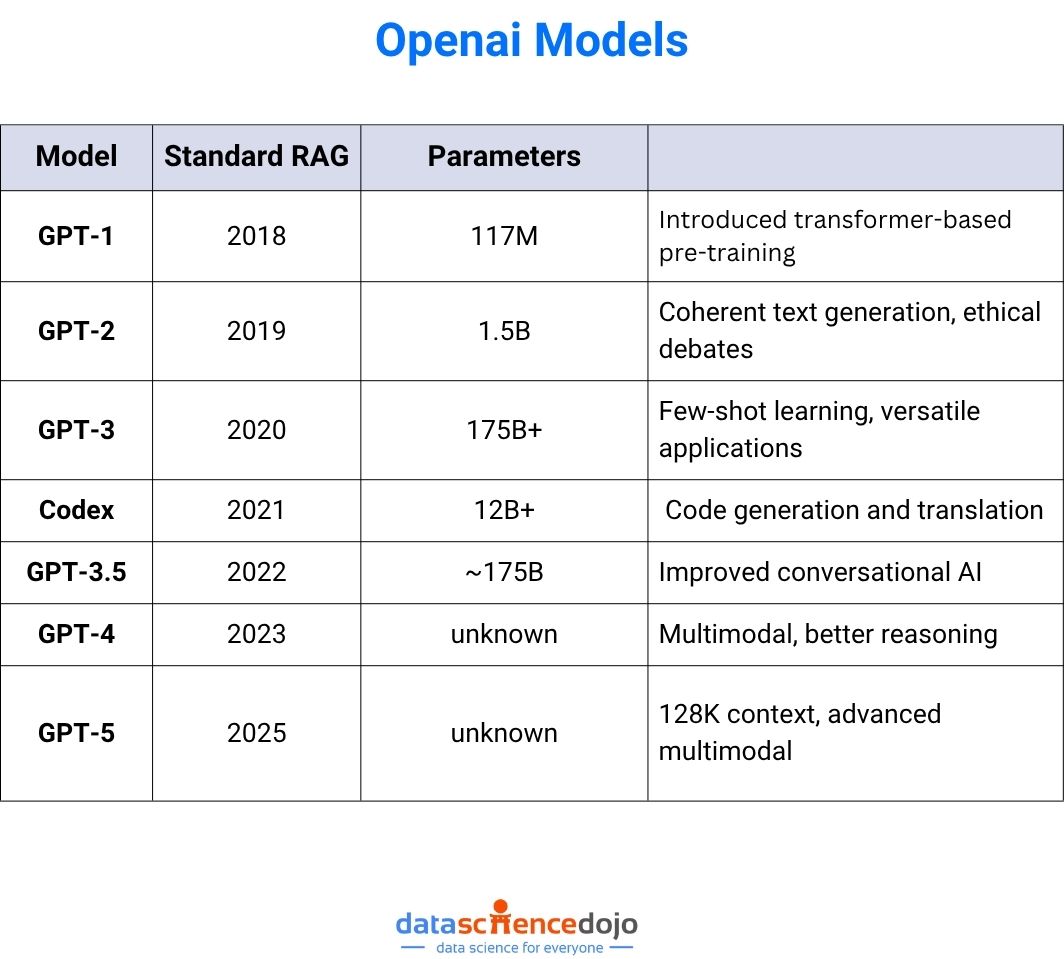
OpenAI models have transformed the landscape of artificial intelligence, redefining what’s possible in natural language processing, machine learning, and generative AI. From the early days of GPT-1 to the groundbreaking capabilities of GPT-5, each iteration has brought significant advancements in architecture, training data, and real-world applications.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the evolution of OpenAI models, highlighting the key changes, improvements, and technological breakthroughs at each stage. Whether you’re a data scientist, AI researcher, or tech enthusiast, understanding this progression will help you appreciate how far we’ve come and where we’re headed next.
GPT-1 (2018) – The Proof of Concept
The first in the series of OpenAI models, GPT-1, was based on the transformer models architecture introduced by Vaswani et al. in 2017. With 117 million parameters, GPT-1 was trained on the BooksCorpus dataset (over 7,000 unpublished books), making it a pioneer in large-scale unsupervised pre-training.
