This blog discusses the different nlp techniques and tasks. We will be using python code to demo what and how each task works. We will also discuss why these tasks and techniques are essential for natural language processing.
Introduction
According to a survey, only 32 percent of the business data is put to work, and 68 percent goes unleveraged. Most data are often unstructured. According to estimations, 80 to 90 percent of business data is unstructured, and so are emails, reports, social media posts, websites, and documents.
Using NLP techniques, it became possible for machines to manage and analyze unstructured data accurately and quickly.
Computers can now understand, manipulate, and interpret human language. Businesses use NLP to improve customer experience, listen to customer feedback, and find market gaps. Almost 50% of companies today use NLP applications, and 25% plan to do so in 12 months.
The future of customer care is NLP. Customers prefer mobile messaging and chatbots over the legacy voice channel. It is four times more accurate. According to the IBM market survey, 52% of global IT professionals reported using or planning to use NLP to improve customer experience.
Chatbots can resolve 80% of routine tasks and customer questions with a 90% success rate by 2022. Estimates show that using NLP in chatbots will save companies USD 8 billion annually.
The NLP market was at 3 billion US dollars in 2017 and is predicted to rise to 43 billion US dollars in 2025, around 14 times higher.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing is a branch of artificial intelligence that enables computers to analyze, understand, and drive meaning from a human language using machine learning and respond to it. NLP combines computational linguistics with artificial intelligence and machine learning to create an intelligent system capable of understanding and responding to text or voice data the same way humans do.
NLP analyzes the syntax and semantics of the text to understand the meaning and structure of human language. Then it transforms this linguistic knowledge into a machine-learning algorithm to solve real-world problems and perform specific tasks.
Read more about NLP Applications
Natural language is challenging to comprehend, which makes NLP a challenging task. Mastering a language is easy for humans, but implementing NLP becomes difficult for machines because of the ambiguity and imprecision of natural language.
NLP requires syntactic and semantic analysis to convert human language into a machine-readable form that can be processed and interpreted.
Syntactic Analysis
Syntactic analysis is the process of analyzing language with its formal grammatical rules. It is also known as syntax analysis or parsing formal grammatical rules applied to a group of words but not a single word.
After verifying the correct syntax, it takes text data as input and creates a structural input representation. It creates a parse tree. A syntactically correct sentence does not necessarily make sense. It needs to be semantically correct to make sense.
Explore how transformer models are shaping the future of NLP
Semantic Analysis
Semantic analysis is the process of figuring out the meaning of the text. It enables computers to interpret the words by analyzing sentence structure and the relationship between individual words of the sentence.
Because of language’s ambiguous and polysemic nature, semantic analysis is a particularly challenging area of NLP. It analyzes the sentence structure, word interaction, and other aspects to discover the meaning and topic of the text.
NLP Techniques and Tasks
Before proceeding further, ensure you run the below code block to install all the dependencies.
!pip install -U spacy !python -m spacy download en !pip install nltk !pip install prettytable
Here are some everyday tasks performed in syntactic and semantic analysis:
Tokenization
Tokenization is a common task in NLP. It separates natural language text into smaller units called tokens. For example, in Sentence tokenization paragraph separates into sentences, and word tokenization splits the words of a sentence.
The code below shows an example of word tokenization using spaCy.
Code:
import spacy nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm") doc = nlp("Data Science Dojo is the leading platform providing data science training.") for token in doc: print(token.text)
Output:
Data Science Dojo is the leading platform providing data science training .
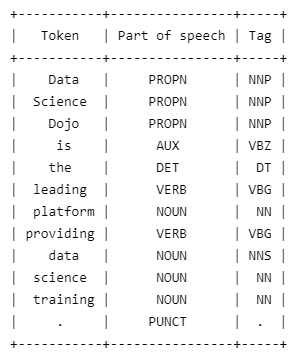
Part-of-Speech Tagging
Part of speech or grammatical tagging labels each word as an appropriate part of speech based on its definition and context. POS tagging helps create a parse tree that helps understand word relationships. It also helps in Named Entity Recognition, as most named entities are nouns, making it easier to identify them.
In the code below, we use pos_ attribute of the token to get the part of speech for the universal pos tag set.
