Data analysis and data science are very closely related professions in many respects. If one enjoys problem-solving, data-driven decision-making, and critical thinking, both occupations are a good fit. While all alternatives draw on the same core skill set and strive toward comparable goals, there are differences in schooling, talents, daily responsibilities, and compensation ranges.
The data science certification course offers insight into the tools, technology, and trends driving the data science revolution. We have developed this guide to enable you to go through the abilities and background required to become a data scientist or data analyst, and their corresponding course fee.
Data Scientist vs. Data Analyst
Data analysis and data science are often misunderstood since they rely on the same fundamental skills, not to mention the very same broad educational foundation (e.g., advanced mathematics, and statistical analysis).
However, the day-to-day responsibilities of each role are vastly different. The difference, in its most basic form, is how they utilize the data they collect.
Role of a Data Analyst
A data analyst examines gathered information, organizes it, and cleans it to make it clear and helpful. Based on the data acquired, they make recommendations and judgments. They are part of a team that converts raw data into knowledge that can assist organizations in making sound choices and investments.
Role of a Data Scientist
A data scientist creates the tools that will be used by an analyst. They write programs, algorithms, and data-gathering technologies. Data scientists are innovative problem solvers who are constantly thinking of new methods to acquire, store, and view data.
Differences in the role of data scientist and data analyst

While both data analysts and data scientists deal with data, the primary distinction is what they do with it. Data analysts evaluate big data sets for insights, generate infographics, and generate visualizations to assist corporations in making better strategic choices. Data scientists, on the other hand, use models, methods, predictive analytics, and specialized analyses to create and build current innovations for data modeling and manufacturing.
Data experts and data scientists typically have comparable academic qualifications. Most have Bachelor’s degrees in economics, statistics, computer programming, or machine intelligence. They have in-depth knowledge of data, marketing, communication, and algorithms. They can work with advanced systems, databases, and Programming environments.
What is data analysis?
Data analysis is the thorough examination of data to uncover trends that can be turned into meaningful information. When formatted and analyzed correctly, previously meaningless data can become a wealth of useful and valuable information that firms in various industries can use.
Data analysis, for example, can tell a technical store what product is most successful at what period and with which population, which can then help employees decide what kind of incentives to run. Data analysis may also assist social media companies in determining when, what, and how they should promote particular users to optimize clicks.
What is data science?
Data science and data analysis both aim to unearth significant insights within piles of complicated or seemingly minor information. Rather than performing the actual analytics, data science frequently aims at developing the models and implementing the techniques that will be used during the process of data analysis.
While data analysis seeks to reveal insights from previous data to influence future actions, data science seeks to anticipate the result of future decisions. Artificial image processing and pattern recognition, which are still in their early stages, are used to create predictions based on large amounts of historical data.
Responsibilities: Data Scientist vs Data Analyst
Professionals in data science and data analysis must be familiar with managing data, information systems, statistics, and data analysis. They must alter and organize data for relevant stakeholders to find it useful and comprehensible. They also assess how effectively firms perform on predefined metrics, uncover trends, and explain the differentiated strategy. While job responsibilities frequently overlap, there are contrasts between data scientists and data analysts, and the methods they utilize to attain these goals.