Technical Highlights:
- Architecture: 12-layer transformer decoder.
- Training Objective: Predict the next word in a sequence (causal language modeling).
- Impact: Demonstrated that pre-training on large text corpora followed by fine-tuning could outperform traditional machine learning models on NLP benchmarks.
While GPT-1’s capabilities were modest, it proved that scaling deep learning architectures could yield significant performance gains.
GPT-2 (2019) – Scaling Up and Raising Concerns
GPT-2 expanded the GPT architecture to 1.5 billion parameters, trained on the WebText dataset (8 million high-quality web pages). This leap in scale brought dramatic improvements in natural language processing tasks.
Key Advancements:
- Longer Context Handling: Better at maintaining coherence over multiple paragraphs.
- Zero-Shot Learning: Could perform tasks without explicit training examples.
- Risks: OpenAI initially withheld the full model due to AI ethics concerns about misuse for generating misinformation.
Architectural Changes:
- Increased depth and width of transformer layers.
- Larger vocabulary and improved tokenization.
- More robust positional encoding for longer sequences.
This was the first time OpenAI models sparked global debate about responsible AI deployment — a topic we cover in Responsible AI with Guardrails.
GPT-3 (2020) – The 175 Billion Parameter Leap
GPT-3 marked a paradigm shift in large language models, scaling to 175 billion parameters and trained on a mixture of Common Crawl, WebText2, Books, and Wikipedia.
Technological Breakthroughs:
- Few-Shot and Zero-Shot Mastery: Could generalize from minimal examples.
- Versatility: Excelled in translation, summarization, question answering, and even basic coding.
- Emergent Behaviors: Displayed capabilities not explicitly trained for, such as analogical reasoning.
Training Data Evolution:
- Broader and more diverse datasets.
- Improved filtering to reduce low-quality content.
- Inclusion of multiple languages for better multilingual performance.
However, GPT-3 also revealed challenges:
- Bias and Fairness: Reflected societal biases present in training data.
- Hallucinations: Confidently generated incorrect information.
- Cost: Training required massive computational resources.
For a deeper dive into LLM fine-tuning, see our Fine-Tune, Serve, and Scale AI Workflows guide.
Codex (2021) – Specialization for Code
Codex was a specialized branch of OpenAI models fine-tuned from GPT-3 to excel at programming tasks. It powered GitHub Copilot and could translate natural language into code.
Technical Details:
- Training Data: Billions of lines of code from public GitHub repositories, Stack Overflow, and documentation.
- Capabilities: Code generation, completion, and explanation across multiple languages (Python, JavaScript, C++, etc.).
- Impact: Revolutionized AI applications in software development, enabling rapid prototyping and automation.
Architectural Adaptations:
- Fine-tuning on code-specific datasets.
- Adjusted tokenization to handle programming syntax efficiently.
- Enhanced context handling for multi-file projects.
Explore the top open-source tools powering the new era of agentic AI in this detailed breakdown.
GPT-3.5 (2022) – The Conversational Bridge
GPT-3.5 served as a bridge between GPT-3 and GPT-4, refining conversational abilities and reducing latency. It powered the first public release of ChatGPT in late 2022.
Improvements Over GPT-3:
- RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback): Improved alignment with user intent.
- Reduced Verbosity: More concise and relevant answers.
- Better Multi-Turn Dialogue: Maintained context over longer conversations.
Training Data Evolution:
- Expanded dataset with more recent internet content.
- Inclusion of conversational transcripts for better dialogue modeling.
- Enhanced filtering to reduce toxic or biased outputs.
Architectural Enhancements:
- Optimized inference for faster response times.
- Improved safety filters to reduce harmful outputs.
- More robust handling of ambiguous queries.
GPT-4 (2023) – Multimodal Intelligence
GPT-4 represented a major leap in generative AI capabilities. Available in 8K and 32K token context windows, it could process and generate text with greater accuracy and nuance.