Code:
import spacy from prettytable import PrettyTable table = PrettyTable(['Token', 'Part of speech', 'Tag']) nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm") doc = nlp("Data Science Dojo is the leading platform providing data science training.") for token in doc: table.add_row([token.text, token.pos_, token.tag_]) print(table)
Output:
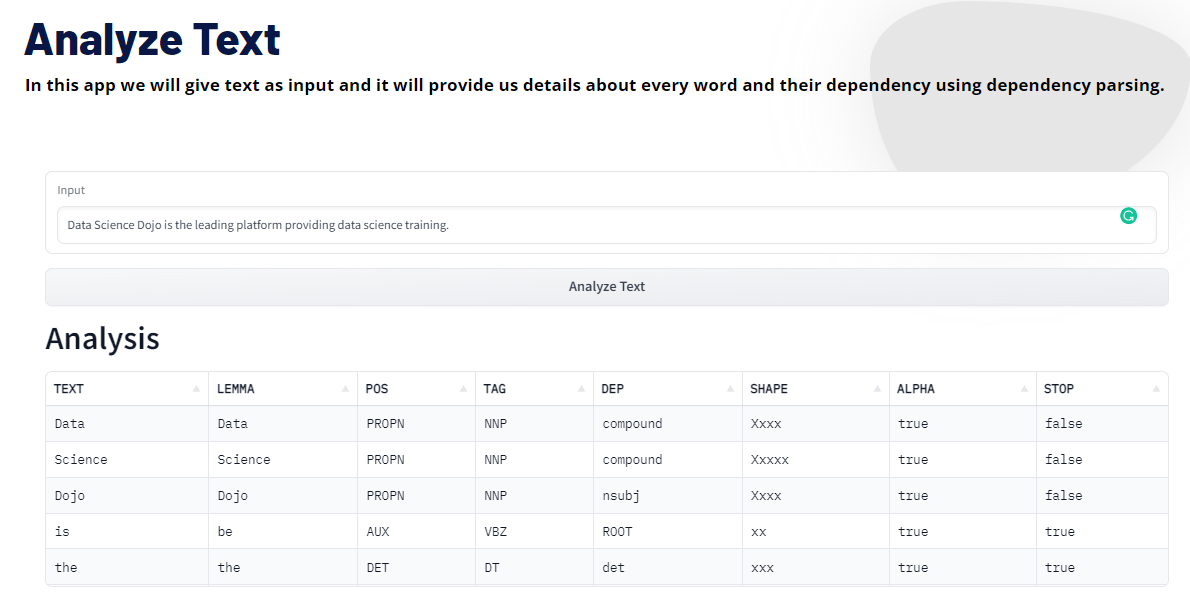
Demo
Try it yourself with this Analyze Text Demo.
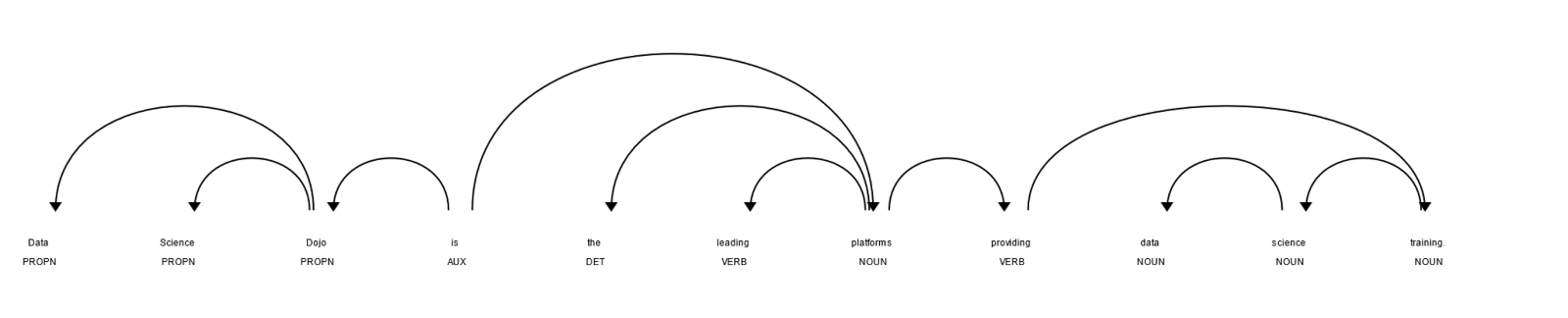
Dependency and Consistency Parsing
Dependency parsing is how grammatical structure in a sentence is analyzed to find out the related word and their relationship. Each relationship has one head and one dependent. Then, a label based on the nature of dependency is assigned between the head and the dependent.
