In the realm of machine learning, data is the cornerstone of effective model training and performance. However, acquiring high-quality, diverse, and privacy-compliant datasets can be a daunting task. That’s where synthetic data in machine learning comes into play.
Synthetic data is generated artificially rather than sourced from real-world environments, providing a powerful solution to challenges like data scarcity, privacy concerns, and bias in machine learning models.
From boosting AI model performance to ensuring compliance with data regulations, synthetic data offers a multitude of applications across various industries. In this article, we delve into seven compelling reasons why synthetic data is indispensable and how it can propel innovation in machine learning.
To train machine learning models, you need data. However, collecting and labeling real-world data can be costly, time-consuming, and inaccurate. Synthetic data offers a solution to these challenges.
- Scalability: Easily generate synthetic data for large-scale projects.
- Accuracy: Synthetic data can match real data quality.
- Privacy: No need to collect personal information.
- Safety: Generate safe data for accident prevention.
Why do you need Synthetic Data in Machine Learning?
In the realm of machine learning, the foundation of successful models lies in high-quality, diverse, and well-balanced datasets. To achieve accuracy, models need data that mirrors real-world scenarios accurately. Some of the key features of synthetic data include:
- Realistic Yet Artificial: Synthetic data mirrors real-world data distributions while being artificially created, preserving statistical properties without posing privacy risks.
- Scalable and Customizable: Unlike real-world data, synthetic data can be generated in vast quantities and tailored to meet specific model requirements.
- Inherently Privacy-Compliant: As synthetic data doesn’t originate from real users, it naturally aligns with data protection laws like GDPR and CCPA.
- Wide Applicability Across Domains: Synthetic data is utilized in sectors like healthcare, finance, retail, and autonomous systems, making it a versatile tool across industries.
Learn how AI in healthcare has improved patient care
Synthetic data, which replicates the statistical properties of real data, serves as a crucial solution to address the challenges posed by data scarcity and imbalance. This article delves into the pivotal role that synthetic data plays in enhancing model performance, enabling data augmentation, and tackling issues arising from imbalanced datasets.
Improving model performance
Synthetic data serves as a powerful catalyst for improving machine learning models. It expands and enriches existing datasets by introducing artificial samples that closely mimic real-world data, making models more robust, diverse, and reliable.
How Synthetic Data Improves Machine Learning Models
-
Reduces Overfitting
Models trained on limited real-world data often struggle with overfitting. Synthetic data introduces additional variability, preventing models from memorizing patterns and improving generalization. -
Enhances Generalization
By generating synthetic samples with statistical patterns similar to real-world data, models learn to recognize underlying trends rather than just specific instances. This leads to better adaptability to new, unseen data. -
Improves Accuracy
With a more diverse training set, models gain exposure to edge cases and rare scenarios, leading to higher accuracy and better predictions across different conditions. -
Balances Imbalanced Datasets
Many real-world datasets suffer from class imbalances. Synthetic data helps by creating more samples for underrepresented classes, ensuring fairer and more balanced training. -
Enables Privacy-Preserving AI
In cases where real-world data is sensitive or regulated (e.g., healthcare or finance), synthetic data provides a privacy-friendly alternative, allowing AI development without compromising user confidentiality.
By leveraging synthetic data, machine learning models become more efficient, scalable, and capable of handling real-world complexities with greater precision.
Crack the large language models code and explore top technical terms in the LLM vicinity
Data Augmentation
Data augmentation is a widely used technique in machine learning that enhances training datasets by creating diverse variations of existing samples. This helps models gain a broader understanding of the data distribution and improves their ability to generalize.