Breakthrough Features:
- Multimodal Input: Accepted both text and images.
- Improved Reasoning: Better at complex problem-solving and logical deduction.
- Domain Specialization: Performed well in law, medicine, and finance.
Architectural Innovations:
- Enhanced attention mechanisms for longer contexts.
- More efficient parameter utilization.
- Improved safety alignment through iterative fine-tuning.
We explored GPT-4’s enterprise applications in our LLM Data Analytics Agent Guide.
GPT-4.1 (2025) – High-Performance Long-Context Model
Launched in April 2025, GPT-4.1 and its mini/nano variants deliver massive speed, cost, and capability gains over earlier GPT-4 models. It’s built for developers who need long-context comprehension, strong coding performance, and responsive interaction at scale.
Breakthrough Features:
-
1 million token context window: Supports ultra-long documents, codebases, and multimedia transcripts.
-
Top-tier coding ability: 54.6% on SWE-bench Verified, outperforming previous GPT-4 versions by over 20%.
-
Improved instruction following: Higher accuracy on complex, multi-step tasks.
-
Long-context multimodality: Stronger performance on video and other large-scale multimodal inputs.
Technological Advancements:
-
40% faster & 80% cheaper per query than GPT-4o.
-
Developer-friendly API with variants for cost/performance trade-offs.
-
Optimized for production — Balances accuracy, latency, and cost in real-world deployments.
GPT-4.1 stands out as a workhorse model for coding, enterprise automation, and any workflow that demands long-context precision at scale.
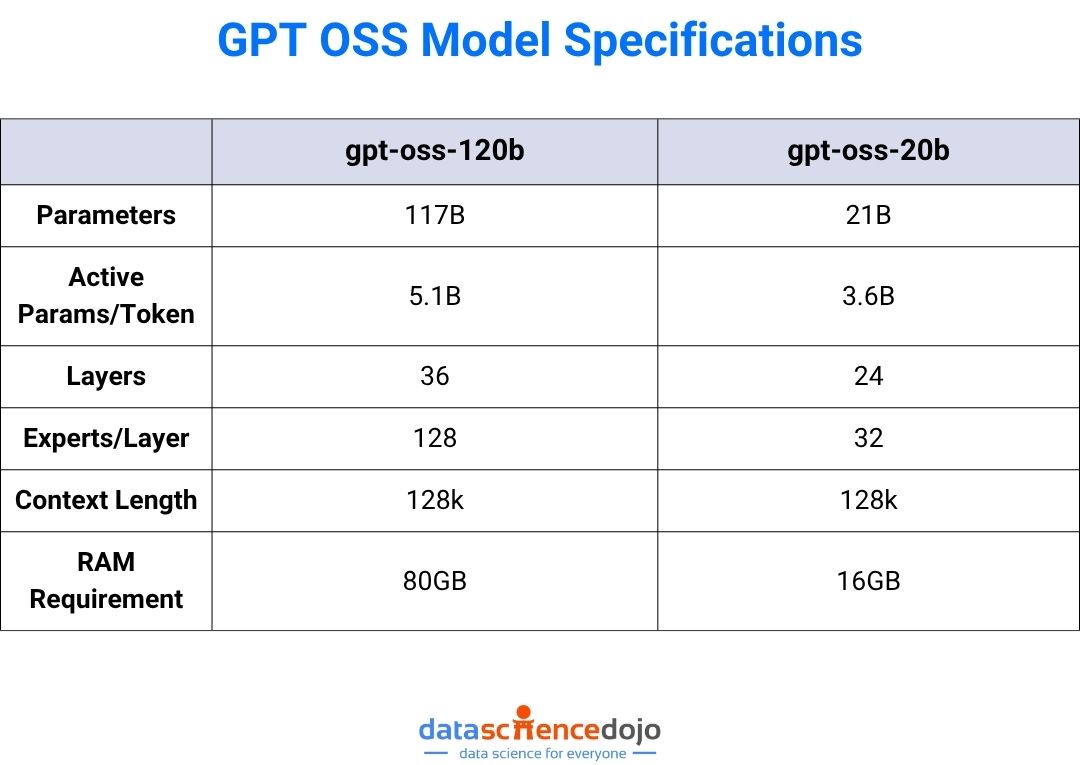
GPT-OSS (2025) – Open-Weight Freedom
OpenAI’s GPT-OSS marks its first open-weight model release since GPT-2, a major shift toward transparency and developer empowerment. It blends cutting-edge reasoning, efficient architecture, and flexible deployment into a package that anyone can inspect, fine-tune, and run locally.
