Sentiment analysis, a dynamic process, extracts opinions, emotions, and attitudes from text. Its versatility spans numerous realms, but one shining application is marketing.
Here, sentiment analysis or text sentiment evaluation becomes the compass guiding marketing campaigns. By deciphering customer responses, it measures campaign effectiveness.
The insights gleaned from this process become invaluable ammunition for campaign enhancement, enabling precise targeting and ultimately yielding superior results.
In this digital age, where every word matters, text sentiment evaluation stands as a cornerstone in understanding and harnessing the power of language for strategic marketing success. It’s the art of turning words into results, and it’s transforming the marketing landscape.
Under the lens: How does sentiment analysis work?
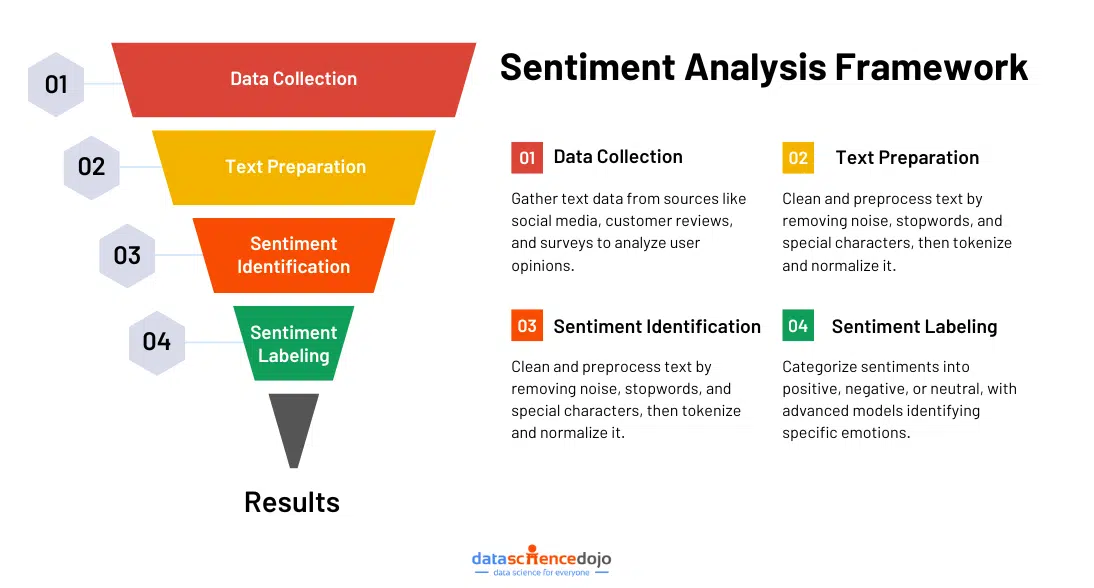
Sentiment analysis operates by breaking down text into smaller components, identifying their sentiment, and then aggregating these sentiments to determine the overall tone of the text. This process involves multiple techniques, each contributing to a more accurate interpretation of emotions and opinions.
1. Identifying Sentiment in Words or Phrases
The first step is analyzing individual words or phrases to determine their emotional tone. This can be done using different methods:
- Lexicon-Based Analysis – This method relies on predefined dictionaries of words labeled with sentiment values (e.g., “happy” = positive, “terrible” = negative).
- Machine Learning Models – AI models trained on large datasets learn to recognize patterns in sentiment based on past examples.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) – NLP techniques help analyze sentence structure, context, and even nuances like sarcasm or negation (e.g., “not bad” should be positive, not negative).
2. Aggregating Sentiments to Determine Overall Tone
Once individual words or phrases are classified, their sentiments are combined to evaluate the overall emotion of the text. This can be done using:
- Sentiment Scoring – Assigning numerical values to words (e.g., -1 for negative, 0 for neutral, +1 for positive) and calculating an overall sentiment score.
- Sentiment Classification – Categorizing the entire text into broad sentiment labels like positive, negative, or neutral, sometimes with additional granularity (e.g., very positive, slightly negative).
More advanced sentiment analysis also considers sentence structure, context, and intensity to refine accuracy. For example, the phrase “I love the product, but the delivery was awful” contains both positive and negative sentiments, requiring aspect-based sentiment analysis to evaluate different components separately.
