Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has completely transformed how we search and interact with large language models (LLMs), making information retrieval smarter and more dynamic. But here’s the catch—one key factor that can make or break your RAG system’s performance is chunk size.
Get it wrong, and you might end up with incomplete answers or sluggish retrieval. Get it right, and your system runs like a well-oiled machine, delivering fast, accurate, and contextually rich responses.
So, how do you find that sweet spot for chunk size? That’s where LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation tool comes in. In this article, we’ll walk you through how to leverage this powerful tool to fine-tune your RAG application and optimize chunk size for seamless, efficient retrieval. Let’s dive in!
Why Chunk Size Matters in the RAG Application System?
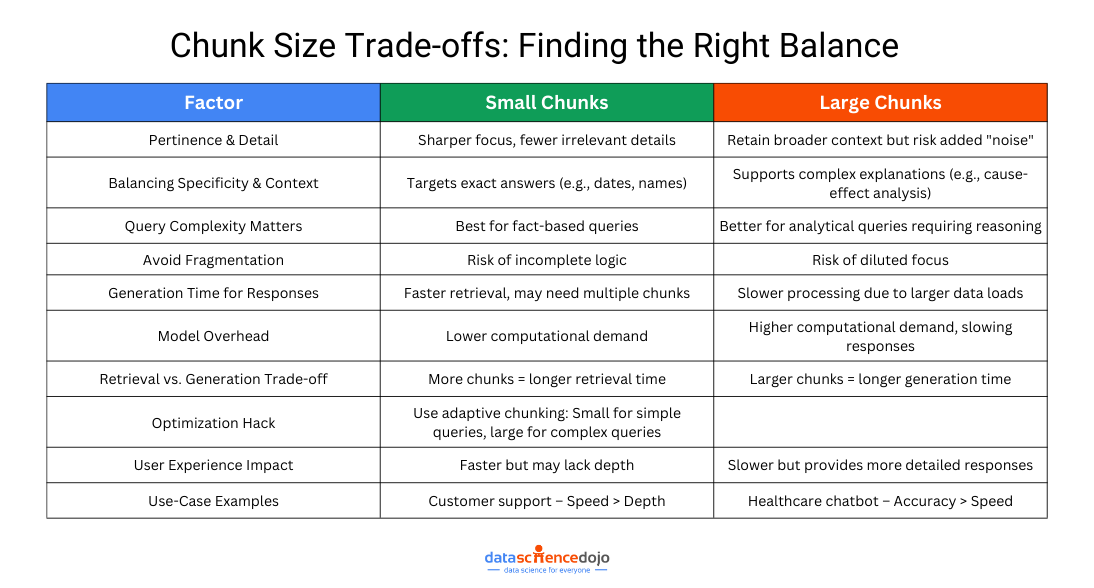
When retrieving information, precision is everything. If your chunks are too small, key details might get lost. If they’re too large, the model might struggle to pinpoint the most relevant information quickly. This delicate balance directly affects how well your RAG system understands and responds to queries.
In this section, we’ll explore how chunk size affects pertinence and detail and response speed, helping you strike the perfect balance for seamless performance.
Pertinence and Detail
When retrieving information, detail and relevance go hand in hand. If a chunk is too small, it captures fine details but risks leaving out crucial context. If it’s too large, it ensures all necessary information is included but might overwhelm the model with unnecessary data.
Take a chunk size of 256 tokens—it creates more detailed, focused segments, but the downside is that important details might get split across multiple chunks, making retrieval less efficient.
On the other hand, a chunk size of 512 tokens keeps more context within each chunk, increasing the chances of retrieving all vital information at once. But if too much is packed into a single chunk, the model might struggle to pinpoint the most relevant parts.
To navigate this challenge, we look at two key factors:
- Faithfulness: Does the model stick to the original source, or does it introduce inaccuracies (hallucinations)? A well-balanced chunk size helps keep responses grounded in reliable data.
- Relevance: Is the retrieved information actually useful for answering the query? The right chunking ensures responses are clear, focused, and on-point.
Master LLM Evaluation Metrics and Real-Life Applications
By finding the ideal chunk size, you can create RAG applications that retrieves detailed yet relevant information—striking the perfect balance between accuracy and efficiency.