Breakthrough Features:
-
Two model sizes: gpt-oss-120B for state-of-the-art reasoning and gpt-oss-20B for edge and real-time applications.
-
Open-weight architecture: Fully released under the Apache 2.0 license for unrestricted use and modification.
-
Advanced reasoning: Supports full chain-of-thought, tool use, and variable “reasoning effort” modes (low, medium, high).
-
Mixture-of-Experts design: Activates only a fraction of parameters per token for speed and efficiency.
Technological Advancements:
-
Transparent safety: Publicly documented safety testing and adversarial evaluations.
-
Broad compatibility: Fits on standard high-memory GPUs (80 GB for 120B; 16 GB for 20B).
-
Benchmark strength: Matches or exceeds proprietary OpenAI reasoning models in multiple evaluations.
By giving developers a high-performance, openly available LLM, GPT-OSS blurs the line between cutting-edge research and public innovation.
GPT-5 (2025) – The Next Frontier
The latest in the OpenAI models lineup, GPT-5, marks a major leap in AI capability, combining the creativity, reasoning power, efficiency, and multimodal skills of all previous GPT generations into one unified system. Its design intelligently routes between “fast” and “deep” reasoning modes, adapting on the fly to the complexity of your request.
Breakthrough Features:
-
Massive context window: Up to 256K tokens in ChatGPT and up to 400K tokens via the API, enabling deep document analysis, extended conversations, and richer context retention.
-
Advanced multimodal processing: Natively understands and generates text, interprets images, processes audio, and supports video analysis.
-
Native chain-of-thought reasoning: Delivers stronger multi-step logic and more accurate problem-solving.
-
Persistent memory: Remembers facts, preferences, and context across sessions for more personalized interactions.
Technological Advancements:
-
Intelligent routing: Dynamically balances speed and depth depending on task complexity.
-
Improved zero-shot generalization: Adapts to new domains with minimal prompting.
-
Multiple variants: GPT-5, GPT-5-mini, and GPT-5-nano offer flexibility for cost, speed, and performance trade-offs.
GPT-5’s integration of multimodality, long-context reasoning, and adaptive processing makes it a truly all-in-one model for enterprise automation, education, creative industries, and research.
Comparing the Evolution of OpenAI Models
Technological Trends Across OpenAI Models
-
Scaling Laws in Deep Learning
Each generation has exponentially increased in size and capability.
-
Multimodal Integration
Moving from text-only to multi-input processing.
-
Alignment and Safety
Increasing focus on AI ethics and responsible deployment.
-
Specialization
Models like Codex show the potential for domain-specific fine-tuning.
The Role of AI Ethics in Model Development
As OpenAI models have grown more powerful, so have concerns about bias, misinformation, and misuse. OpenAI has implemented reinforcement learning from human feedback and content moderation tools to address these issues.
For a deeper discussion, see our Responsible AI Practices article.
Future Outlook for OpenAI Models
Looking ahead, we can expect:
- Even larger machine learning models with more efficient architectures.
- Greater integration of AI applications into daily life.
- Stronger emphasis on AI ethics and transparency.
- Potential for real-time multimodal interaction.
Conclusion
The history of OpenAI models is a story of rapid innovation, technical mastery, and evolving responsibility. From GPT-1’s humble beginnings to GPT-5’s cutting-edge capabilities, each step has brought us closer to AI systems that can understand, reason, and create at human-like levels.
For those eager to work hands-on with these technologies, our Large Language Bootcamp and Agentic AI Bootcamp offers practical training in natural language processing, deep learning, and AI applications.