In the next section, we’ll explore the different types of sentiment analysis in more detail, examining how each method helps refine sentiment detection and provide deeper insights.
Also explore: Text Mining
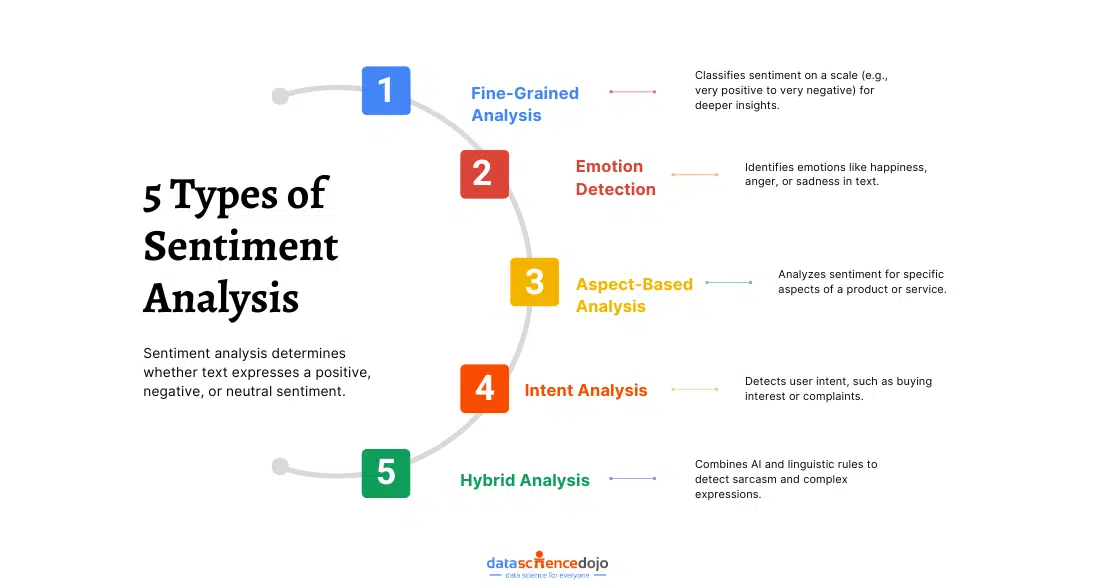
Types of Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis isn’t just about labeling something as positive or negative—it goes much deeper than that. Depending on the context and the level of detail needed, there are different types of mood analysis that help businesses, researchers, and organizations understand emotions, opinions, and even user intent.
Let’s break them down one by one.
1. Fine-Grained Sentiment Analysis
Sometimes, just knowing whether feedback is positive or negative isn’t enough. Fine-grained sentiment analysis takes a more detailed approach by classifying sentiments on a scale.
For example, if you’re analyzing product reviews, you might want to differentiate between:
- Very Positive – “I absolutely love this product! Best purchase ever!”
- Positive – “This product is good, does what it says.”
- Neutral – “It’s okay, nothing special.”
- Negative – “Didn’t meet my expectations.”
- Very Negative – “Terrible! Would never buy again!”
This method is especially useful in surveys, online reviews, and social media monitoring, where understanding the degree of satisfaction or dissatisfaction can be crucial.
2. Emotion Detection Sentiment Analysis
Basic sentiment analysis tells you if a statement is positive or negative, but emotion detection takes it a step further by identifying which emotion is being expressed. This can include:
- Happiness – “This news made my day!”
- Anger – “I’m so frustrated with this service!”
- Sadness – “This was a huge disappointment.”
- Fear – “I’m really worried about this change.”
- Surprise – “Wow, I didn’t see that coming!”
This type of sentiment analysis is often used in customer support to identify frustrated users or in marketing to gauge emotional reactions to products and campaigns. AI models use emotional dictionaries and machine learning to classify emotions based on word choices and sentence structures.
Also learn about Exploratory Data Analysis in R
3. Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA)
Not all opinions are straightforward. Sometimes, people feel positive about one aspect of a product or service but negative about another.
For example, if someone writes a review about a hotel saying:
“The rooms were spacious and clean, but the service was extremely slow.”
Regular sentiment analysis might label this as neutral since it has both positive and negative aspects. But aspect-based sentiment analysis breaks it down further:
- Rooms – Positive sentiment
- Service – Negative sentiment
This method is particularly useful for businesses that need to pinpoint what exactly customers like or dislike. It helps in making targeted improvements rather than general assumptions about customer feedback.
