In today’s data-driven world, businesses rely on advanced technologies to gain insights and make informed decisions.
Predictive analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are two powerful tools used to uncover patterns, forecast trends, and automate decisions.
While both leverage data, they differ in approach, capabilities, and applications.
This blog explores the key differences between predictive analytics and AI, highlighting their unique strengths and how they complement each other in modern data science.
Different Approaches to Analytics
In the realm of analytics, different strategies help businesses and professionals extract insights from data and make informed decisions. These approaches—descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics—each serves a unique purpose in understanding data and driving actions.
Descriptive Analytics
Descriptive Analytics focuses on summarizing historical data to identify trends and patterns. It answers the question, “What happened?” by analyzing past events and presenting the findings through reports, dashboards, and visualizations. This approach is commonly used in business intelligence to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and monitor business performance.
Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic Analytics takes analysis a step further by identifying the causes behind past outcomes. It answers, “Why did it happen?” using techniques such as data mining, correlation analysis, and root cause analysis. This method helps businesses and industries understand the factors influencing their successes or failures, enabling better decision-making.
Also explore: Trending GitHub Repositories for Data Science & AI
Predictive Analytics
Predictive Analytics plays a crucial role, especially in fields like engineering, finance, and healthcare. It uses historical data, machine learning models, and statistical techniques to forecast future trends and outcomes. In engineering, for example, predictive analytics helps professionals anticipate equipment failures, optimize product design, and improve maintenance schedules, reducing operational risks and costs.
Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive Analytics goes beyond prediction by recommending specific actions to optimize results. It answers, “What should be done next?” by leveraging AI, machine learning, and optimization algorithms. This approach is widely used in supply chain management, personalized marketing, and healthcare, where decision-makers need actionable insights to maximize efficiency and effectiveness.
AI: Empowering Engineers
AI isn’t here to replace engineers—it’s here to enhance their capabilities. It acts as a collaborative partner, helping engineers make better decisions and interact more efficiently with digital tools.
AI automates repetitive tasks, such as calculations, simulations, and optimizations, freeing up engineers to focus on innovation. It provides data-driven insights, detecting patterns, predicting failures, and improving efficiency in fields like manufacturing and construction.
With AI-powered CAD software, digital twins, and simulations, engineers can test models in virtual environments, reducing costs and risks. AI also enhances human creativity, offering smart design recommendations and optimizing complex structures.
By embracing AI, engineers can work faster, smarter, and more efficiently, using it as a tool to push boundaries and drive progress.
AI and Predictive Analytics: Bridging the Gap
AI and Predictive Analytics are closely connected but serve different purposes. While Predictive Analytics uses historical data, statistical models, and machine learning to forecast future trends, AI goes a step further by learning, adapting, and making autonomous decisions. Together, they bridge the gap between insight and action, turning data into intelligent, real-time decision-making.
Some examples of this synergy include predictive maintenance, risk modeling, and personalized customer engagement.
Predictive Maintenance: Predictive analytics identifies patterns in sensor data and past performance trends to anticipate equipment failures. This allows businesses to schedule maintenance before a breakdown occurs.
By preventing failures in advance, companies can minimize downtime and lower operational costs.
AI takes this further by processing real-time sensor data and detecting subtle anomalies. It dynamically adjusts maintenance schedules based on emerging patterns.
AI-powered automation can even trigger self-healing mechanisms in some systems. This reduces the need for human intervention and enhances efficiency.
Risk Modeling: Financial institutions and insurance companies use predictive analytics to assess risks. They analyze historical data on fraud, market fluctuations, and operational vulnerabilities.
This helps businesses prepare for threats before they escalate.
AI enhances this by continuously monitoring real-time financial transactions. It learns from new fraud patterns and instantly adjusts risk models.
AI-driven fraud detection systems can flag suspicious activities and automate security measures. This enables faster and more accurate responses to emerging threats.