Generation Time for Responses
Chunk size doesn’t just determine what information gets retrieved—it also affects how quickly responses are generated. Larger chunks provide more context but require more processing power, potentially slowing down response time. Smaller chunks, on the other hand, allow for faster retrieval but may lack the full context needed for a high-quality answer.
Striking the right balance depends on your use case. If speed is the priority, such as in real-time applications, smaller chunks are the better choice. But if depth and accuracy matter more, slightly larger chunks help ensure completeness.
Ultimately, it’s all about optimization—finding the ideal chunk size that keeps responses fast, relevant, and contextually rich without unnecessary delays.
All About Application Evaluation
Evaluating a RAG system’s performance is just as important as fine-tuning its chunk size. However, traditional NLP evaluation methods—like BLEU or F1 scores—are becoming less reliable, as they don’t always align with human judgment. With the rapid advancements in LLMs, more sophisticated evaluation techniques are needed to ensure accuracy and relevance.
We’ve already touched on faithfulness and relevance earlier in this blog, but now it’s time to take a deeper dive into how these aspects can be effectively measured. Ensuring that a model retrieves accurate and relevant information is crucial for maintaining trust and usability, and that’s where dedicated evaluation mechanisms come into play.
Explore NLP Techniques and Tasks
- Faithfulness Evaluation – This goes beyond just checking if a response is based on the retrieved chunks. It specifically identifies whether the model introduces hallucinations—statements that seem plausible but aren’t actually supported by the source data. A faithful response should strictly adhere to the retrieved information without adding anything misleading.
- Relevance Evaluation – Even if a response is factually correct, it must also be useful and on-point. This evaluation ensures that the retrieved information directly answers the query, rather than providing vague or tangential details. A relevant response should closely align with what the user is asking for.
To put these evaluation methods into practice, we’ll configure GPT-3.5-turbo as our core evaluation tool. By leveraging its capabilities, we can systematically assess responses and refine our RAG system for both accuracy and efficiency.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
Defining the Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (GPT-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiates evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
Read this blog about the Orchestration Framework
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (LLM) with the model set to GPT-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (LLM) and the chunk size (chunk size).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (query engine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable total questions.
Learn 7 Best Large Language Models (LLMs)
Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
Testing Different Chunk Sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of the evaluator method.
After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Use LlamaIndex to Construct a RAG Application System
Selecting the right chunk size for a RAG system isn’t just a one-time decision—it’s an ongoing process of testing and refinement. While intuition can provide a starting point, real optimization comes from data-driven experimentation.
By leveraging LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can systematically test different chunk sizes, analyze their impact on response time, faithfulness, and relevance, and make well-informed decisions. This ensures that our system strikes the right balance between speed, accuracy, and contextual depth.
Revolutionize LLM with Llama 2 fine-tuning
At the end of the day, chunk size plays a pivotal role in a RAG system’s overall effectiveness. Taking the time to carefully evaluate and fine-tune it leads to a system that is not only faster and more reliable but also delivers more precise and contextually relevant responses.
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here
Optimizing RAG Efficiency with LlamaIndex: Finding the Perfect Chunk Size
The integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) has revolutionized the fusion of robust search capabilities with the LLM, amplifying the potential for dynamic information retrieval. Within the implementation of a RAG system, a pivotal factor governing its efficiency and performance lies in the determination of the optimal chunk size. How does one identify the most effective chunk size for seamless and efficient retrieval? This is precisely where the comprehensive assessment provided by the LlamaIndex Response Evaluation tool becomes invaluable. In this article, we will provide a comprehensive walkthrough, enabling you to discern the ideal chunk size through the powerful features of LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module.
Why chunk size matters
Selecting the appropriate chunk size is a crucial determination that holds sway over the effectiveness and precision of a RAG system in various ways:
- Pertinence and Detail: Opting for a smaller chunk size, such as 256, results in more detailed segments. However, this heightened detail brings the potential risk that pivotal information might not be included in the foremost retrieved segments. On the contrary, a chunk size of 512 is likely to encompass all vital information within the leading chunks, ensuring that responses to inquiries are readily accessible. To navigate this challenge, we will employ the Faithfulness and Relevancy metrics. These metrics gauge the absence of ‘hallucinations’ and the ‘relevancy’ of responses concerning the query and the contexts retrieved, respectively.