4. Intent-Based Sentiment Analysis
Not all text is just expressing emotion—sometimes, people are hinting at their intentions. Intent-based sentiment analysis helps determine whether a user is expressing:
- A need for action – “I need a new laptop. Any recommendations?” (Buying Intent)
- A complaint – “My internet keeps disconnecting. So frustrating!” (Frustration, needs resolution)
- A suggestion – “It would be great if this app had a dark mode.” (Feature Request)
This is widely used in customer service, marketing, and sales. If a business can detect buying intent in social media or online forums, they can engage with potential customers at the right moment. Similarly, recognizing frustration can help companies respond to complaints quickly and improve customer satisfaction.
5. Hybrid Sentiment Analysis
AI is powerful, but sometimes, it struggles with nuances like sarcasm, slang, or double meanings. That’s where hybrid sentiment analysis comes in—it combines:
- Machine learning models – To detect patterns and sentiment from vast amounts of data
- Linguistic rules – Predefined rules for detecting sarcasm, slang, or complex expressions
For example, if someone says:
“Oh great, another software update that makes everything slower.”
A basic sentiment model might label this as positive because of the word great, but a hybrid system would recognize the sarcasm and classify it as negative.
This method is widely used in industries where high accuracy is required, such as healthcare, finance, and social media monitoring.
A detailed guide on essential types of data analysis
Sentiment Analysis and Marketing Campaigns
In the ever-evolving landscape of marketing, understanding how your audience perceives your campaigns is essential for success. Sentiment analysis, a powerful tool in the realm of data analytics, enables you to gauge public sentiment surrounding your brand and marketing efforts.
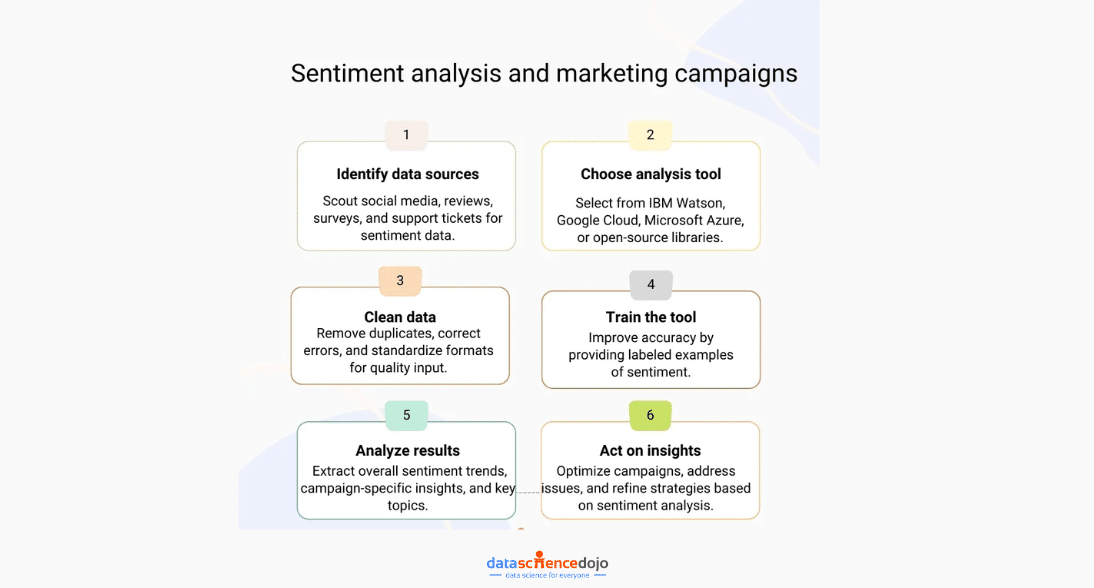
Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to effectively use sentiment analysis to track the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns:
1.Identify Your Data Sources
Begin by identifying the sources from which you’ll gather data for sentiment analysis. These sources may include:
- Social Media: Monitor platforms like Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, and LinkedIn for mentions, comments, and shares related to your campaigns.
- Online Reviews: Scrutinize reviews on websites such as Yelp, Amazon, or specialized industry review sites.
- Customer Surveys: Conduct surveys to directly gather feedback from your audience.
- Customer Support Tickets: Review tickets submitted by customers to gauge their sentiments about your products or services.