Next Best Action in Customer Engagement: Predictive analytics examines customer behavior, past interactions, and preferences. It helps businesses identify the most effective engagement strategies.
With these insights, companies can personalize marketing efforts and improve customer retention.
AI takes this further by automating real-time interactions and analyzing customer sentiment. It optimizes responses dynamically based on evolving trends.
AI-driven chatbots, recommendation engines, and automated campaigns ensure personalized and timely engagement. This boosts conversion rates and enhances customer satisfaction.
Read more –> Data Science vs AI
Navigating Engineering with AI
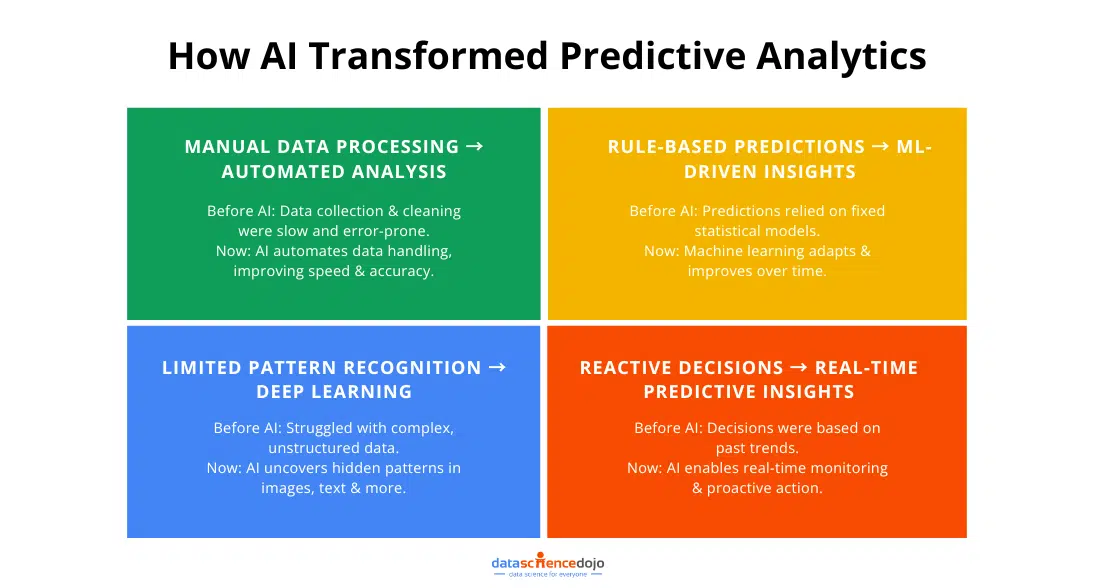
Before AI, engineers used predictive analytics tools based on mathematical models. These methods were time-consuming and required extensive manual effort. Processing large datasets and fine-tuning models made predictions slow.
The introduction of Deep Learning in 2018 revolutionized predictive analytics. This AI-driven approach uses neural networks to analyze data quickly and accurately. Unlike traditional models, it automates pattern recognition and adapts to new data.
Industries like manufacturing, aerospace, and civil engineering have greatly benefited. AI enhances structural assessments, optimizes maintenance, and predicts failures. It speeds up product design and engineering decisions.
With AI, engineers can automate complex calculations and gain real-time insights. This transformation makes engineering processes faster, smarter, and more efficient.
The Role of Data Analysts
Data analysts are essential in predictive analytics, identifying trends and patterns in data. They use statistical models and machine learning to forecast future outcomes.
Their expertise helps in deciphering complex data and ensuring predictions are accurate. By analyzing historical data, they uncover insights that drive business and engineering decisions.
With AI and automation, analysts can process data faster and refine predictive models. Their role remains crucial in transforming raw data into actionable intelligence.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning: The Power Duo
Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) are two powerful branches of AI that revolutionize predictive analytics. Both enable machines to analyze data, recognize patterns, and make intelligent predictions.