How Synthetic Data Enhances Data Augmentation
-
Expands Training Data
Synthetic data introduces new, artificially generated samples that closely resemble real-world data, increasing dataset diversity without requiring additional real data collection. -
Improves Model Robustness
By generating varied versions of existing data, models learn to recognize patterns under different conditions, making them more adaptable to real-world variations. -
Enhances Image Classification Performance
In image classification, synthetic data can be used to create augmented images with:- Different lighting conditions
- Rotations and flips
- Scaling and distortions
- Color transformations
-
Reduces Overfitting
Augmenting data with synthetic variations prevents models from becoming too reliant on specific features, reducing overfitting and improving generalization. -
Supports Rare Scenario Training
Real-world datasets often lack rare or edge-case scenarios. Synthetic data helps fill these gaps, ensuring models are trained on a wider range of possibilities.
By integrating synthetic data into data augmentation, machine learning models become more resilient, adaptive, and capable of handling real-world complexities with greater precision.
Handling Imbalanced Datasets
Imbalanced datasets, where certain classes have significantly fewer samples than others, create challenges for machine learning models. Models trained on such datasets tend to favor the majority class, leading to biased predictions and poor performance on minority classes.
How Synthetic Data Helps Balance Datasets
-
Generates More Samples for Minority Classes
Synthetic data can be created specifically for underrepresented classes, increasing their presence in the dataset and ensuring the model gets sufficient exposure to all classes. -
Prevents Model Bias
When trained on imbalanced data, models often lean towards predicting the dominant class. Synthetic data helps balance the class distribution, ensuring fairer and more accurate predictions. -
Improves Model Generalization
By introducing diverse synthetic samples, models learn to identify patterns in both majority and minority classes, enhancing their ability to generalize across different data points. -
Enhances Classification Accuracy
With a more balanced dataset, models can make more precise predictions across all classes, leading to higher overall performance and improved decision-making. -
Supports Rare Event Detection
In fields like fraud detection, medical diagnosis, and fault prediction, minority class instances are often the most critical. Synthetic data helps create more training examples, enabling models to better detect rare events.
By leveraging synthetic data in machine learning models become more reliable, unbiased, and effective in handling real-world scenarios where class imbalances are common.
Benefits and Considerations
Leveraging synthetic data in machine learning presents a multitude of benefits. It reduces reliance on scarce or sensitive real data, enabling researchers and practitioners to work with more extensive and diverse datasets. This, in turn, leads to improved model performance, shorter development cycles, and reduced data collection costs.
Furthermore, synthetic data can simulate rare or extreme events, allowing models to learn and respond effectively in challenging scenarios.