| Data Analyst | Data Scientist |
| Data analyzers are expert interpreters. They use massive amounts of information to comprehend what is going on in the industry and how corporate actions affect how customers perceive and engage with the company. They are motivated by the need to understand people’s perspectives and behaviors through data analysis. | Data scientists build the framework for capturing data and better understanding the narrative it conveys about the industry, enterprise, and decisions taken. They are designers that can create a system that can handle the volume of data required while also making it valuable for understanding patterns and advising the management team. |
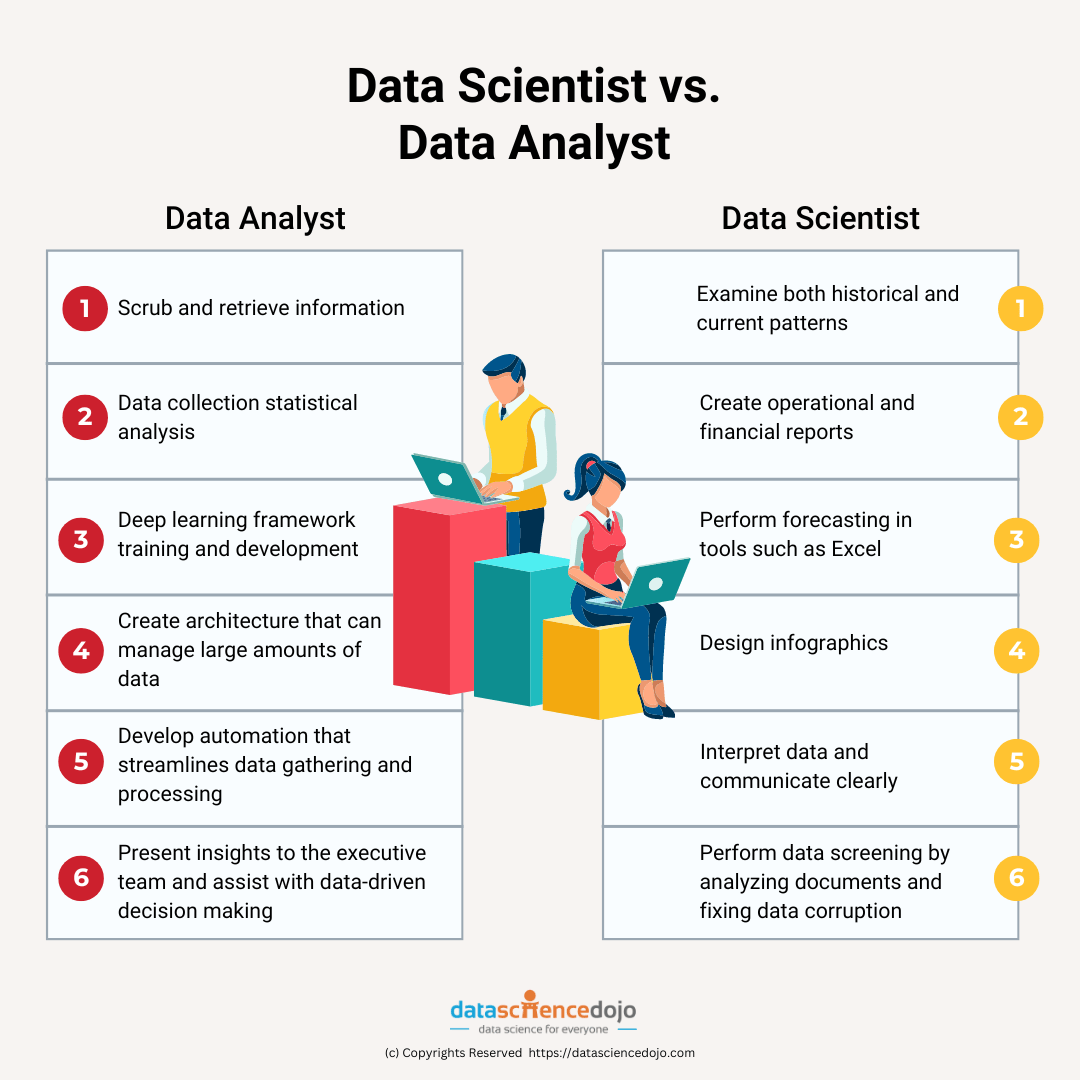
| Everyday data analyst tasks may involve examining both historical and current patterns and trends. | Data scientists are typically responsible for the scrubbing and information retrieval. |
| Create operational and financial reports. | Data collection statistical analysis. |
| Forecasting in tools such as Excel. | Deep learning framework training and development. |
| Designing infographics. | Creating architecture that can manage large amounts of data. |
| Data interpretation and clear communication. | Developing automation that streamlines data gathering and processing chores daily. |
| Data screening is accomplished by analyzing documents and fixing data corruption. | Presenting insights to the executive team and assisting with data-driven decision making |
| Using predictive modeling to discover and impact future trends. |
Role: Data Scientist vs Data Analyst
Data Analyst job description
A data analyst, unsurprisingly, analyzes data. This entails gathering information from various sources and processing it via data manipulation and statistical techniques. These procedures organize and extract insights from data, which are subsequently given to individuals who may act on them.
Become a pro with Data Analytics with these 12 amazing books
Users and decision-makers frequently ask data analysts to discover answers to their inquiries. This entails gathering and comparing pertinent facts and stitching it together to form a larger picture. Knowledgehut looks more closely at a career path in analytics and science, and helps you determine which employment best matches your interests, experience, and ambitions.