ML uses algorithms to learn from data without explicit programming. It includes techniques like decision trees, regression models, and clustering, allowing computers to identify trends and improve over time. ML is widely used in fraud detection, recommendation systems, and predictive maintenance.
Also explore: AI and Deep Learning in Stock Market Predictions
Deep Learning (DL) takes ML a step further by using deep neural networks. These networks mimic the human brain, making DL ideal for processing complex, unstructured data like images, speech, and text. It powers autonomous vehicles, medical diagnostics, and advanced AI assistants.
Together, ML and DL enhance predictive analytics, making forecasts more accurate and automation more efficient. Their ability to process vast datasets with precision drives innovation across industries.
AI and Predictive Analytics: A Powerful Combination
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with Predictive Analytics is transforming industries by making forecasts faster, smarter, and more efficient. AI enhances predictive analytics by automating data analysis, reducing processing time, and improving accuracy. This enables businesses and engineers to test more scenarios, optimize designs, and make better decisions with less effort.
For example, in heat exchanger applications, AI—specifically the NCS AI model—is used to predict efficiency, temperature, and pressure drop. By applying generative design techniques, AI helps engineers develop more efficient and cost-effective designs, reducing trial-and-error and manual adjustments.
Understanding the Difference: Predictive Analytics vs. AI
Both Predictive Analytics and AI deal with data-driven decision-making, but they serve different purposes. Predictive Analytics relies on historical data to identify patterns and make forecasts. It uses statistical models and machine learning to predict future trends, helping businesses anticipate customer behavior, financial risks, or equipment failures.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), on the other hand, goes beyond predictions. It learns from data, makes decisions, and even improves itself over time. AI uses advanced techniques like deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to perform complex tasks, such as recognizing speech, driving autonomous cars, or diagnosing diseases.
Give it a read too: Business Analytics vs Data Science
Strengths and Limitations
Predictive analytics is widely used and effective in forecasting future events, but it has limitations. It can be biased if the data it is trained on is incomplete or inaccurate. Meanwhile, AI can analyze massive amounts of data and make highly accurate decisions, but it requires significant computing power and resources to develop.
While Predictive Analytics is already well-established, AI is rapidly evolving and continuously improving. As AI becomes more accessible, its ability to enhance predictive analytics will lead to even more advanced, automated, and intelligent decision-making systems across industries.
Realizing the Potential: Unified Applications in a Data-Driven World
Understanding the differences between predictive analytics and AI is only part of the picture. The real magic happens when these technologies work together to transform industries. Let’s explore how their combined strengths are being applied in everyday business challenges.
Healthcare
In healthcare, every second counts. AI analyzes real-time data to help medical professionals quickly triage patients, ensuring those in critical condition receive immediate attention.
At the same time, predictive analytics leverages historical patient data and statistical trends to support early disease diagnosis. When you add AI-powered medical imaging into the mix—delivering clearer, faster visualizations—the result is a more proactive, patient-focused approach to care.
Customer Service
Today’s consumers expect swift and personalized support. AI-driven smart call routing directs customers to the right agents, cutting down on wait times and frustration. Online chatbots, capable of handling routine inquiries efficiently, free up human agents for more complex issues.
Meanwhile, smart analytics tools provide real-time insights that help companies refine their customer engagement strategies, ensuring a seamless and satisfying service experience.
Finance
In the finance sector, precision and security are paramount. AI monitors financial behavior in real time to detect anomalies and flag potential fraud before it escalates. Expense management systems powered by AI automatically categorize expenses, making tracking and forecasting more accurate.
Furthermore, automated billing systems streamline financial operations—reducing errors and saving time—so that financial teams can focus on strategic decision-making.