- Generation Time for Responses: With an increase in the chunk size, the volume of information directed into the LLM for generating a response also increases. While this can guarantee a more comprehensive context, it might potentially decelerate the system. Ensuring that the added depth doesn’t compromise the system’s responsiveness, is pivot.
Ultimately, finding the ideal chunk size boils down to achieving a delicate equilibrium. Capturing all crucial information while maintaining operational speed. It’s essential to conduct comprehensive testing with different sizes to discover a setup that aligns with the unique use case and dataset requirements.
Why evaluation?
The discussion surrounding evaluation in the field of NLP has been contentious, particularly with the advancements in NLP methodologies. Consequently, traditional evaluation techniques like BLEU or F1, once relied upon for assessing models, are now considered unreliable due to their limited correspondence with human evaluations. As a result, the landscape of evaluation practices continues to shift, emphasizing the need for cautious application.
In this blog, our focus will be on configuring the gpt-3.5-turbo model to serve as the central tool for evaluating the responses in our experiment. To facilitate this, we establish two key evaluators, Faithfulness Evaluator and Relevancy Evaluator, utilizing the service context. This approach aligns with the evolving standards of LLM evaluation, reflecting the need for more sophisticated and reliable evaluation mechanisms.
- Faithfulness Evaluator: This evaluator is instrumental in determining whether the response was artificially generated and checks if the response from a query engine corresponds with any source nodes.
- Relevancy Evaluator: This evaluator is crucial for gauging whether the query was effectively addressed by the response and examines whether the response, combined with source nodes, matches the query.
In order to determine the appropriate chunk size, we will calculate metrics such as average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevancy across different chunk sizes.
Setup
!pip install llama_index pypdf
import openai
import time
import pypdf
import pandas as pd
from llama_index.evaluation import (
RelevancyEvaluator,
FaithfulnessEvaluator,
)
from llama_index import (
SimpleDirectoryReader,
VectorStoreIndex,
ServiceContext
)
from llama_index.llms import OpenAI
OpenAI API Key
openai.api_key = ‘OPENAI_API_KEY’
Downloading Dataset
We will be using the IRS armed forces tax guide for this experiment.
- mkdir is used to make a folder. Here we are making a folder named dataset in the root directory.
- wget command is used for non-interactive downloading of files from the web. It allows users to retrieve content from web servers, supporting various protocols like HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP.
!mkdir -p ‘dataset’
!wget ‘https://www.irs.gov/pub/irs-pdf/p3.pdf’ -O ‘dataset/IRS.pdf’
Load Dataset
- SimpleDirectoryReader class will help us to load all the files in the dataset directory.
- document[0:10] represents that we will only be loading the first 10 pages of the file for the sake of simplicity.
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader(“./dataset/”).load_data()
# To evaluate for each chunk size,
# we will first generate a set of 10 questions from first 10 pages.
documents = documents[0:10]
Defining Question Bank
These questions will help us to evaluate metrics for different chunk sizes.
questionBank = [‘What is the purpose of Publication 3 by the Internal Revenue Service?’,
‘How can individuals access forms and information related to taxes faster and easier?’,
‘What are some examples of income items that are excluded from gross income for servicemembers?’,
‘What is the definition of a combat zone and how does it affect the taxation of servicemembers?’,
‘How are travel expenses of Armed Forces Reservists treated for tax purposes?’,
‘What are some adjustments to income that individuals can make on their tax returns?’,
‘How does the Combat Zone Exclusion impact the reporting of combat zone pay?’,
‘What are some credits available to taxpayers, specifically related to children and dependents?’,
‘How is the Earned Income Credit calculated and who is eligible for it?’,
‘What are the requirements for claiming tax forgiveness related to terrorist or military action?’]
Establishing Evaluators
This code initializes an OpenAI language model (gpt-3.5-turbo) with temperature=0 settings and instantiate evaluators for measuring faithfulness and relevancy, utilizing the ServiceContext module with default configurations.
