The use of AI in culture raises interesting ethical reflections termed AI ethics nowadays.
In 2016, a Rembrandt painting, “The Next Rembrandt”, was designed by a computer and created by a 3D printer, 351 years after the painter’s death.
The achievement of this artistic prowess became possible when 346 Rembrandt paintings were together analyzed. The keen analysis of paintings pixel by pixel resulted in an upscale of deep learning algorithms to create a unique database.
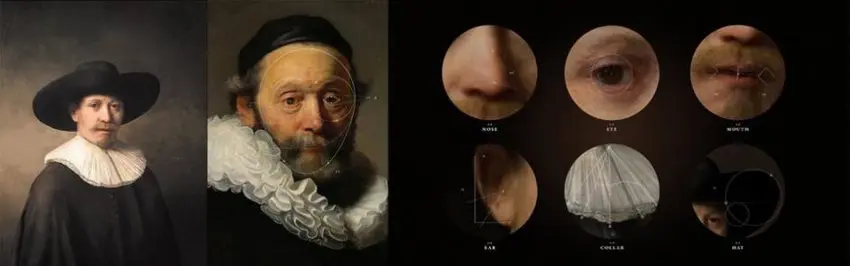
Every detail of Rembrandt’s artistic identity could then be captured and set the foundation for an algorithm capable of creating an unprecedented masterpiece. To bring the painting to life, a 3D printer recreated the texture of brushstrokes and layers of paint on the canvas for a breath-taking result that could trick any art expert.
The ethical dilemma arose when it came to crediting the author of the painting. Who could it be?
Curious about how generative AI is reshaping the creative industry and what it means for artists and creators? Watch this podcast now!
We cannot overlook the transformations brought by intelligent machine systems in today’s world for the better. To name a few, artificial intelligence contributed to optimizing planning, detecting fraud, composing art, conducting research, and providing translations.
Undoubtedly, it all contributed to the more efficient and consequently richer world of today. Leading global tech companies emphasize adopting a boundless landscape of artificial intelligence and step ahead of the competitive market.
Amidst the boom of overwhelming technological revolutions, we cannot undermine the new frontier for ethics and risk assessment.
Regardless of the risks AI offers, many real-world problems are begging to be solved by data scientists. Check out this informative session by Raja Iqbal (Founder and lead instructor at Data Science Dojo) on AI For Social Good
Some of the key ethical issues in AI you must learn about are:
1. Privacy & surveillance – Is your sensitive information secured?
Access to personally identifiable information must only be accessible to authorized users only. The other key aspects of privacy to consider in artificial intelligence are information privacy, privacy as an aspect of personhood, control over information about oneself, and the right to secrecy.
Business today is going digital. We are associated with the digital sphere. Most digital data available online connects to a single Internet. There is increasingly more sensor technology in use that generates data about non-digital aspects of our lives. AI not only contributes to data collection but also drives possibilities for data analysis.

Much of the most privacy-sensitive data analysis today–such as search algorithms, recommendation engines, and AdTech networks–are driven by machine learning and decisions by algorithms. However, as artificial intelligence evolves, it defines ways to intrude privacy interests of users.
For instance, facial recognition introduces privacy issues with the increased use of digital photographs. Machine recognition of faces has progressed rapidly from fuzzy images to rapid recognition of individual humans.
2. Manipulation of behavior – How does the internet know our preferences?
The use of the internet and online activities keeps us engaged every day. We do not realize that our data is constantly collected, and information is tracked. Our personal data is used to manipulate our behavior online and offline as well.
If you are thinking about exactly when businesses make use of the information gathered and how they manipulate us, then marketers and advertisers are the best examples. To sell the right product to the right customer, it is significant to know the behavior of your customer.
Their interests, past purchase history, location, and other key demographics. Therefore, advertisers retrieve the personal information of potential customers that is available online.

Social media has become the hub of manipulating user behaviors by marketers to maximize profits. AI with its advanced social media algorithms identifies vulnerabilities in human behavior and influences our decision-making process.
Artificial intelligence integrates such algorithms with digital media that exploit human biases detected by AI algorithms. It implies personalized addictive strategies for consumption of (online) goods or benefits from the vulnerable state of individuals to promote products and services that match well with their temporary emotions.
3. Opacity of AI systems – Complexed AI processes
Danaher stated, “we are creating decision-making processes that constrain and limit opportunities for human participation”
Artificial Intelligence supports automated decision-making, thus neglecting the free will of personnel to speak of their choice. AI processes work in a way that no one knows how the output is generated. Therefore, the decision will remain opaque even for the experts
AI systems use machine learning techniques in neural networks to retrieve patterns from a given dataset. With or without “correct” solutions provided, i.e., supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.