Consistency parsing is a process by which phrase structure grammar is identified to visualize the entire syntactic structure.
In the code below, we created a dependency tree using the displacy visualizer of spacy.
Code:
import spacy nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm") doc = nlp("Data Science Dojo is the leading platform providing data science training.") spacy.displacy.render(doc, style="dep")
Output:
Demo
Try it yourself with this Analyze Text Demo.
Lemmatization and Stemming
We use inflected forms of the word when we speak or write. These inflected forms are created by adding prefixes or suffixes to the root form. In the process of lemmatization and stemming, we are grouping similar inflected forms of a word into a single root word.
In this way, we link all the words with the same meaning as a single word, which is simpler to analyze by the computer.
The word’s root form in lemmatization is lemma, and in stemming is a stem. Lemmatization and stemming do the same task of grouping inflected forms, but they are different. Lemmatization considers the word and its context in the sentence while stemming only considers the single word.
So, we consider POS tags in lemmatization but not in stemming. That is why lemma is an actual dictionary word, but stem might not be.
Now we are applying lemmatization using spacy.
Code:
import spacy nlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm', disable=['parser', 'ner']) doc = nlp("Data Science Dojo is the leading platform providing data science training.") lemmatized = [token.lemma_ for token in doc] print("Original: \n", doc) print("\nAfter Lemmatization: \n", " ".join(lemmatized))
Output:
Original: Data Science Dojo is the leading platform providing data science training. After Lemmatization: Data Science Dojo is the lead platform to provide datum science training.
Unfortunately, spacy does not contain any function for stemming.
Let us use Porter Stemmer from nltk to see how stemming works.
Code:
import nltk nltk.download('punkt') from nltk.stem import PorterStemmer from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize ps = PorterStemmer() sentence = "Data Science Dojo is the leading platform providing data science training." words = word_tokenize(sentence) stemmed = [ps.stem(token) for token in words] print("Original: \n", " ".join(words)) print("\nAfter Stemming: \n", " ".join(stemmed))
Output:
Original: Data Science Dojo is the leading platform providing data science training . After Stemming: data scienc dojo is the lead platform provid data scienc train .
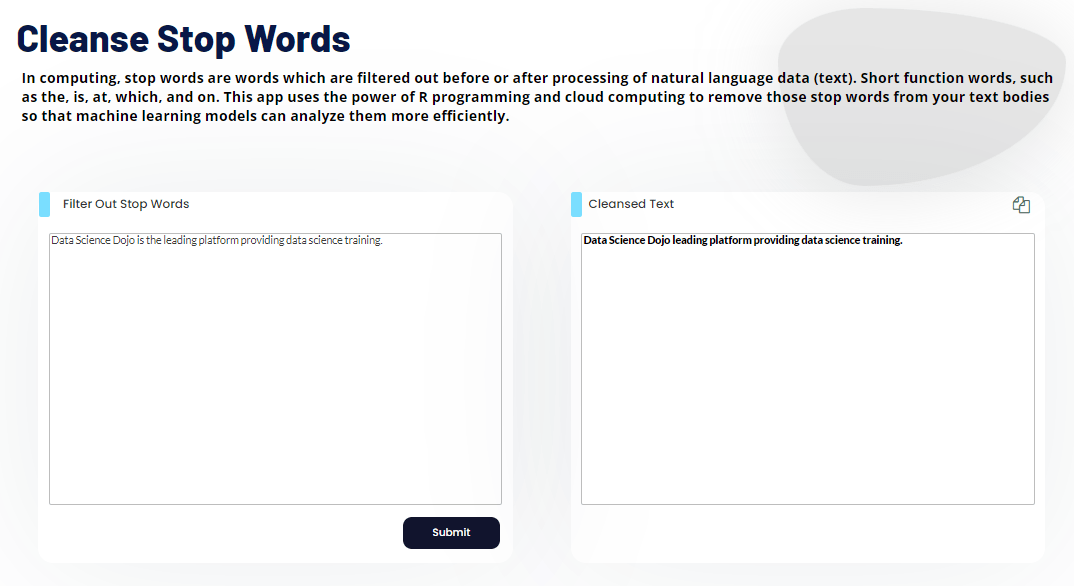
Stop Word Removal
Stop words are the frequent words that are used in any natural language. However, they are not particularly useful for text analysis and NLP tasks. Therefore, we remove them, as they do not play any role in defining the meaning of the text.