However, it is imperative to consider the limitations and potential pitfalls associated with the use of synthetic data. The synthetic data generated must faithfully replicate the statistical characteristics of real data to ensure models generalize effectively.
Rigorous evaluation metrics and techniques should be employed to assess the quality and utility of synthetic datasets. Ethical concerns, including privacy preservation and the inadvertent introduction of biases, demand meticulous attention when both generating and utilizing synthetic data.
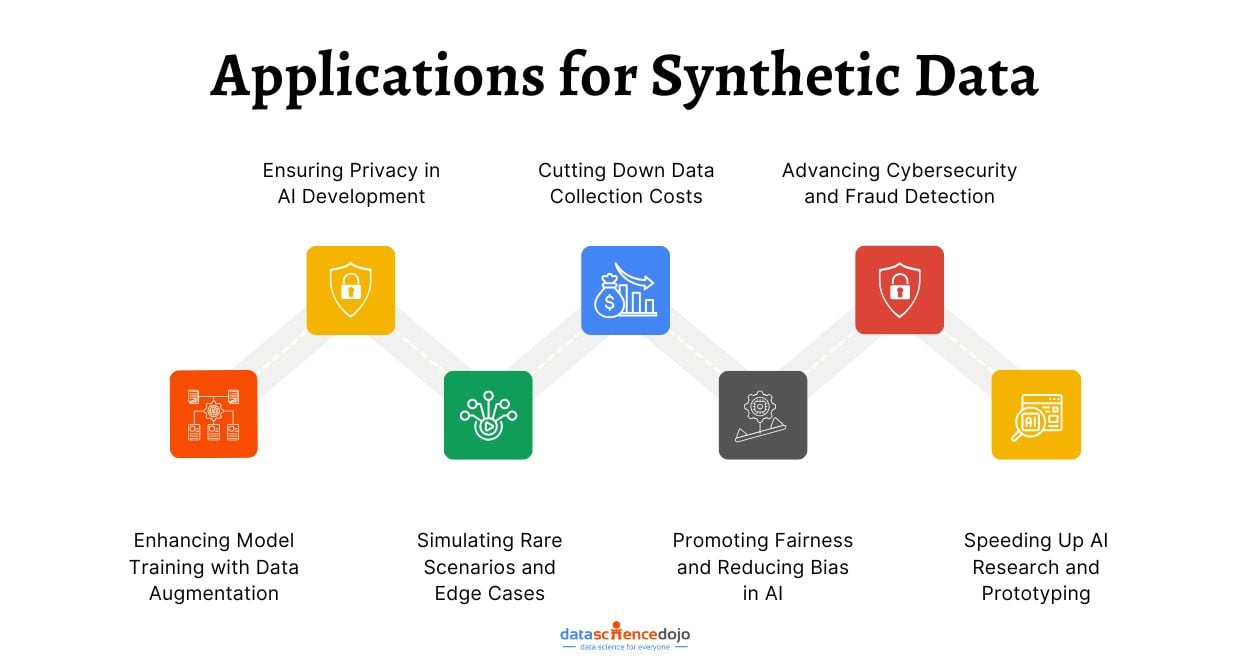
Applications of Synthetic Data
Following indicates key applications of synthetic data:
- Enhancing Model Training with Data Augmentation: Machine learning models thrive on diverse datasets to perform well. Synthetic data helps by expanding dataset size, reducing the risk of overfitting, and enhancing model accuracy.
- Ensuring Privacy in AI Development: Real-world data often includes sensitive information. Synthetic data mitigates privacy risks by substituting real data with artificial yet statistically similar versions, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- Simulating Rare Scenarios and Edge Cases: Gathering real-world data on rare events, such as medical anomalies or autonomous driving challenges, is tough. Synthetic data allows AI models to learn from simulated scenarios, boosting their robustness in real-world situations.
- Cutting Down Data Collection Costs: Obtaining high-quality labeled datasets is both costly and time-consuming. Synthetic data offers a cost-effective alternative, minimizing the need for extensive manual data collection and annotation.
- Promoting Fairness and Reducing Bias in AI: Real-world datasets can be biased, resulting in unfair AI outcomes. Synthetic data helps balance datasets by producing diverse samples, thus enhancing fairness in machine learning models.
- Advancing Cybersecurity and Fraud Detection: Synthetic datasets can train AI models to detect fraud and cybersecurity threats without risking exposure of actual confidential data, ensuring safer and privacy-compliant security training.
- Speeding Up AI Research and Prototyping: Rapid experimentation is key in AI model development. Synthetic data accelerates research by supplying on-demand datasets, enabling quicker testing and validation of models.
In conclusion, synthetic data in machine learning emerges as a potent tool, addressing the challenges posed by data scarcity, diversity, and class imbalance. It unlocks the potential for heightened accuracy, robustness, and generalization in machine learning models.
Nevertheless, a meticulous evaluation process, rigorous validation, and an unwavering commitment to ethical considerations are indispensable to ensure the responsible and effective use of synthetic data in real-world applications.
Final Thoughts
Synthetic data in machine learning enhances models by addressing data scarcity, diversity, and class imbalance. It unlocks potential accuracy, robustness, and generalization. However, rigorous evaluation, validation, and ethical considerations are essential for responsible real-world use.
Whether it’s for training resilient AI models, cutting costs, or bolstering security, synthetic data is a revolutionary tool. As AI continues to advance, leveraging synthetic data will be pivotal in driving innovation and ensuring the ethical development of AI systems.