Read this blog to learn more about AI powered document search
Machine learning captures existing patterns in the data with the help of these techniques. And then label these patterns in such a way that it gets useful for the decision the system makes, while the programmer does not really know which patterns in the data the system has used.
4. Human-robot interaction – Are robots more capable than us?
As AI is now widely used to manipulate human behavior, it is also actively driving robots. It can get problematic if their processes or appearance involve deception or threatening human dignity
The key ethical issue here is, “Should robots be programmed to deceive us?” If we answer this question with a yes, then the next question to ask is “What should be the limits of deception?” If we say that robots can deceive us if it does not seriously harm us, then the robot might lie about its abilities or pretend to have more knowledge than it has.
If we believe that robots should not be programmed to deceive humans, then the next ethical question becomes “Should robots be programmed to lie at all?” The answer would depend on what kind of information they are giving and whether humans can provide an alternative source.
Robots are now being deployed in the workplace to do jobs that are dangerous, difficult, or dirty. The automation of jobs is inevitable in the future, and it can be seen as a benefit to society or a problem that needs to be solved. The problem arises when we start talking about human-robot interaction and how robots should behave around humans in the workplace.
5. Autonomous systems – AI gaining self-sufficiency
An autonomous system can be defined as a self-governing or self-acting entity that operates without external control. It can also be defined as a system that can make its own decisions based on its programming and environment.
The next step in understanding the ethical implications of AI is to analyze how it affects society, humans, and our economy. This will allow us to predict the future of AI and what kind of impact it will have on society if left unchecked.
In societies where AI is rapidly replacing humans can get harmed or suffer in the longer run. For instance, thinking of AI writers as a replacement for human copywriters when it is just designed to bring efficiency to a writer’s job, assist, and help in getting rid of writer’s block while generating content ideas at scale.
Secondly, autonomous vehicles are the most relevant examples for a heated debate topic of ethical issues in AI. It is not yet clear what the future of autonomous vehicles will be. The main ethical concern around autonomous cars is that they could cause accidents and fatalities.
Some people believe that because these cars are programmed to be safe, they should be given priority on the road. Others think that these vehicles should have the same rules as human drivers.
Enroll in Data Science Bootcamp today to learn about advanced technological revolutions
6. Machine ethics – Can we infuse good behavior in machines?
Before we get into the ethical issues associated with machines, we need to know that machine ethics is not about humans using machines. But it is solely related to the machines operating independently as subjects.
The topic of machine ethics is a broad and complex one that includes a few areas of inquiry. It touches on the nature of what it means for something to be intelligent, the capacity for artificial intelligence to perform tasks that would otherwise require human intelligence, the moral status of artificially intelligent agents, and more.
Read this blog to learn about Big Data Ethics
The field is still in its infancy, but it has already shown promise in helping us understand how we should deal with certain moral dilemmas.
In the past few years, there has been a lot of research on how to make AI more ethical. But how can we define ethics for machines?
AI programmed machines with rules for good behavior and to avoid making bad decisions based on the principles. It is not difficult to imagine that in the future, we will be able to tell if an AI has ethical values by observing its behavior and its decision-making process.
Three laws of robotics by Isaac for machine ethics are:
First Law—A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm.
Second Law—A robot must obey the orders given it by human beings except where such orders would conflict with the First Law.
Third Law—A robot must protect its own existence if such protection does not conflict with the First or Second Laws.
Artificial Moral Agents
The development of artificial moral agents (AMA) is a hot topic in the AI space. The AMA has been designed to be a moral agent that can make moral decisions and act according to these decisions. As such, it has the potential to have significant impacts on human lives.
The development of AMA is not without ethical issues. The first issue is that AMAs (Artificial Moral Agents) will have to be programmed with some form of morality system that could be based on human values or principles from other sources.
This means that there are many possibilities for diverse types of AMAs and several types of morality systems, which may lead to disagreements about what an AMA should do in each situation. Secondly, we need to consider how and when these AMAs should be used as they could cause significant harm if they are not used properly
Closing on AI ethics
Over the years, we went from, “AI is impossible” (Dreyfus 1972) and “AI is just automation” (Lighthill 1973) to “AI will solve all problems” (Kurzweil 1999) and “AI may kill us all” (Bostrom 2014).
Several questions arise with the increasing dependency on AI and robotics. Before we rely on these systems further, we must have clarity about what the systems themselves should do, and what risks they have in the long term.
Let us know in the comments if you also think it also challenges the human view of humanity as the intelligent and dominant species on Earth.