Data Scientist job description
A data scientist can have various tasks inside a corporation, among which are very comparable to those of a data analyst, such as gathering, processing, and analyzing data to get meaningful information.
Whereas a data analyst is likely to have been given particular questions to answer, a data scientist may indeed evaluate the same collection of data with the goal of diverse variables that may lead to a new line of inquiry. In other words, a data scientist must identify both the appropriate questions and the proper answers.
A data scientist will make designs and write algorithms and software to assist them as well as their research analyst team members with the analysis of data. A data scientist is also deeply engaged in the field of artificial intelligence and tries to push the limits and develop new methods to apply this technology in a corporate context.
How can Data Scientists become ethical hackers?
Yes, you heard it right. Data scientists can definitely become ethical hackers. There are several skills data scientists possess that can help them with the smooth transition from data scientists to ethical hackers. The skills are extensive knowledge of programming languages, databases, and operating systems. Data science is an important tool that can prevent hacking.
The necessary skills for a data scientist to become an ethical hacker include mathematical and statistical expertise, and extensive hacking skills. With the rise of cybercrimes, the need for cyber security is increasing. When data scientists become ethical hackers, they can protect an organization’s data and prevent cyber-attacks.
Skill set required for data analysis and data science
| Data analysis | Data science |
| Qualification: A Bachelor’s or Master’s degree in a related discipline, such as mathematics or statistics. | Qualification: An advanced degree, such as a master’s degree or possibly a Ph.D., in a relevant discipline, such as statistics, computer science, or mathematics. |
| Language skills: To understand data analysis, such as Python, SQL, CQL, and R. | Language skills: Demonstrate proficiency in data-related programming languages such as SQL, R, Java, and Python. |
Soft skills:
|
Soft skills:
|
Technical skills:
|
Technical skills:
|
| Microsoft Office proficiency:
Proficient in Microsoft Office applications, notably Excel, to properly explain their findings and translate them for others to grasp. |
Knowledge of statistical techniques and technology: Data processing technologies such as MySQL and Gurobi, as well as technological advances such as machine learning models, deep learning, artificial intelligence, artificial neural networks, and decision tree learning, will play a significant role. |
Conclusion
Each career is a good fit for an individual who enjoys statistics, analytics, and evaluating business decisions. As a data analyst or data scientist, you will make logical sense of large amounts of data, articulate patterns and trends, and participate in great responsibilities in a corporate or government organization.
When picking between a data analytics and a data science profession, evaluate your career aspirations, skills, and how much time you want to devote to higher learning and intensive training. Start your data analyst or data scientist journey with a data science course with nominal data science course fee to learn in-demand skills used in realistic, long-term projects, strengthening your resume and commercial viability.
FAQs
- Which is better: Data science or data analyst?
Data science is suitable for candidates who want to develop advanced machine learning models and make human tasks easier. On the other hand, the data analyst role is appropriate for candidates who want to begin their career in data analysis.
- What is the career path for data analytics and data science?
Most data analysts will begin their careers as junior members of a bigger data analysis team, where they will learn the fundamentals of the work in a hands-on environment and gain valuable experience in data manipulation. At senior level, data analysts become team leaders, in control of project selection and allocation.
A junior data scientist will most likely obtain a post with a focus on data manipulation before delving into the depths of learning algorithms and mapping out forecasts. The procedure of preparing data for analysis varies so much from case to case that it’s far simpler to learn by doing.
Once conversant with the mechanics of data analysis, data scientists might expand their understanding of artificial intelligence and its applications by designing algorithms and tools. A more experienced data scientist may pursue team lead or management positions, distributing projects and collaborating closely with users and decision-makers. Alternatively, they could use their seniority to tackle the most difficult and valuable problems using their specialist expertise in patterns and machine learning.
- What is the salary for a data scientist and a data analyst in India?
2 to 4 years (Senior Data Analyst): $98,682 whereas the average data scientist salary is $100,560, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
References
Difference Between Data Science and Data Analytics – GeeksforGeeks
Business analytics vs data science – Data Science Dojo
Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: Key Differences Explained | Upwork
Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: What’s the Difference? | Coursera
Data Analytics vs. Data Science: A Breakdown (northeastern.edu)
Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: Salary, Skills, & Background (springboard.com)
Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist: Which Should You Pursue? – UT Austin Boot Camps (utexas.edu)