Machine Learning in Action: The AI Advantage
While predictive analytics focuses on recognizing patterns and making forecasts based on historical data, machine learning—a key subset of AI—goes a step further by continuously learning from new information and adapting its decision-making process. Here’s how machine learning is reshaping real-world applications:
- Social Media Moderation: Platforms use machine learning algorithms to scan text, images, and videos for hate speech, misinformation, and explicit content. Unlike traditional rule-based systems, ML continuously refines its ability to detect harmful content based on new data, making moderation more accurate over time.
- Email Automation & Spam Filtering: Traditional predictive models can identify spam based on predefined rules, but machine learning adapts to emerging threats by analyzing sender behavior, content patterns, and evolving phishing tactics—helping users maintain a cleaner, more secure inbox.
- Facial Recognition: While predictive analytics could suggest trends in biometric security, ML actively improves facial recognition accuracy by learning from thousands of facial data points, enhancing security for device unlocking, airport checks, and even social media tagging.
The Bigger Picture: Complementary, Not Competing
While predictive analytics focuses on structured, data-driven forecasts, AI—especially through machine learning—adds adaptability and automation, allowing businesses to move beyond static predictions toward intelligent, self-improving systems. By combining both, industries can leverage data not only to anticipate the future but also to dynamically respond to it, making smarter decisions in real time.
Enhance Supply Chain Efficiency with Predictive Analytics and AI
The convergence of predictive analytics and AI holds the key to improving supply chain forecast accuracy, especially in the wake of the pandemic. Real-time data access is critical for every resource in today’s dynamic environment.
Consider the example of the plastic supply chain, which can be disrupted by shortages of essential raw materials due to unforeseen events like natural disasters or shipping delays. AI systems can proactively identify potential disruptions, enabling more informed decision-making.
AI is poised to become a $309 billion industry by 2026, and 44% of executives have reported reduced operational costs through AI implementation. Let’s delve deeper into how AI can enhance predictive analytics within the supply chain:
Also explore the role of data normalization in predictive modelling
1. Inventory Management:
Even prior to the pandemic, inventory mismanagement led to significant financial losses due to overstocking and understocking. The lack of real-time inventory visibility exacerbated these issues. When you combine real-time data with AI, you move beyond basic reordering.
Technologies like Internet of Things (IoT) devices in warehouses offer real-time alerts for low inventory levels, allowing for proactive restocking. Over time, AI-driven solutions can analyze data and recognize patterns, facilitating more efficient inventory planning.
To kickstart this process, a robust data collection strategy is essential. From basic barcode scanning to advanced warehouse automation technologies, capturing comprehensive data points is vital. When every barcode scan and related data is fed into an AI-powered analytics engine, you gain insights into inventory movement patterns, sales trends, and workforce optimization possibilities.
2. Delivery Optimization:
Predictive analytics has been employed to optimize trucking routes and ensure timely deliveries. However, unexpected events such as accidents, traffic congestion, or severe weather can disrupt supply chain operations. This is where analytics and AI shine.
By analyzing these unforeseen events, AI can provide insights for future preparedness and decision-making. Route optimization software, integrated with AI, enables real-time rerouting based on historical data. AI algorithms can predict optimal delivery times, potential delays, and other transportation factors.
IoT devices on trucks collect real-time sensor data, allowing for further optimization. They can detect cargo shifts, load imbalances, and abrupt stops, offering valuable insights to enhance operational efficiency.
Turning Data into Actionable Insights
The pandemic underscored the potency of predictive analytics combined with AI. Data collection is a cornerstone of supply chain management, but its true value lies in transforming it into predictive, actionable insights. To embark on this journey, a well-thought-out plan and organizational buy-in are essential for capturing data points and deploying the appropriate technology to fully leverage predictive analytics with AI.
Wrapping Up
AI and Predictive Analytics are transforming engineering with precision, efficiency, and smarter decision-making.
Engineers no longer need extensive data science training to excel in their roles. These technologies give them the tools to navigate product design and decision-making with confidence.
As the future unfolds, the possibilities for engineers are limitless. AI and Predictive Analytics are paving the way for innovation like never before.