Code:
import spacy nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm") doc = nlp("Data Science Dojo is the leading platform providing data science training.") token_list = [ token.text for token in doc ] filtered_sentence = [ word for word in token_list if nlp.vocab[word].is_stop == False ] print("Tokens:\n",token_list) print("\nAfter stop word removal:\n", filtered_sentence)
Output:
Tokens: ['Data', 'Science', 'Dojo', 'is', 'the', 'leading', 'platform', 'providing', 'data', 'science', 'training', '.'] After stop word removal: ['Data', 'Science', 'Dojo', 'leading', 'platform', 'providing', 'data', 'science', 'training', '.']
Demo
Try it yourself with this Cleanse Stop Words Demo.
Named Entity Recognition
Named entity recognition is an NLP technique that extracts named entities from the text and categorizes them into semantic types like organization, people, quantity, percentage, location, time, etc. Identifying named entities helps identify the critical element in the text, which can help sort the unstructured data and find valuable information.
Code:
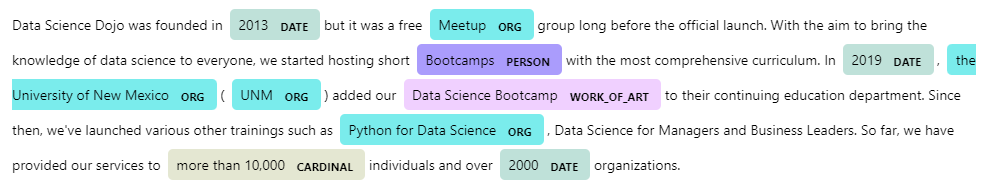
import spacy from prettytable import PrettyTable nlp = spacy.load("en_core_web_sm") doc = nlp("Data Science Dojo was founded in 2013 but it was a free Meetup group long before the official launch. With the aim to bring the knowledge of data science to everyone, we started hosting short Bootcamps with the most comprehensive curriculum. In 2019, the University of New Mexico (UNM) added our Data Science Bootcamp to their continuing education department. Since then, we've launched various other trainings such as Python for Data Science, Data Science for Managers and Business Leaders. So far, we have provided our services to more than 10,000 individuals and over 2000 organizations.") table = PrettyTable(["Entity", "Start Position", "End Position", "Label"]) for ent in doc.ents: table.add_row([ent.text, ent.start_char, ent.end_char, ent.label_]) print(table) spacy.displacy.render(doc, style="ent")
Output:
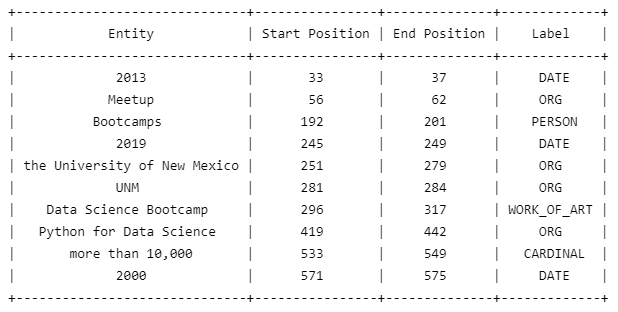
Visualization
Demo
Try it yourself with this Text Entity Extractor Demo.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis, also referred to as opinion mining, uses natural language processing to find and extract sentiments from the text. It determines whether the data is positive, negative, or neutral.
Some of the real-world applications of sentiment analysis are:
- Customer support
- Customer feedback
- Brand monitoring
- Product analysis
- Market research
Demo
Try it yourself with this Opinion Mining Demo.
Conclusion
We have discussed natural language processing and what common tasks it performs in natural language processing. Then, we saw how we can perform different functions in spacy and nltk and why they are essential in natural language processing.
We know about the different tasks and techniques we perform in natural language processing, but we have yet to discuss the applications of natural language processing. For that, you can follow this blog.
Upgrade your data science skillset with our Python for Data Science and Data Science Bootcamp training!