI, adaptation and continuous learning will be essential for both individuals and organizations. Embracing this future with a commitment to ethics and staying informed will be the key to thriving in this evolving employment landscape.