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, model=“gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContextLLM = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm)
faithfulnessLLM = FaithfulnessEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
relevancyLLM = RelevancyEvaluator(service_context=serviceContextLLM)
Main Evaluator Method
We will be evaluating each chunk size based on 3 metrics.
- Average Response Time
- Average Faithfulness
- Average Relevancy
- The function evaluator takes two parameters, chunkSize and questionBank.
- It first initializes an OpenAI language model (llm) with the model set to gpt-3.5-turbo.
- Then, it creates a serviceContext using the ServiceContext.from_defaults method, specifying the language model (llm) and the chunk size (chunkSize).
- The function uses the VectorStoreIndex.from_documents method to create a vector index from a set of documents, with the service context specified.
- It builds a query engine (queryEngine) from the vector index.
- The total number of questions in the question bank is determined and stored in the variable totalQuestions.
- Next, the function initializes variables for tracking various metrics:
- totalResponseTime: Tracks the cumulative response time for all questions.
- totalFaithfulness: Tracks the cumulative faithfulness score for all questions.
- totalRelevancy: Tracks the cumulative relevancy score for all questions.
- It records the start time before querying the queryEngine for a response to the current question.
- It calculates the elapsed time for the query by subtracting the start time from the current time.
- The function evaluates the faithfulness of the response using faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the faithfulnessResult variable.
- Similarly, it evaluates the relevancy of the response using relevancyLLM.evaluate_response and stores the result in the relevancyResult variable.
- The function accumulates the elapsed time, faithfulness result, and relevancy result in their respective total variables.
- After evaluating all the questions, the function computes the averages
def evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank):
llm = OpenAI(model = “gpt-3.5-turbo”)
serviceContext = ServiceContext.from_defaults(llm = llm,
chunk_size = chunkSize)
vectorIndex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents,
service_context = serviceContext
)
# building query engine
queryEngine = vectorIndex.as_query_engine()
# Defining Total Questions
totalQuestions = len(questionBank)
totalResponseTime = 0
totalFaithfulness = 0
totalRelevancy = 0
# Traversing through the question bank
for question in questionBank:
startTime = time.time()
responseVector = queryEngine.query(question)
elapsedTime = time.time() – startTime
faithfulnessResult = faithfulnessLLM.evaluate_response(
response=responseVector
).passing
relevancyResult = relevancyLLM.evaluate_response(
query=question, response=responseVector
).passing
totalResponseTime += elapsedTime
totalFaithfulness += faithfulnessResult
totalRelevancy += relevancyResult
averageRelevancy = totalRelevancy / totalQuestions
averageFaithfulness = totalFaithfulness / totalQuestions
averageResponseTime = totalResponseTime / totalQuestions
return averageResponseTime, averageFaithfulness, averageRelevancy
Testing different chunk sizes
To find out the best chunk size for our data, we have defined a list of chunk sizes then we will traverse through the list of chunk sizes and find out the average response time, average faithfulness, and average relevance with the help of evaluator method. After this, we will convert our data list into a data frame with the help of Pandas DataFrame class to view it in a fine manner.
chunkSizes = [128, 256, 512, 1024]
data = []
for chunkSize in chunkSizes:
avgResponseTime, avgFaithfulness, avgRelevancy = evaluator(chunkSize, questionBank)
data.append({‘Chunk Size’: chunkSize, ‘Average Response Time’: avgResponseTime, ‘Average Faithfulness’: avgFaithfulness, ‘Average Relevancy’: avgRelevancy})
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.head()
Result
From the illustration, it is evident that the chunk size of 128 exhibits the highest average faithfulness and relevancy while maintaining the second-lowest average response time.
Conclusion
Identifying the best chunk size for a RAG system depends on a combination of intuition and empirical data. By utilizing LlamaIndex’s Response Evaluation module, we can experiment with different sizes and make well-informed decisions. When constructing a RAG system, it is crucial to remember that the chunk size plays a pivotal role. Therefore, it is essential to invest the necessary time to thoroughly evaluate and fine-tune the chunk size for optimal outcomes.
You can find the complete code here