2.Choose a Sentiment Analysis Tool or Service
Selecting the right sentiment analysis tool is crucial. There are various options available, each with its own set of features. Consider factors like accuracy, scalability, and integration capabilities. Some popular tools and services include:
- IBM Watson Natural Language Understanding
- Google Cloud Natural Language API
- Microsoft Azure Text Analytics
- Open-source libraries like NLTK and spaCy
Read more –> LLM Use-Cases: Top 10 industries that can benefit from using large language models
3.Clean and Prepare Your Data
Before feeding data into your chosen tool, ensure it’s clean and well-prepared. This involves:
- Removing irrelevant or duplicate data to avoid skewing results.
- Correcting errors such as misspelled words or incomplete sentences.
- Standardizing text formats for consistency.
4.Train the Sentiment Analysis Tool
To improve accuracy, train your chosen sentiment analysis tool on your specific data. This involves providing labeled examples of text as either positive, negative, or neutral sentiment. The tool will learn from these examples and become better at identifying sentiment in your context.
5.Analyze the Results
Once your tool is trained, it’s time to analyze the sentiment of the data you’ve collected. The results can provide valuable insights, including:
- Overall Sentiment Trends: Determine whether the sentiment is predominantly positive, negative, or neutral.
- Campaign-Specific Insights: Break down sentiment by individual marketing campaigns to see which ones resonate most with your audience.
- Identify Key Topics: Discover what aspects of your products, services, or campaigns are driving sentiment.
6. Act on Insights
The true value of sentiment analysis lies in its ability to guide your marketing strategies. Use the insights gained to:
- Adjust campaign messaging to align with positive sentiment trends.
- Address issues highlighted by negative sentiment.
- Identify opportunities for improvement based on neutral sentiment feedback.
- Continuously refine your marketing campaigns to better meet customer expectations.
Learn how programming languages assist data analysts
Benefits Of Using Sentiment Analysis To Track Campaigns
There are many benefits to using sentiment analysis to track marketing campaigns. Here are a few of the most important benefits:
- Improved decision-making: Sentiment analysis can help marketers make better decisions about their marketing campaigns. By understanding how customers are responding to their campaigns, marketers can make more informed decisions about how to allocate their resources.
- Increased ROI: Mood analysis can help marketers increase the ROI of their marketing campaigns. By targeting campaigns more effectively and optimizing ad campaigns, marketers can get better results from their marketing spend.
- Improved customer experience: Sentiment analysis can help marketers improve the customer experience. By identifying areas where customer satisfaction can be improved, marketers can make changes to their products, services, and marketing campaigns to create a better experience for their customers.
Real-Life Scenarios: LLM & Sentiment Analysis
LLMs have several advantages over traditional sentiment analysis methods. They are more accurate, can handle more complex language, and can be trained on a wider variety of data. This makes them well-suited for use in marketing, where the goal is to understand the nuances of customer sentiment.
One example of how LLMs are being used in marketing is by Twitter. Twitter uses LLMs to analyze tweets about its platform and its users. This information is then used to improve the platform’s features and to target ads more effectively.
Another example is Netflix. Netflix uses LLMs to analyze customer reviews of its movies and TV shows. This information is then used to recommend new content to customers and to improve the overall user experience.
Recap:
Mood analysis is a powerful tool that can be used to track the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. By understanding how customers are responding to their campaigns, marketers can make better decisions, increase ROI, and improve the customer experience.
If you are looking to improve the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns, I encourage you to consider using sentiment /mood analysis. It is a powerful tool that can help you get better results from your marketing efforts.
Sentiment analysis is the process of identifying and extracting subjective information from text, such as opinions, appraisals, emotions, or attitudes. It is a powerful tool that can be used in a variety of applications, including marketing.
In marketing, mood analysis can be used to:
- Understand customer sentiment towards a product, service, or brand.
- Identify opportunities to improve customer satisfaction.
- Monitor social media for mentions of a brand or product.
- Target marketing campaigns more effectively.
In a Nutshell
In conclusion, sentiment analysis, coupled with the power of Large Language Models, is a dynamic duo that can elevate your marketing strategies to new heights. By understanding and acting upon customer sentiments, you can refine your campaigns, boost ROI, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Embrace this technological synergy to stay ahead in the ever-evolving world of marketing.